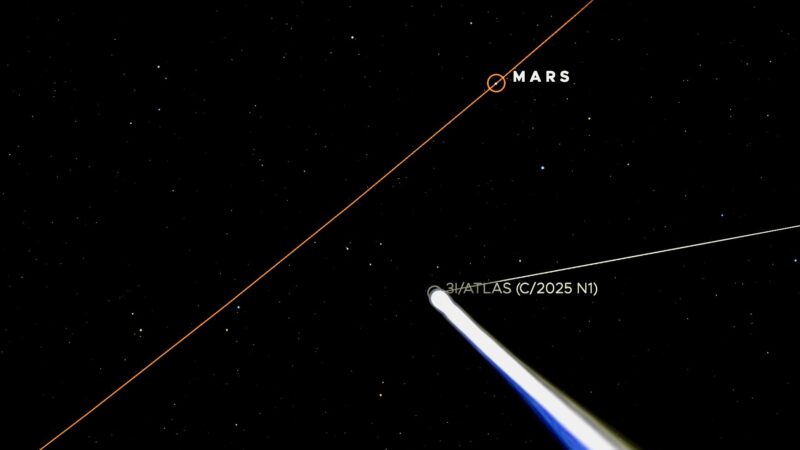

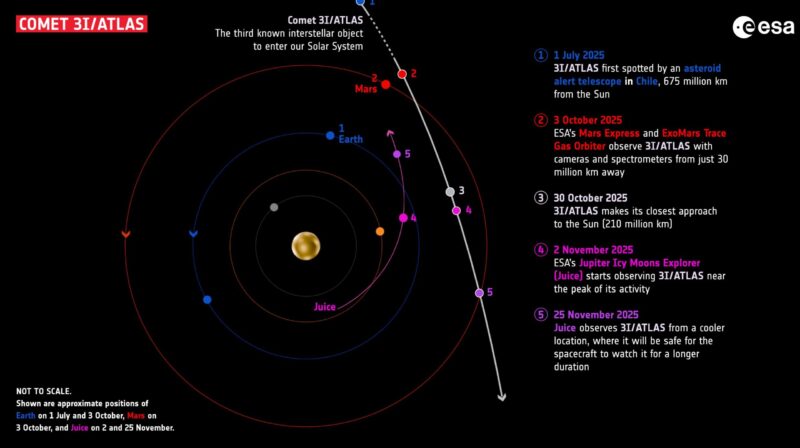
The world’s 3rd known interstellar object – 3I/ATLAS – will make its closest approach to Mars at 4 UTC on October 3, 2025 (11 p.m. CDT on October 2). At that time, the comet will be approximately 18 million miles (29 million kilometers) from Mars. It will be the object’s closest approach to any planet during its one-time journey through our solar system.
Multiple space agencies, including NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), will be coordinating observations using various spacecraft and orbiters around Mars. Instruments on ESA’s Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, as well as NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, will focus on capturing detailed data from this interstellar visitor. In an October 2 story from AP, Marcia Dunn reported:
Both of the European Space Agency’s satellites around Mars [Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter] are already aiming their cameras at the comet, which is only the 3rd interstellar object known to have passed our way. NASA’s satellite and rovers at the red planet are also available to assist in the observations.
Previously, Marshall Eubanks of Space Initiatives had said:
During the Mars close approach, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter will observe 3I with HiRISE, observing between 1 – 4 a.m. on October 2, and the CaSSIS camera on ESA’s Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Mars Express’s High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) will be observing on October 3.
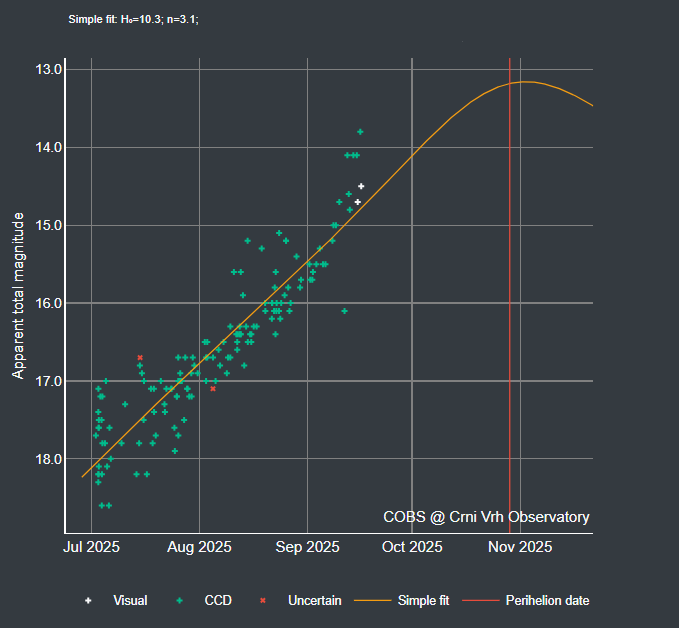
The object will reach perihelion, its closest point to the sun, 3I/ on October 29, 2025. Its perihelion distance will be roughly 1.36 astronomical units (AU) from the sun — just inside the orbit of Mars.
If you’re interested in tracking the object, NASA’s Eyes on the Solar System tool offers interactive simulations of its path. Also, NASA just launched a new page devoted to 3I/ATLAS.
Please note that 3I/ATLAS will not be visible to the unaided eye from Earth at this Mars approach, or at any time. It will be possible to view the object with 8-inch or larger telescopes … but the best time for that won’t come until November. If you spot it then, you’ll be in good company. Between November 2 and 25, ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) will be observing the comet with various instruments. As Juice looks towards 3I/ATLAS so soon after its closest approach to the sun, it is likely to have the best view of the comet in a very active state, with a bright halo around its nucleus and a long tail stretching out behind it.
The latest updates on ESA observations are here
Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS: A look backward
Where did 3I/ATLAS come from. We know it came from the Sagittarius direction in our sky; that is, it came from the direction of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. But there are billions of stars in that direction. Which one is the home system of this object?
There have been many studies and ideas. One team of scientists, led by Xabier Pérez-Couto of the University of A Coruña in Spain, traced the path of interstellar object 3I/ATLAS back 10 million years. The astronomers were seeking its origin star, or any stars that might have perturbed its path as it traveled from its point of origin to our solar system.
The researchers examined 3I/ATLAS’s trajectory with the help of the Gaia space observatory’s data on stars. For 12 years, Gaia collected data on billions of stars in our Milky Way galaxy, precisely noting their positions again and again and thereby determining their motions. These astronomers’ calculations took them more than 100 million astronomical units (AU, or Earth-sun units) from our solar system. With these data in hand, researchers said they identified 93 nominal “encounters” for 3I/ATLAS, 62 of which were “significant.” Yet, they found that none of those encounters produced any meaningful perturbation of ATLAS’s orbit.
So, in other words, all of those 93 (or 62) encounters happened too fast, with the stars too far from 3I/ATLAS to meaningfully impact its trajectory. In the end, they didn’t find a star along 3I/ATLAS’s path that might have been responsible for bringing this 3rd-known interstellar object to us.

Tracing 3I/ATLAS’ path a daunting task
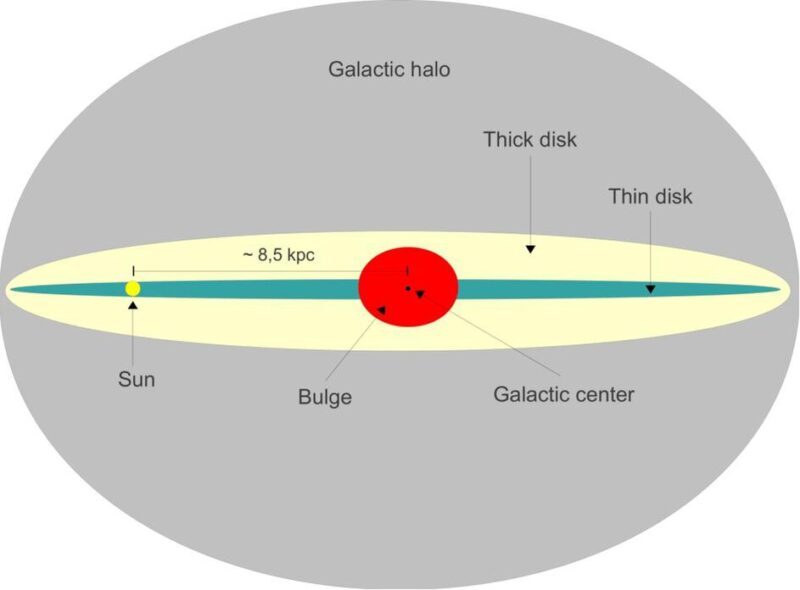
And, as you might imagine, tracing 3I/ATLAS’s path backward through the galaxy is a daunting task. That’s in part because small uncertainties in orbits and stellar motions grow rapidly over time. But based on the researchers’ analyses of the interstellar object’s vertical motion in the galaxy (its path is known to weave up and down in the galactic disk), they concluded that it likely originated from the Milky Way’s thin disk, not its thick disk as was mentioned some months ago. The thin disk contains somewhat younger objects than the thick disk. But the researchers’ paper said:
[3I/ATLAS] may nonetheless be an old object, consistent with ejection from a long-lived primordial planetesimal disk in an early-formed system.
The scientists published their not-yet peer-reviewed paper on arXiv on September 10, 2025.
Unlocking galactic mysteries with 3I/ATLAS
3I/ATLAS is thought to have been drifting through interstellar space for many billions of years before encountering our solar system. Pérez-Couto and team said that the interstellar comet is a:
… key probe of the galactic population of icy planetesimals.
In other words, the formation of solar systems is a messy process. In a solar system’s earliest days, rocks and pockets of gas and dust bang into each other and get swept up into clumps, which eventually get big enough to begin gathering yet more rocks, gas and dust to themselves via the force of gravity. Thus, planets come to be, astronomers think. According to theories of planet formation, clearing processes are also common, and those sometimes involve material – often the outer, icy regions of debris – getting ejected from a system altogether. As the paper said:
… interstellar space should be filled with planetesimals.
Other possibilities
Plus, there are other ways these interstellar interlopers might have achieved their lonely paths through our Milky Way galaxy. The possibiities range from close passages of other stars to tidal fragmentation of comets. So, as the paper said:
Identifying the origin of interstellar objects is key to understanding planet formation efficiency, the distribution of volatiles and organics in the galaxy, and the dynamical pathways by which planetary systems evolve.
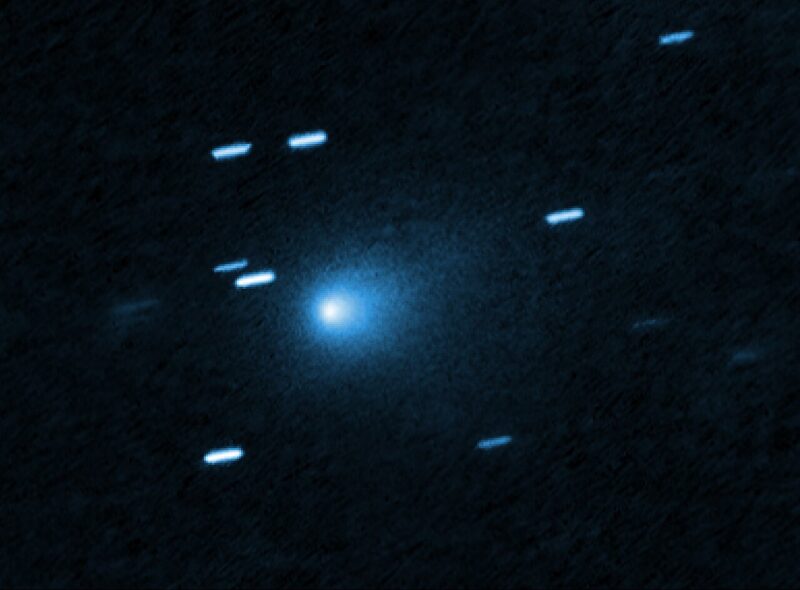
All that from a small chunk of icy stuff (we know it’s icy in part because 3I/ATLAS has formed a tail, as icy comets do)!
EarthSky interview with Colin Orion Chandler
On August 7, 2025, NASA shared an updated estimate of the size of the object’s nucleus, or core. Shortly after the object was first identified on July 1, 2025, 3I/ATLAS was estimated to have a diameter of about 20 km (12 miles). Then in late July – using data from the new Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile – the size estimate dropped to 10 km (6 miles). The latest analysis uses data from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. It reduces the estimated diameter of 3I/ATLAS’s nucleus still further, to 5.6 km (3.5 miles).
And, the astronomers using Hubble data said, the object could be even smaller, as small as 320 meters (1,050 feet) across!
EarthSky’s Deborah Byrd interviewed Colin Orion Chandler of the DiRAC Institute of the University of Washington about size estimates for 3I/ATLAS. Watch in the player below, or on YouTube.
By the way, the two previously known interstellar objects are 1I/ ‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov. ‘Oumuamua’s size is thought to be about 200 meters across at its widest (you’ll recall it has an elongated shape). And Borisov is thought to be less than a kilometer across.

An early EarthSky interview with Matthew Hopkins
Shortly after the discovery of 3I/ATLAS – on July 1, 2025 – astronomers were saying it was likely the oldest comet we’ve ever seen. That claim came from University of Oxford astronomer Matthew Hopkins, whose analysis suggested 3I/ATLAS might be more than 7 billion years old, predating our solar system by more than 3 billion years! Hear him explain in the player below, or on YouTube.
EarthSky interview with Colin Snodgrass
Scientists first spotted 3I/ATLAS in early July 2025. And since then, one question has been asked countless times: will we send out a spacecraft to take a closer look? EarthSky’s Will Triggs spoke to University of Edinburgh astronomer Colin Snodgrass on August 21, 2025, to find out the answer. Colin essentially said, no, we don’t have time to organize a space mission specifically for 3I/ATLAS. But he talked about a future mission, the European Space Agency’s Comet Interceptor. This upcoming spacecraft will be primed to intercept future interstellar objects. Watch Will’s interview with Colin in the player below, or on YouTube.
It’s worth noting that the behavior of 3I/ATLAS is much like the signature of previously seen sun-bound comets originating within our solar system. But 3I/ATLAS is moving fast. In fact, it’s traveling through our solar system at roughly 210,000 kilometers per hour (130,000 mph). That’s the highest velocity ever recorded for a solar system visitor.
How they spotted interstellar object 3I/ ATLAS
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) – a system of survey telescopes – detected our new interstellar visitor on July 1, 2025. And the Minor Planet Center confirmed its interstellar nature the following day (July 2, 2025), naming it 3I/ATLAS (or C/2025 N1). The “3I” means it’s the 3rd interstellar visitor that we’ve found. Its trajectory and speed revealed it as an object not from our solar system, but from another star system.
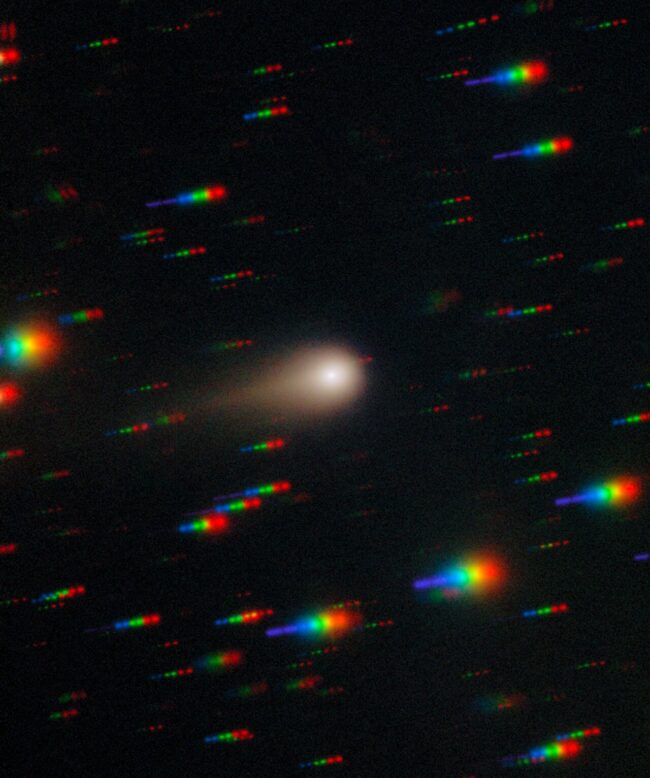
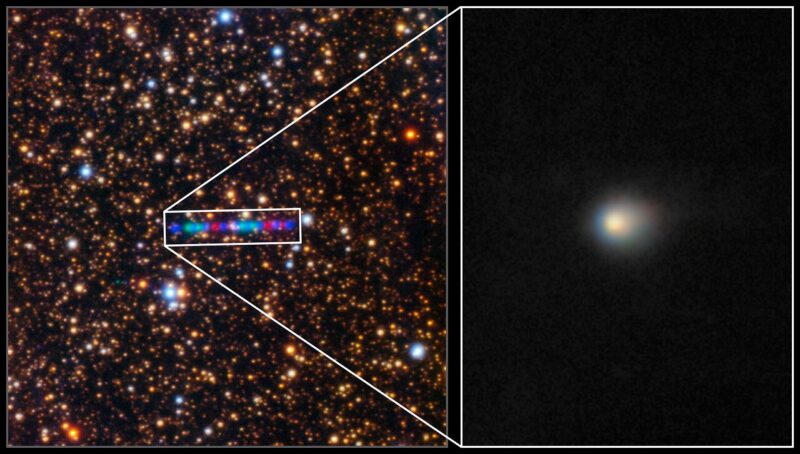
The Hubble Space Telescope imaged the object on July 21, 2025. See the post from Bluesky below.
Hubble Space Telescope images of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS are out! These were taken 5 hours ago. Plenty of cosmic rays peppering the images, but the comet's coma looks very nice and puffy. Best of luck to the researchers trying to write up papers for this… archive.stsci.edu/proposal_sea… ?
— astrafoxen (@astrafoxen.bsky.social) July 21, 2025 at 4:28 PM

It’s still heading sunward
Our new visitor will get its closest to the sun – at about 2 astronomical units (AU), or twice as far as Earth is from the sun – in October. As it reaches perihelion – its closest point to the sun – it will be traveling at almost 15,500 miles per hour (25,000 kph).
The speedy nature of Comet 3I/ATLAS is another indication of its interstellar nature. It has to be moving at a blistering pace in order to escape the sun’s gravitational pull.
Marshall Eubanks, a physicist and VLBI radio astronomer and co-founder of Space Initiatives, said the comet will come within about 0.4 AU of Mars in October. That would make it just barely observable by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.


Morning star charts here
After Comet 3I/ATLAS makes its close approach to the sun, you can find it in the morning sky.
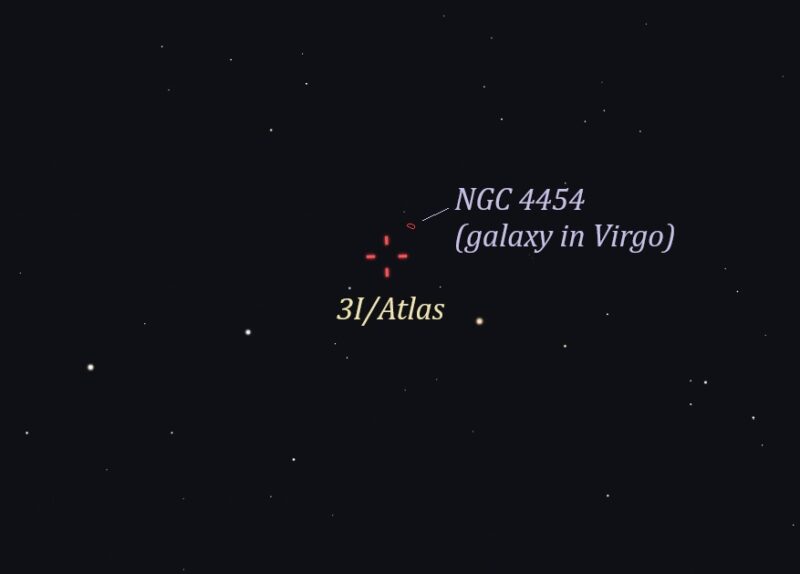


Bottom line: Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS will sweep closest to Mars at 11 p.m. CDT on October 2 (4 UTC on October 3). Read about plans to observe it with spacecraft.
Via:
The post Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS to pass Mars October 2-3 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/my0bCHL

The world’s 3rd known interstellar object – 3I/ATLAS – will make its closest approach to Mars at 4 UTC on October 3, 2025 (11 p.m. CDT on October 2). At that time, the comet will be approximately 18 million miles (29 million kilometers) from Mars. It will be the object’s closest approach to any planet during its one-time journey through our solar system.
Multiple space agencies, including NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), will be coordinating observations using various spacecraft and orbiters around Mars. Instruments on ESA’s Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, as well as NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, will focus on capturing detailed data from this interstellar visitor. In an October 2 story from AP, Marcia Dunn reported:
Both of the European Space Agency’s satellites around Mars [Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter] are already aiming their cameras at the comet, which is only the 3rd interstellar object known to have passed our way. NASA’s satellite and rovers at the red planet are also available to assist in the observations.
Previously, Marshall Eubanks of Space Initiatives had said:
During the Mars close approach, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter will observe 3I with HiRISE, observing between 1 – 4 a.m. on October 2, and the CaSSIS camera on ESA’s Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Mars Express’s High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) will be observing on October 3.
The object will reach perihelion, its closest point to the sun, 3I/ on October 29, 2025. Its perihelion distance will be roughly 1.36 astronomical units (AU) from the sun — just inside the orbit of Mars.
If you’re interested in tracking the object, NASA’s Eyes on the Solar System tool offers interactive simulations of its path. Also, NASA just launched a new page devoted to 3I/ATLAS.
Please note that 3I/ATLAS will not be visible to the unaided eye from Earth at this Mars approach, or at any time. It will be possible to view the object with 8-inch or larger telescopes … but the best time for that won’t come until November. If you spot it then, you’ll be in good company. Between November 2 and 25, ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) will be observing the comet with various instruments. As Juice looks towards 3I/ATLAS so soon after its closest approach to the sun, it is likely to have the best view of the comet in a very active state, with a bright halo around its nucleus and a long tail stretching out behind it.
The latest updates on ESA observations are here

Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS: A look backward
Where did 3I/ATLAS come from. We know it came from the Sagittarius direction in our sky; that is, it came from the direction of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. But there are billions of stars in that direction. Which one is the home system of this object?
There have been many studies and ideas. One team of scientists, led by Xabier Pérez-Couto of the University of A Coruña in Spain, traced the path of interstellar object 3I/ATLAS back 10 million years. The astronomers were seeking its origin star, or any stars that might have perturbed its path as it traveled from its point of origin to our solar system.
The researchers examined 3I/ATLAS’s trajectory with the help of the Gaia space observatory’s data on stars. For 12 years, Gaia collected data on billions of stars in our Milky Way galaxy, precisely noting their positions again and again and thereby determining their motions. These astronomers’ calculations took them more than 100 million astronomical units (AU, or Earth-sun units) from our solar system. With these data in hand, researchers said they identified 93 nominal “encounters” for 3I/ATLAS, 62 of which were “significant.” Yet, they found that none of those encounters produced any meaningful perturbation of ATLAS’s orbit.
So, in other words, all of those 93 (or 62) encounters happened too fast, with the stars too far from 3I/ATLAS to meaningfully impact its trajectory. In the end, they didn’t find a star along 3I/ATLAS’s path that might have been responsible for bringing this 3rd-known interstellar object to us.

Tracing 3I/ATLAS’ path a daunting task
And, as you might imagine, tracing 3I/ATLAS’s path backward through the galaxy is a daunting task. That’s in part because small uncertainties in orbits and stellar motions grow rapidly over time. But based on the researchers’ analyses of the interstellar object’s vertical motion in the galaxy (its path is known to weave up and down in the galactic disk), they concluded that it likely originated from the Milky Way’s thin disk, not its thick disk as was mentioned some months ago. The thin disk contains somewhat younger objects than the thick disk. But the researchers’ paper said:
[3I/ATLAS] may nonetheless be an old object, consistent with ejection from a long-lived primordial planetesimal disk in an early-formed system.
The scientists published their not-yet peer-reviewed paper on arXiv on September 10, 2025.

Unlocking galactic mysteries with 3I/ATLAS
3I/ATLAS is thought to have been drifting through interstellar space for many billions of years before encountering our solar system. Pérez-Couto and team said that the interstellar comet is a:
… key probe of the galactic population of icy planetesimals.
In other words, the formation of solar systems is a messy process. In a solar system’s earliest days, rocks and pockets of gas and dust bang into each other and get swept up into clumps, which eventually get big enough to begin gathering yet more rocks, gas and dust to themselves via the force of gravity. Thus, planets come to be, astronomers think. According to theories of planet formation, clearing processes are also common, and those sometimes involve material – often the outer, icy regions of debris – getting ejected from a system altogether. As the paper said:
… interstellar space should be filled with planetesimals.

Other possibilities
Plus, there are other ways these interstellar interlopers might have achieved their lonely paths through our Milky Way galaxy. The possibiities range from close passages of other stars to tidal fragmentation of comets. So, as the paper said:
Identifying the origin of interstellar objects is key to understanding planet formation efficiency, the distribution of volatiles and organics in the galaxy, and the dynamical pathways by which planetary systems evolve.
All that from a small chunk of icy stuff (we know it’s icy in part because 3I/ATLAS has formed a tail, as icy comets do)!
EarthSky interview with Colin Orion Chandler
On August 7, 2025, NASA shared an updated estimate of the size of the object’s nucleus, or core. Shortly after the object was first identified on July 1, 2025, 3I/ATLAS was estimated to have a diameter of about 20 km (12 miles). Then in late July – using data from the new Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile – the size estimate dropped to 10 km (6 miles). The latest analysis uses data from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. It reduces the estimated diameter of 3I/ATLAS’s nucleus still further, to 5.6 km (3.5 miles).
And, the astronomers using Hubble data said, the object could be even smaller, as small as 320 meters (1,050 feet) across!
EarthSky’s Deborah Byrd interviewed Colin Orion Chandler of the DiRAC Institute of the University of Washington about size estimates for 3I/ATLAS. Watch in the player below, or on YouTube.
By the way, the two previously known interstellar objects are 1I/ ‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov. ‘Oumuamua’s size is thought to be about 200 meters across at its widest (you’ll recall it has an elongated shape). And Borisov is thought to be less than a kilometer across.

An early EarthSky interview with Matthew Hopkins
Shortly after the discovery of 3I/ATLAS – on July 1, 2025 – astronomers were saying it was likely the oldest comet we’ve ever seen. That claim came from University of Oxford astronomer Matthew Hopkins, whose analysis suggested 3I/ATLAS might be more than 7 billion years old, predating our solar system by more than 3 billion years! Hear him explain in the player below, or on YouTube.
EarthSky interview with Colin Snodgrass
Scientists first spotted 3I/ATLAS in early July 2025. And since then, one question has been asked countless times: will we send out a spacecraft to take a closer look? EarthSky’s Will Triggs spoke to University of Edinburgh astronomer Colin Snodgrass on August 21, 2025, to find out the answer. Colin essentially said, no, we don’t have time to organize a space mission specifically for 3I/ATLAS. But he talked about a future mission, the European Space Agency’s Comet Interceptor. This upcoming spacecraft will be primed to intercept future interstellar objects. Watch Will’s interview with Colin in the player below, or on YouTube.
It’s worth noting that the behavior of 3I/ATLAS is much like the signature of previously seen sun-bound comets originating within our solar system. But 3I/ATLAS is moving fast. In fact, it’s traveling through our solar system at roughly 210,000 kilometers per hour (130,000 mph). That’s the highest velocity ever recorded for a solar system visitor.
How they spotted interstellar object 3I/ ATLAS
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) – a system of survey telescopes – detected our new interstellar visitor on July 1, 2025. And the Minor Planet Center confirmed its interstellar nature the following day (July 2, 2025), naming it 3I/ATLAS (or C/2025 N1). The “3I” means it’s the 3rd interstellar visitor that we’ve found. Its trajectory and speed revealed it as an object not from our solar system, but from another star system.
The Hubble Space Telescope imaged the object on July 21, 2025. See the post from Bluesky below.
Hubble Space Telescope images of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS are out! These were taken 5 hours ago. Plenty of cosmic rays peppering the images, but the comet's coma looks very nice and puffy. Best of luck to the researchers trying to write up papers for this… archive.stsci.edu/proposal_sea… ?
— astrafoxen (@astrafoxen.bsky.social) July 21, 2025 at 4:28 PM


It’s still heading sunward
Our new visitor will get its closest to the sun – at about 2 astronomical units (AU), or twice as far as Earth is from the sun – in October. As it reaches perihelion – its closest point to the sun – it will be traveling at almost 15,500 miles per hour (25,000 kph).
The speedy nature of Comet 3I/ATLAS is another indication of its interstellar nature. It has to be moving at a blistering pace in order to escape the sun’s gravitational pull.
Marshall Eubanks, a physicist and VLBI radio astronomer and co-founder of Space Initiatives, said the comet will come within about 0.4 AU of Mars in October. That would make it just barely observable by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.


Morning star charts here
After Comet 3I/ATLAS makes its close approach to the sun, you can find it in the morning sky.



Bottom line: Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS will sweep closest to Mars at 11 p.m. CDT on October 2 (4 UTC on October 3). Read about plans to observe it with spacecraft.
Via:
The post Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS to pass Mars October 2-3 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/my0bCHL

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire