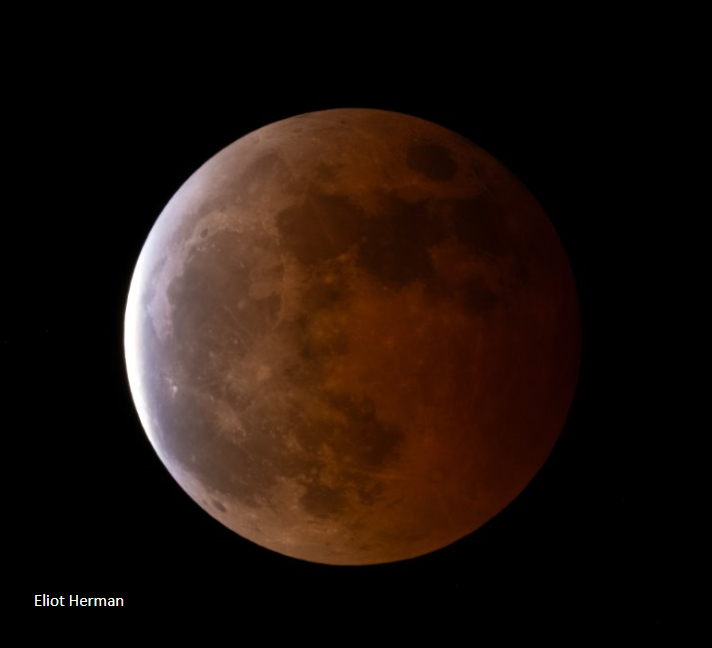

The second eclipse season of 2025 is about to start. This eclipse season will feature a total lunar eclipse on September 7, 2025. And it’ll also include a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 2025.
An eclipse season is an approximate 35-day period during which it’s inevitable for at least two (and possibly three) eclipses to take place. It’s a time period in which the Earth, moon and sun can line up in space. We have to be in an eclipse season for an eclipse to take place. Eclipse seasons happen every six months, and during this time, a lunar eclipse can occur during a full moon, and a solar eclipse can occur during a new moon.
The first eclipse season of 2025 was in March. There was a lunar eclipse on March 13-14, 2025, followed two weeks later by a partial solar eclipse on March 29, 2025.
What’s an eclipse season
During an eclipse season – when the Earth, moon and sun are able to make a line in space – it’s inevitable that at least two (and possibly three) eclipses will take place. Typically, there are two eclipses in one eclipse season, and two eclipse seasons in one calendar year. So we typically have at least four eclipses per year. Eclipse seasons repeat in cycles of 173.3 days (somewhat shy of six calendar months).
So, why don’t you see that many eclipses then? To see a lunar eclipse, the moon has to be above your horizon. So it has to be night, or close to night, and that only happens for half of Earth at once. Solar eclipses are even harder to catch. In fact, a total solar eclipse can be seen only from a narrow track along Earth’s surface. The accompanying partial solar eclipse can be seen only in areas adjacent to that track.

The 2025 eclipse seasons
The March 2025 eclipse season featured a total lunar eclipse on March 13-14, 2025, and a partial solar eclipse on March 29, 2025.
The September 2025 eclipse season will consist of a total lunar eclipse on September 7, 2025, followed two weeks later by a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 2025.
By the way, in 2025, the middles of the eclipse seasons are on March 17 and September 10. At the middle of an eclipse season, which recurs in periods of about 173 days, the lunar nodes are in exact alignment with the Earth and sun.
What causes an eclipse season?
There are many cycles in the heavens. In fact, an eclipse season is just one of these many celestial cycles.
Consider a scenario where the moon orbited Earth on the same plane as the Earth orbits the sun. Then we’d have a solar eclipse at every new moon, and a lunar eclipse at every full moon.
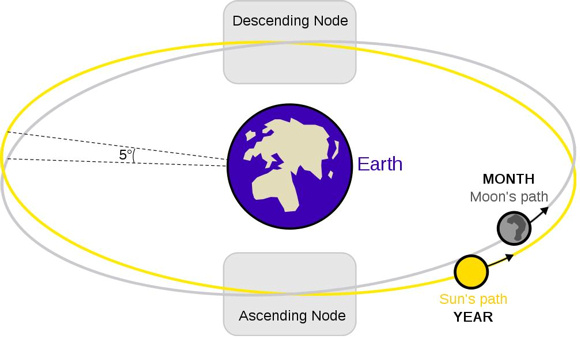
But, in reality, the moon’s orbit is inclined by 5 degrees to the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane). Most of the time the new moon or full moon swings too far north, or south, of the ecliptic for an eclipse to take place.
For instance, in the year 2025, we will have 12 new moons and 12 full moons, but only two solar eclipses and two lunar eclipses.
Why we have eclipses
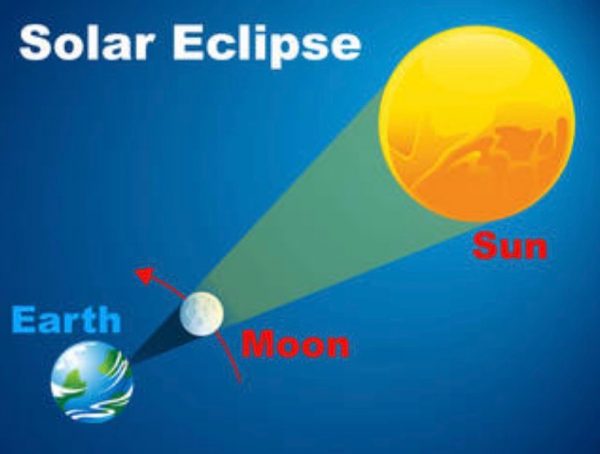


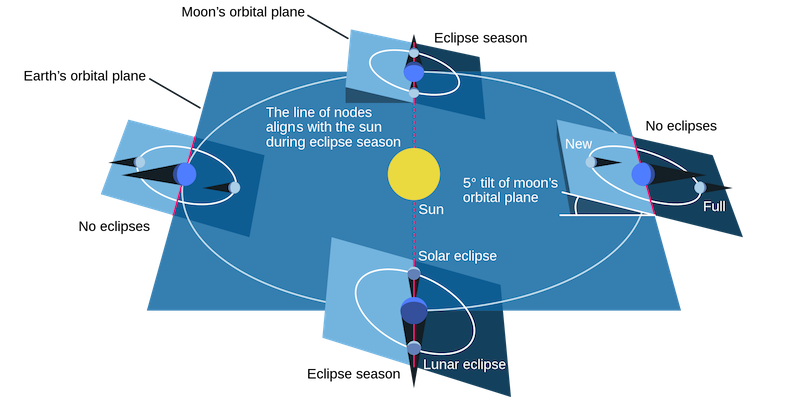
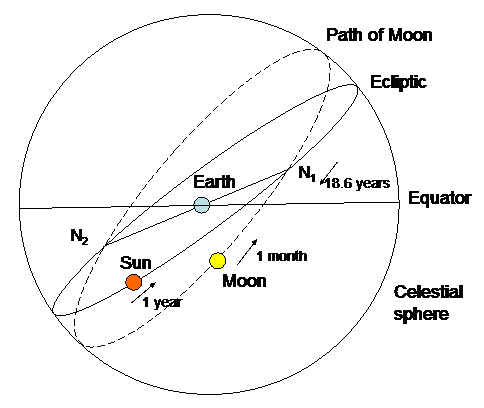
Lunar nodes point at the sun
Twice every month, as the moon circles Earth in its orbit, the moon crosses the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane) at points called nodes. If the moon is going from south to north, it’s called the moon’s ascending node. If the moon is moving from north to south, it’s called the moon’s descending node.
Read more: Node passages of the moon: 2001 to 2100
Whenever the lunar nodes point directly at the sun, that momentous event marks the middle of the eclipse season. The alignment of the moon, sun and Earth is most exact when an eclipse happens at the middle of an eclipse season. It’s the least so when an eclipse occurs at the start or the end of an eclipse season. Any lunar eclipse happening early or late in the eclipse season presents a penumbral lunar eclipse, whereas any solar eclipse happening early or late in the eclipse season features a skimpy partial eclipse of the sun.
2 or 3 eclipses in one eclipse season?
An eclipse season most often presents only two eclipses. However, if the first eclipse falls early in the eclipse season, then it’s possible for a third eclipse to occur before the eclipse season ends.
For example, the last time three eclipses happened in one eclipse season was June-July 2020:
June 5, 2020: Penumbral lunar eclipse
June 21, 2020: Annular solar eclipse
July 5, 2020: Penumbral lunar eclipse
Likewise, the next time three eclipses will occur in one eclipse season will be June-July 2029:
June 12, 2029: Partial solar eclipse
June 26, 2029: Total lunar eclipse
July 11, 2029: Partial solar eclipse
Eclipse season terminology
With this in mind, here are some words you need to know to understand eclipse seasons: lunar nodes and ecliptic. The ecliptic is the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the sun. A lunar node is the point where, in its monthly orbit of Earth, the moon’s orbit intersects that plane. An eclipse season is when – from Earth’s perspective – the sun is close enough to a lunar node to allow an eclipse to take place. If the sun is close to a lunar node at full moon, we see a lunar eclipse. If the sun is close to a lunar node at new moon, we see a solar eclipse.
To put it another way, if the moon turns new or full in close concert with the moon’s crossing of one of its nodes, then an eclipse is not only possible, but inevitable.
Minimum of 4 eclipses in one year
A lunar month (period of time between successive new moons or successive full moons) is about 29.5 days long. So a minimum of two eclipses (one solar and one lunar, in either order) happens in one eclipse season. A maximum of three eclipses is possible (either lunar/solar/lunar or solar/lunar/solar), though the first eclipse of the eclipse season has to come quite early to allow for a third eclipse near the end.
So a minimum of two lunar eclipses and two solar eclipses occurs in one calendar year. Yet, depending on how the eclipse seasons and lunar phases align, it’s possible to also have five, six or seven eclipses in one year.
For the maximum of seven eclipses to occur in one calendar year, the first eclipse must come in early January. That leaves enough room for the seventh eclipse in late December. In one scenario, an eclipse season sporting two eclipses comes early in the year and late in the year. The middle eclipse season stages three eclipses.
It’s quite rare for seven eclipses to occur in one calendar year, however. Seven eclipses last happened in the year 1982, and will next occur in the year 2038.
Maximum of 7 eclipses in one year
Also, it’s remotely possible for a calendar year to sport two eclipse seasons with three eclipses each, and one eclipse from an eclipse season that straddles into the previous or following year. For example, we present the years 1935 and 1879-80.
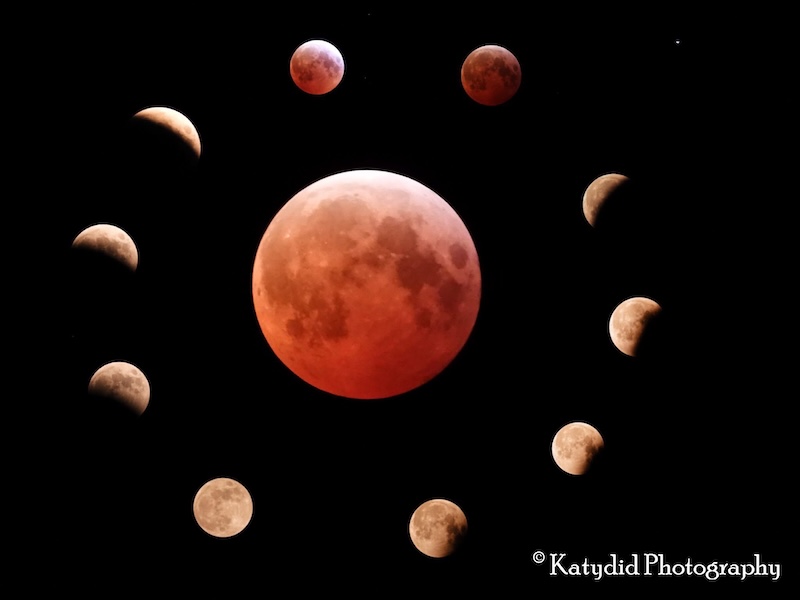


Bottom line: Eclipse seasons are periods during which eclipses not only can take place, but must take place. There’s a minimum of two eclipses (one solar and one lunar, in either order) in one eclipse season. Or there’s a maximum of three eclipses possible (either lunar/solar/lunar, or solar/lunar/solar). In 2025, the 1st eclipse season was in March, and the 2nd eclipse season is in September.
The post The 2nd eclipse season of 2025 starts this week first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/zwEtLHR

The second eclipse season of 2025 is about to start. This eclipse season will feature a total lunar eclipse on September 7, 2025. And it’ll also include a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 2025.
An eclipse season is an approximate 35-day period during which it’s inevitable for at least two (and possibly three) eclipses to take place. It’s a time period in which the Earth, moon and sun can line up in space. We have to be in an eclipse season for an eclipse to take place. Eclipse seasons happen every six months, and during this time, a lunar eclipse can occur during a full moon, and a solar eclipse can occur during a new moon.
The first eclipse season of 2025 was in March. There was a lunar eclipse on March 13-14, 2025, followed two weeks later by a partial solar eclipse on March 29, 2025.
What’s an eclipse season
During an eclipse season – when the Earth, moon and sun are able to make a line in space – it’s inevitable that at least two (and possibly three) eclipses will take place. Typically, there are two eclipses in one eclipse season, and two eclipse seasons in one calendar year. So we typically have at least four eclipses per year. Eclipse seasons repeat in cycles of 173.3 days (somewhat shy of six calendar months).
So, why don’t you see that many eclipses then? To see a lunar eclipse, the moon has to be above your horizon. So it has to be night, or close to night, and that only happens for half of Earth at once. Solar eclipses are even harder to catch. In fact, a total solar eclipse can be seen only from a narrow track along Earth’s surface. The accompanying partial solar eclipse can be seen only in areas adjacent to that track.

The 2025 eclipse seasons
The March 2025 eclipse season featured a total lunar eclipse on March 13-14, 2025, and a partial solar eclipse on March 29, 2025.
The September 2025 eclipse season will consist of a total lunar eclipse on September 7, 2025, followed two weeks later by a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 2025.
By the way, in 2025, the middles of the eclipse seasons are on March 17 and September 10. At the middle of an eclipse season, which recurs in periods of about 173 days, the lunar nodes are in exact alignment with the Earth and sun.
What causes an eclipse season?
There are many cycles in the heavens. In fact, an eclipse season is just one of these many celestial cycles.
Consider a scenario where the moon orbited Earth on the same plane as the Earth orbits the sun. Then we’d have a solar eclipse at every new moon, and a lunar eclipse at every full moon.
But, in reality, the moon’s orbit is inclined by 5 degrees to the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane). Most of the time the new moon or full moon swings too far north, or south, of the ecliptic for an eclipse to take place.
For instance, in the year 2025, we will have 12 new moons and 12 full moons, but only two solar eclipses and two lunar eclipses.
Why we have eclipses




Lunar nodes point at the sun
Twice every month, as the moon circles Earth in its orbit, the moon crosses the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane) at points called nodes. If the moon is going from south to north, it’s called the moon’s ascending node. If the moon is moving from north to south, it’s called the moon’s descending node.
Read more: Node passages of the moon: 2001 to 2100
Whenever the lunar nodes point directly at the sun, that momentous event marks the middle of the eclipse season. The alignment of the moon, sun and Earth is most exact when an eclipse happens at the middle of an eclipse season. It’s the least so when an eclipse occurs at the start or the end of an eclipse season. Any lunar eclipse happening early or late in the eclipse season presents a penumbral lunar eclipse, whereas any solar eclipse happening early or late in the eclipse season features a skimpy partial eclipse of the sun.

2 or 3 eclipses in one eclipse season?
An eclipse season most often presents only two eclipses. However, if the first eclipse falls early in the eclipse season, then it’s possible for a third eclipse to occur before the eclipse season ends.
For example, the last time three eclipses happened in one eclipse season was June-July 2020:
June 5, 2020: Penumbral lunar eclipse
June 21, 2020: Annular solar eclipse
July 5, 2020: Penumbral lunar eclipse
Likewise, the next time three eclipses will occur in one eclipse season will be June-July 2029:
June 12, 2029: Partial solar eclipse
June 26, 2029: Total lunar eclipse
July 11, 2029: Partial solar eclipse
Eclipse season terminology
With this in mind, here are some words you need to know to understand eclipse seasons: lunar nodes and ecliptic. The ecliptic is the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the sun. A lunar node is the point where, in its monthly orbit of Earth, the moon’s orbit intersects that plane. An eclipse season is when – from Earth’s perspective – the sun is close enough to a lunar node to allow an eclipse to take place. If the sun is close to a lunar node at full moon, we see a lunar eclipse. If the sun is close to a lunar node at new moon, we see a solar eclipse.
To put it another way, if the moon turns new or full in close concert with the moon’s crossing of one of its nodes, then an eclipse is not only possible, but inevitable.

Minimum of 4 eclipses in one year
A lunar month (period of time between successive new moons or successive full moons) is about 29.5 days long. So a minimum of two eclipses (one solar and one lunar, in either order) happens in one eclipse season. A maximum of three eclipses is possible (either lunar/solar/lunar or solar/lunar/solar), though the first eclipse of the eclipse season has to come quite early to allow for a third eclipse near the end.
So a minimum of two lunar eclipses and two solar eclipses occurs in one calendar year. Yet, depending on how the eclipse seasons and lunar phases align, it’s possible to also have five, six or seven eclipses in one year.
For the maximum of seven eclipses to occur in one calendar year, the first eclipse must come in early January. That leaves enough room for the seventh eclipse in late December. In one scenario, an eclipse season sporting two eclipses comes early in the year and late in the year. The middle eclipse season stages three eclipses.
It’s quite rare for seven eclipses to occur in one calendar year, however. Seven eclipses last happened in the year 1982, and will next occur in the year 2038.
Maximum of 7 eclipses in one year
Also, it’s remotely possible for a calendar year to sport two eclipse seasons with three eclipses each, and one eclipse from an eclipse season that straddles into the previous or following year. For example, we present the years 1935 and 1879-80.


Bottom line: Eclipse seasons are periods during which eclipses not only can take place, but must take place. There’s a minimum of two eclipses (one solar and one lunar, in either order) in one eclipse season. Or there’s a maximum of three eclipses possible (either lunar/solar/lunar, or solar/lunar/solar). In 2025, the 1st eclipse season was in March, and the 2nd eclipse season is in September.
The post The 2nd eclipse season of 2025 starts this week first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/zwEtLHR

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire