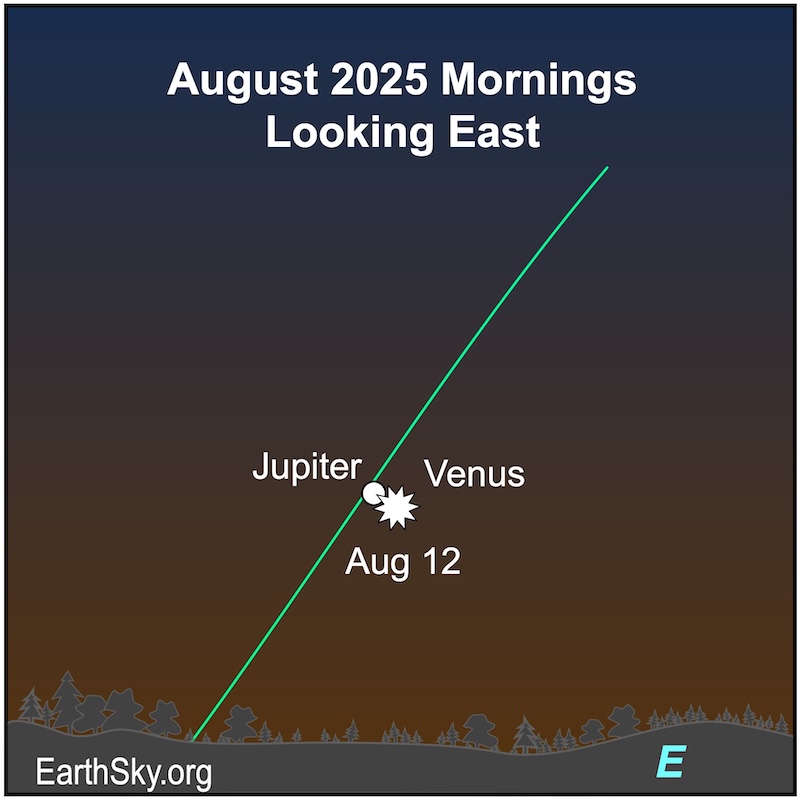
The sky’s two brightest planets, Venus and Jupiter, are about to have a spectacular conjunction in the east before sunrise! They’ll be closest on the morning of August 12, the same morning as the peak of the Perseid meteor shower. Wow!
What’s a conjunction?
Occasionally, two or more objects meet up with each other in our sky. Astronomers use the word conjunction to describe these meetings. The word conjunction comes from Latin, meaning to join together. Maybe you remember the old Conjunction Junction cartoons from the 1970s. In language, conjunctions relate to clauses brought together with words like and. In astronomy, conjunctions relate to two or more objects brought together in the sky.
Technically speaking, objects are said to be in conjunction when they have the same right ascension – sort of like celestial longitude – on our sky’s dome. Practically speaking, objects in conjunction will likely be visible near each other for some days. In fact, Venus and Jupiter will be spectacular for days around their conjunction on August 12.
Sometimes one of these objects in a conjunction is the sun, so the conjunction can’t be seen. But other conjunctions – between stars, our moon, and the planets – can be truly spectacular.

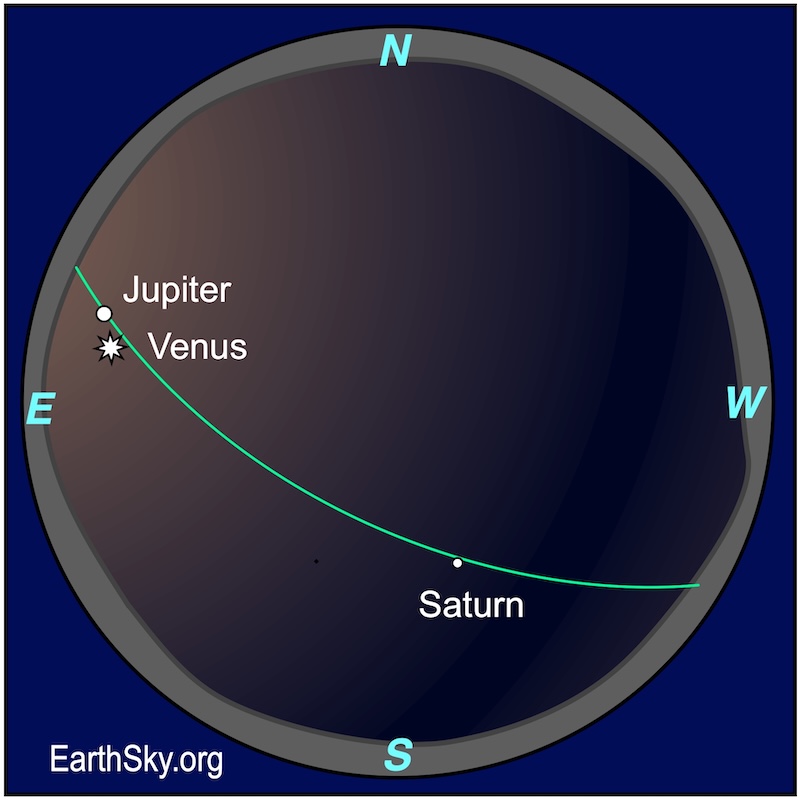
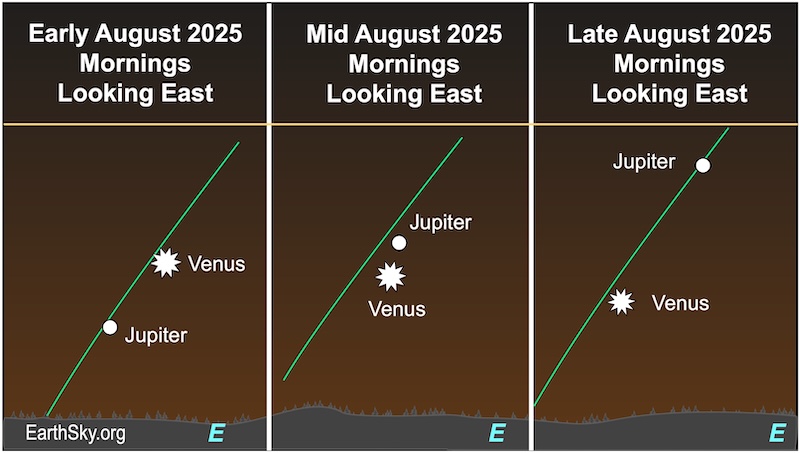
Charts for Venus and Jupiter
You can’t see an inferior conjunction
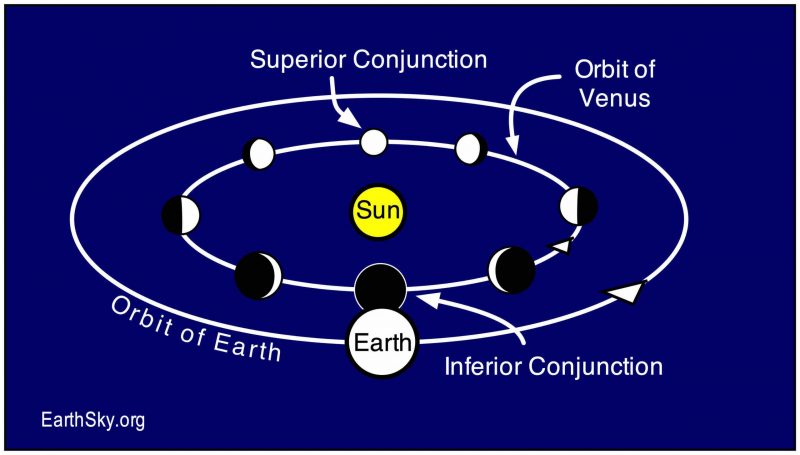
An inferior conjunction is when an object passes between us and the sun. Any object that orbits the sun closer than Earth does might pass through inferior conjunction from time to time. That is assuming its orbit lies more or less close to the ecliptic.
Usually, though, when astronomers speak of an inferior conjunction, they’re talking about Venus or Mercury, which orbit between Earth and the sun. Astronomers sometimes refer to Venus and Mercury as inferior planets. When they’re at or near inferior conjunction, we generally can’t see them. They’re hidden in the sun’s glare. Occasionally, though, Venus or Mercury at inferior conjunction can be seen to transit across the sun’s disk.
We shouldn’t forget the moon here. It passes between Earth and the sun at new moon once each month. Therefore it would be correct, if a little unusual, to say that the moon is at inferior conjunction when it’s at its new phase.
You can’t see a superior conjunction either
A superior conjunction is when an object passes behind the sun from our point of view. Look at Venus’ orbit in the diagram above. Half of its conjunctions with the sun – when they come together on our sky’s dome – are inferior conjunctions, and half are superior conjunctions. It’s fun to imagine the inferior planets on an endless cycle of passing in front of the sun, as seen from Earth, then behind it, and back again, like squirrels running around a tree.
Meanwhile, the superior planets – or planets farther from the sun than Earth – can never be at inferior conjunction. Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune can never pass between us and the sun. So the superior planets only have superior conjunctions.
But other conjunctions can look beautiful
The most common – and most exciting – type of conjunction doesn’t involve the sun. Any time two objects pass each other on the sky’s dome, they’re said to be at conjunction. This sort of conjunction – maybe between two planets, or a planet and a star, or a star and the moon – happens multiple times every month. They are beautiful. The view can stop you in your tracks.
For example, if you were fortunate enough to have looked at the moon on July 21, 1969, the day that Neil Armstrong took the first step on the moon’s Sea of Tranquility, you’d have seen the moon in conjunction with Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo. They were only about 2 degrees apart that night. That’s a bit more than the width of your index finger held out at arm’s length.
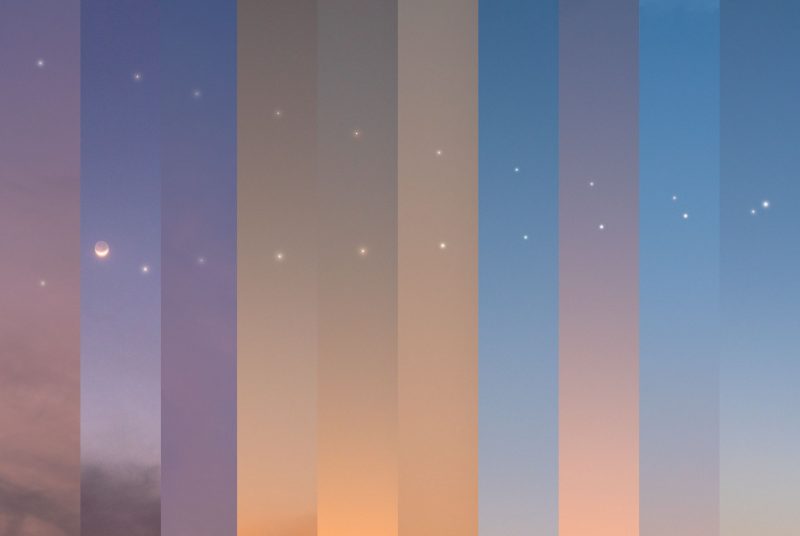
There are always a few particularly good conjunctions every year. On March 1-2, 2023, we were treated to a spectacular conjunction between bright planets Venus and Jupiter, as you can see below. Click here to see a full gallery of Venus-Jupiter conjunction photos captured by members of the EarthSky community.
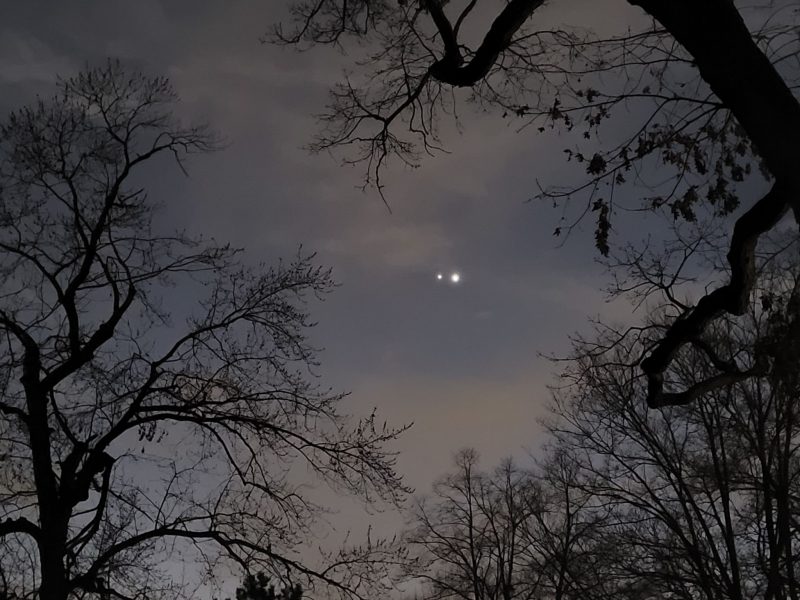

Watch for and enjoy conjunctions
People often think about the night sky as being permanent and unchanging, at least on a human scale. If you watch the skies often, though, you’ve surely noticed that’s not true. The stars don’t move relative to each other, but they do move across the sky over the course of a single night, as Earth spins under the sky. And, from one night to the next, each star rises and sets four minutes earlier each day, as Earth moves around the sun.
Once you’ve found the ecliptic – the sun’s path across the sky – you can see where the real action is. Because they are relatively close to us, the planets and moon do move relative to each other and the stars, and quickly, from our point of view. They change their positions, appear to move closer together and farther apart, and sometimes pass by each other in the sky coming to conjunction. Of all of the pleasures of stargazing, seeing this movement of our nearest neighbors is one of the greatest.
Stay up to date with upcoming conjunctions via EarthSky’s night sky guide.
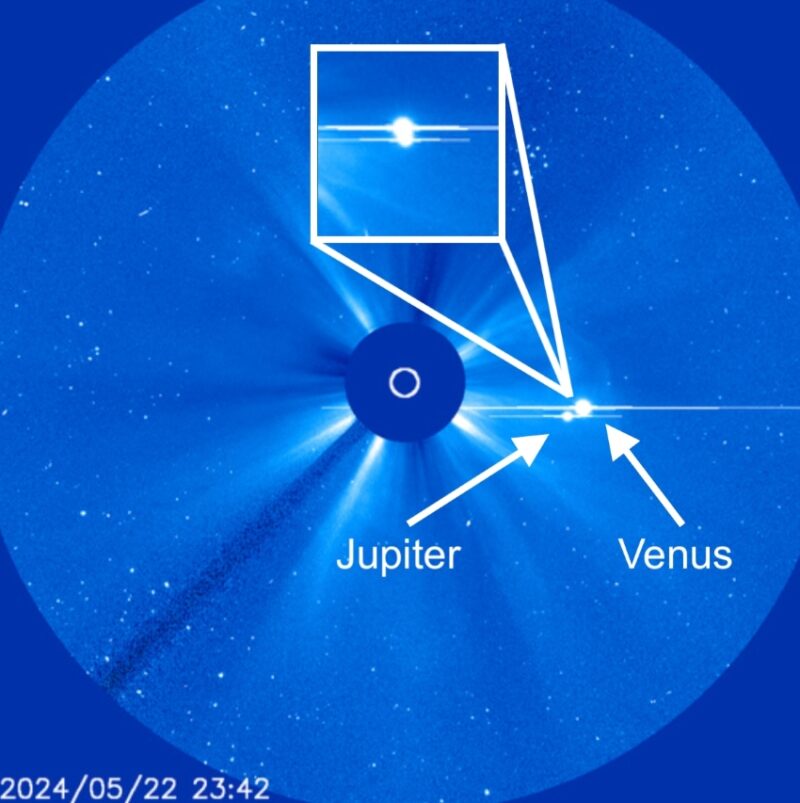
Bottom line: A conjunction is when two objects are close together on our sky’s dome. Practically, they are near each other for some days. Don’t miss the conjunction between Venus and Jupiter around August 12, 2025.
The post What’s a conjunction? See Venus and Jupiter on August 12 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/rec6IO0

The sky’s two brightest planets, Venus and Jupiter, are about to have a spectacular conjunction in the east before sunrise! They’ll be closest on the morning of August 12, the same morning as the peak of the Perseid meteor shower. Wow!
What’s a conjunction?
Occasionally, two or more objects meet up with each other in our sky. Astronomers use the word conjunction to describe these meetings. The word conjunction comes from Latin, meaning to join together. Maybe you remember the old Conjunction Junction cartoons from the 1970s. In language, conjunctions relate to clauses brought together with words like and. In astronomy, conjunctions relate to two or more objects brought together in the sky.
Technically speaking, objects are said to be in conjunction when they have the same right ascension – sort of like celestial longitude – on our sky’s dome. Practically speaking, objects in conjunction will likely be visible near each other for some days. In fact, Venus and Jupiter will be spectacular for days around their conjunction on August 12.
Sometimes one of these objects in a conjunction is the sun, so the conjunction can’t be seen. But other conjunctions – between stars, our moon, and the planets – can be truly spectacular.

Charts for Venus and Jupiter


You can’t see an inferior conjunction
An inferior conjunction is when an object passes between us and the sun. Any object that orbits the sun closer than Earth does might pass through inferior conjunction from time to time. That is assuming its orbit lies more or less close to the ecliptic.
Usually, though, when astronomers speak of an inferior conjunction, they’re talking about Venus or Mercury, which orbit between Earth and the sun. Astronomers sometimes refer to Venus and Mercury as inferior planets. When they’re at or near inferior conjunction, we generally can’t see them. They’re hidden in the sun’s glare. Occasionally, though, Venus or Mercury at inferior conjunction can be seen to transit across the sun’s disk.
We shouldn’t forget the moon here. It passes between Earth and the sun at new moon once each month. Therefore it would be correct, if a little unusual, to say that the moon is at inferior conjunction when it’s at its new phase.

You can’t see a superior conjunction either
A superior conjunction is when an object passes behind the sun from our point of view. Look at Venus’ orbit in the diagram above. Half of its conjunctions with the sun – when they come together on our sky’s dome – are inferior conjunctions, and half are superior conjunctions. It’s fun to imagine the inferior planets on an endless cycle of passing in front of the sun, as seen from Earth, then behind it, and back again, like squirrels running around a tree.
Meanwhile, the superior planets – or planets farther from the sun than Earth – can never be at inferior conjunction. Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune can never pass between us and the sun. So the superior planets only have superior conjunctions.
But other conjunctions can look beautiful
The most common – and most exciting – type of conjunction doesn’t involve the sun. Any time two objects pass each other on the sky’s dome, they’re said to be at conjunction. This sort of conjunction – maybe between two planets, or a planet and a star, or a star and the moon – happens multiple times every month. They are beautiful. The view can stop you in your tracks.
For example, if you were fortunate enough to have looked at the moon on July 21, 1969, the day that Neil Armstrong took the first step on the moon’s Sea of Tranquility, you’d have seen the moon in conjunction with Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo. They were only about 2 degrees apart that night. That’s a bit more than the width of your index finger held out at arm’s length.
There are always a few particularly good conjunctions every year. On March 1-2, 2023, we were treated to a spectacular conjunction between bright planets Venus and Jupiter, as you can see below. Click here to see a full gallery of Venus-Jupiter conjunction photos captured by members of the EarthSky community.

Watch for and enjoy conjunctions
People often think about the night sky as being permanent and unchanging, at least on a human scale. If you watch the skies often, though, you’ve surely noticed that’s not true. The stars don’t move relative to each other, but they do move across the sky over the course of a single night, as Earth spins under the sky. And, from one night to the next, each star rises and sets four minutes earlier each day, as Earth moves around the sun.
Once you’ve found the ecliptic – the sun’s path across the sky – you can see where the real action is. Because they are relatively close to us, the planets and moon do move relative to each other and the stars, and quickly, from our point of view. They change their positions, appear to move closer together and farther apart, and sometimes pass by each other in the sky coming to conjunction. Of all of the pleasures of stargazing, seeing this movement of our nearest neighbors is one of the greatest.
Stay up to date with upcoming conjunctions via EarthSky’s night sky guide.

Bottom line: A conjunction is when two objects are close together on our sky’s dome. Practically, they are near each other for some days. Don’t miss the conjunction between Venus and Jupiter around August 12, 2025.
The post What’s a conjunction? See Venus and Jupiter on August 12 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/rec6IO0

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire