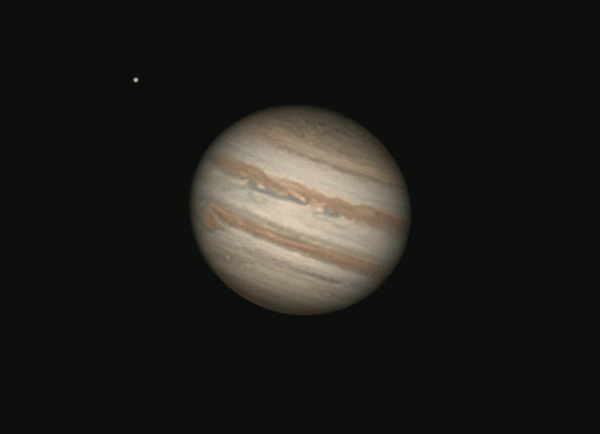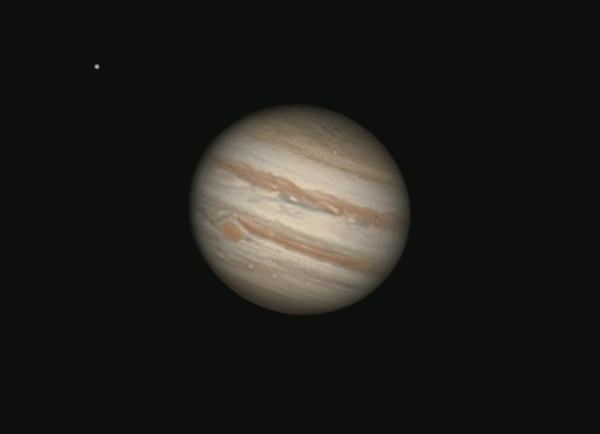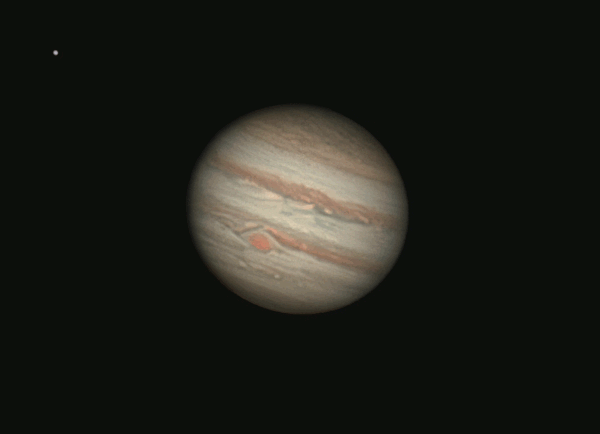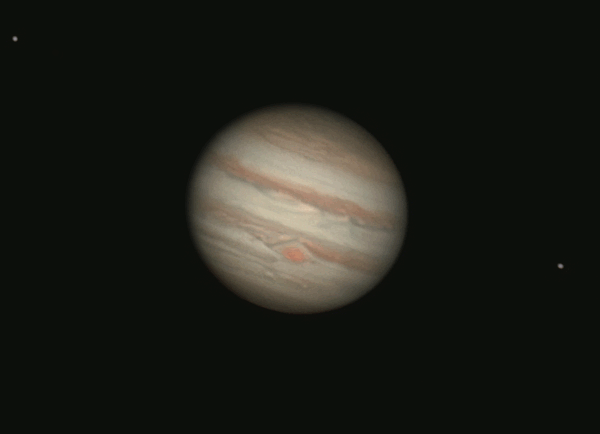
Jupiter closest to Earth December 6, 2024
Have you noticed a very bright object ascending in the east earlier each evening? That’s the giant planet Jupiter, now brighter than all the stars!
Jupiter’s perigee – or closest point to the Earth for 2024 – comes at 10 UTC (5 a.m. CDT) on December 6. That’s when the distance between the Earth and Jupiter will be at its least for 2024. Jupiter will be 380 million miles, or 611 million km, away from Earth (and 471 million miles, or 759 million km, away from the sun). This translates to 34 light-minutes away from Earth.
Less than 24 hours later – at 21 UTC (4 p.m. CDT) on December 7, 2024 – Jupiter will reach opposition, when it’s opposite the sun in our sky. That’ll happen as Earth flies between the sun and Jupiter.
So Jupiter is closest less than a day before we go between it and the sun. Why? Why wouldn’t those two events happen simultaneously?
Exciting news, EarthSky family! The 2025 Lunar Calendar is for sale now.
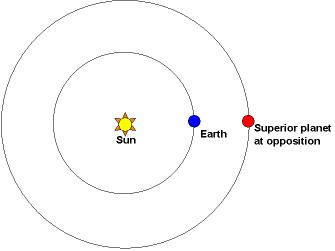
Recent oppositions
Jupiter’s last opposition – last time Earth in its smaller orbit flew between Jupiter and the sun – happened on November 3, 2023. The year before that, Jupiter reached opposition on September 26, 2022. In 2022, Jupiter was closer to Earth than it had been in 70 years … because it was a perihelion year for Jupiter, a year when the giant planet was closest to the sun in its 12-year orbit.
In 2022, during its opposition, Jupiter was 367 million miles (591 million km) from Earth. Then in 2023, Jupiter was 370 million miles, or 595 million km, away from Earth. And Jupiter will be more distant from Earth at perigee this year. Wow, right? Space is vast.
So – here’s the secret – it was the close conjunction in time between Jupiter’s yearly opposition and its once-in-12-years perihelion that gave us the close approach of Jupiter in September 2022.
And guess what? Since space is vast – because space exists over distances and timescales nearly incomprehensibly large to us humans – Jupiter in its orbit is still being affected by its closest point to the sun in 2022. Over time, slowly but surely, Jupiter is now getting farther from the sun each earthly day.
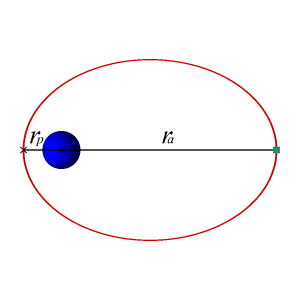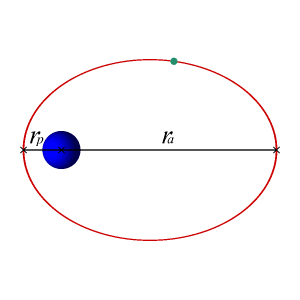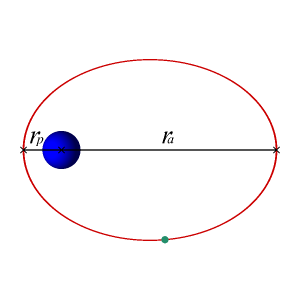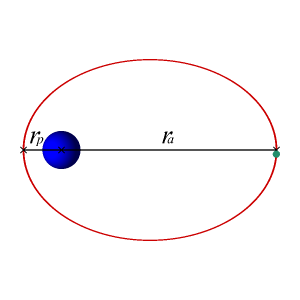
It’s about our orbits
Earth and Jupiter go around the sun on almost the same plane. Jupiter’s orbit takes 11.9 Earth-years. And Earth’s orbit takes one year.
Both Earth and Jupiter have orbits that are very nearly circular. If the orbits were exactly circular, with the sun in the center of the circle, both Earth and Jupiter would always stay at the exact same distance from the sun.
But the orbits of both Earth and Jupiter are very slightly elliptical (like a squashed circle). So Jupiter’s distance from the sun varies, and it has a nearest point to the sun and – half a dozen Earth-years later – a farthest point from the sun.
Earth’s perihelion – or closest point to the sun – occurs every year around January 4. We’re farthest from the sun every year in early July.
Jupiter’s perihelion doesn’t happen so regularly with respect to our earthly calendar. It falls on different dates across an earthly year, every 12 years.
Jupiter last passed aphelion – its farthest point from the sun – on February 18, 2017. Jupiter’s next aphelion will come in 2028.
After 2017, Jupiter was moving closer to the sun – bit by bit, closer and closer – every earthly day.
Then it was closest point to the sun in 2022. Now it’s moving farther away from the sun – bit by bit, farther every day – and will continue to do so until 2028.
2022 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2023 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2024 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2025 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2022 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2023 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2024 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2025 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
Bottom line: Jupiter’s closest point to the Earth in 2024, is on December 6. The distance between the sun and Jupiter will be 380 million miles, or 611 million km.
Read more How to see and enjoy Jupiter’s moons
The post Why is Jupiter closest to Earth 1 day before opposition? first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/kTgmuVK

Jupiter closest to Earth December 6, 2024
Have you noticed a very bright object ascending in the east earlier each evening? That’s the giant planet Jupiter, now brighter than all the stars!
Jupiter’s perigee – or closest point to the Earth for 2024 – comes at 10 UTC (5 a.m. CDT) on December 6. That’s when the distance between the Earth and Jupiter will be at its least for 2024. Jupiter will be 380 million miles, or 611 million km, away from Earth (and 471 million miles, or 759 million km, away from the sun). This translates to 34 light-minutes away from Earth.
Less than 24 hours later – at 21 UTC (4 p.m. CDT) on December 7, 2024 – Jupiter will reach opposition, when it’s opposite the sun in our sky. That’ll happen as Earth flies between the sun and Jupiter.
So Jupiter is closest less than a day before we go between it and the sun. Why? Why wouldn’t those two events happen simultaneously?
Exciting news, EarthSky family! The 2025 Lunar Calendar is for sale now.

Recent oppositions
Jupiter’s last opposition – last time Earth in its smaller orbit flew between Jupiter and the sun – happened on November 3, 2023. The year before that, Jupiter reached opposition on September 26, 2022. In 2022, Jupiter was closer to Earth than it had been in 70 years … because it was a perihelion year for Jupiter, a year when the giant planet was closest to the sun in its 12-year orbit.
In 2022, during its opposition, Jupiter was 367 million miles (591 million km) from Earth. Then in 2023, Jupiter was 370 million miles, or 595 million km, away from Earth. And Jupiter will be more distant from Earth at perigee this year. Wow, right? Space is vast.
So – here’s the secret – it was the close conjunction in time between Jupiter’s yearly opposition and its once-in-12-years perihelion that gave us the close approach of Jupiter in September 2022.
And guess what? Since space is vast – because space exists over distances and timescales nearly incomprehensibly large to us humans – Jupiter in its orbit is still being affected by its closest point to the sun in 2022. Over time, slowly but surely, Jupiter is now getting farther from the sun each earthly day.

It’s about our orbits
Earth and Jupiter go around the sun on almost the same plane. Jupiter’s orbit takes 11.9 Earth-years. And Earth’s orbit takes one year.
Both Earth and Jupiter have orbits that are very nearly circular. If the orbits were exactly circular, with the sun in the center of the circle, both Earth and Jupiter would always stay at the exact same distance from the sun.
But the orbits of both Earth and Jupiter are very slightly elliptical (like a squashed circle). So Jupiter’s distance from the sun varies, and it has a nearest point to the sun and – half a dozen Earth-years later – a farthest point from the sun.
Earth’s perihelion – or closest point to the sun – occurs every year around January 4. We’re farthest from the sun every year in early July.
Jupiter’s perihelion doesn’t happen so regularly with respect to our earthly calendar. It falls on different dates across an earthly year, every 12 years.
Jupiter last passed aphelion – its farthest point from the sun – on February 18, 2017. Jupiter’s next aphelion will come in 2028.
After 2017, Jupiter was moving closer to the sun – bit by bit, closer and closer – every earthly day.
Then it was closest point to the sun in 2022. Now it’s moving farther away from the sun – bit by bit, farther every day – and will continue to do so until 2028.
2022 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2023 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2024 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2025 Geocentric ephemeris for Jupiter
2022 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2023 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2024 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
2025 Geocentric ephemeris for sun
Bottom line: Jupiter’s closest point to the Earth in 2024, is on December 6. The distance between the sun and Jupiter will be 380 million miles, or 611 million km.
Read more How to see and enjoy Jupiter’s moons
The post Why is Jupiter closest to Earth 1 day before opposition? first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/kTgmuVK

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire