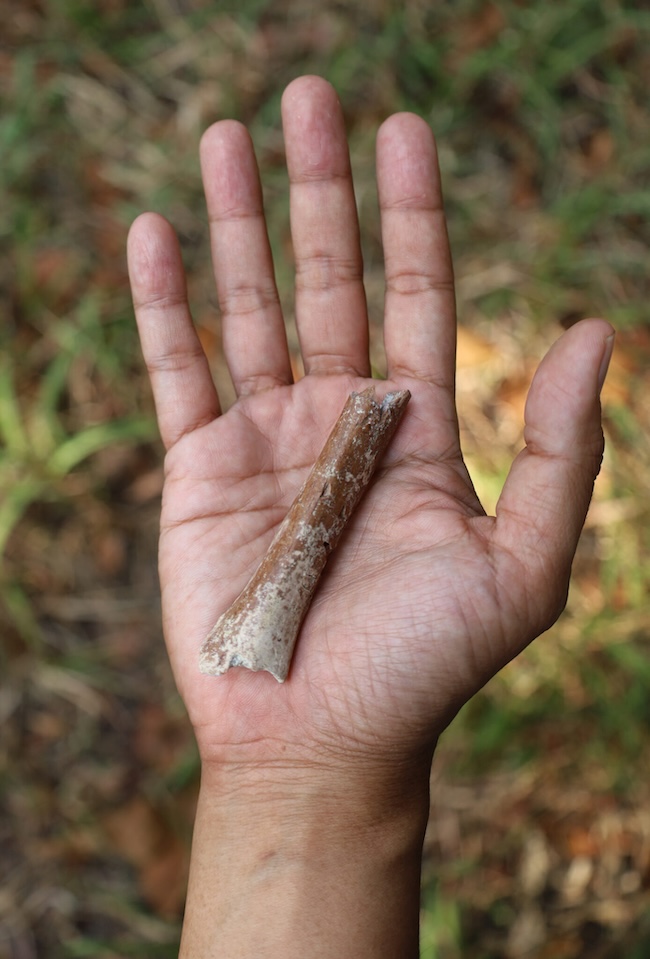

- Homo floresiensis, an extinct human species, once lived on the island of Flores, in Indonesia. They were short in stature, just over 3 feet (1 meter) tall.
- These ancient humans were nicknamed “hobbits” because of their diminutive size.
- Fossils indicate Homo floresiensis’ small size likely occurred when their ancestors, possibly Homo erectus, became isolated on Flores and evolved over time.
Small statured ancient humans once lived on the Indonesian island of Flores. This now-extinct species, Homo floresiensis, is nicknamed “hobbit” because of their diminutive size. Now, scientists report finding a fossil arm bone – a section of the humerus – that reveals new details about the evolution of this enigmatic human species. It turns out that H. floresiensis’ ancestors were smaller than scientists had previously thought.
The researchers published their findings in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications on August 6, 2024.
Adam Brumm, of Griffith University, is a paper co-author. He said, in a statement:
This very rare specimen confirms our hypothesis that the ancestors of Homo floresiensis were extremely small in body size; however, it is now apparent from the tiny proportions of this limb bone that the early progenitors of the “hobbit” were even smaller than we had previously thought.
Homo floresiensis, a real human “hobbit”
A 10-minute video introduction to the “hobbit” humans, Homo floresiensis. Via PBS Eons.
In 2003, scientists uncovered the skeleton of an adult female hominin in a cave named Liang Bua, on the island of Flores, Indonesia. (Hominin is a term often used to refer to modern and extinct human species.) She was just 3 feet 5.7 inches tall (106 cm) and they date her remains as 60,000 years old.
Subsequently, they excavated more partial skeletons from individuals of a similar diminutive stature at this cave, along with stone tools.
They named this unique human species, found only in Flores, Homo floresiensis. Because of their small size, their discoverers nicknamed them “hobbits,” after the fictional little beings created by author J. R. R. Tolkien.
H. floresiensis, scientists think, became extinct about 50,000 years ago.
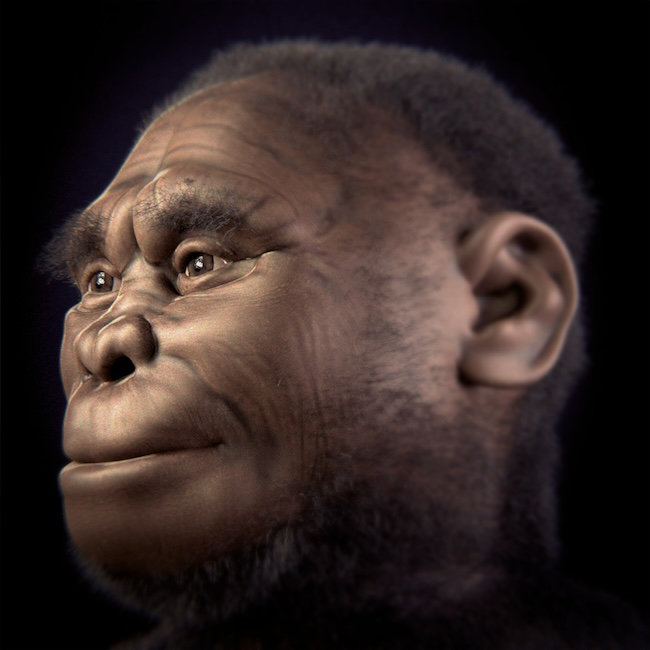

There’s been much controversy over the origins of this enigmatic species. Some scientists think that H. floresiensis descended from an ancient human species called Homo erectus that arrived at Flores about one million years ago. Others wonder if these hominins evolved from another perhaps older human species.
It’s thought their small body size is due to a phenomenon known as insular dwarfism. That’s when large animals confined to a small environment, like an island, evolve to a reduced body size over many generations.
Older fossils discovered on Flores
Since the discoveries of H. floresiensis fossils at Liang Bua Cave, scientists have uncovered even older fossils on the island. They reported, in 2016, that hominin teeth and a jaw fragment, dated 700,000 years old, were unearthed at Mata Menge, a location just 47 miles (75 km) from the Liang Bua Cave.
The researchers were intrigued by these fossils because they are like the Liang Bua Cave individuals but they are a bit smaller in size. However, they needed bones below the head to get a better sense of the size of these hominins.
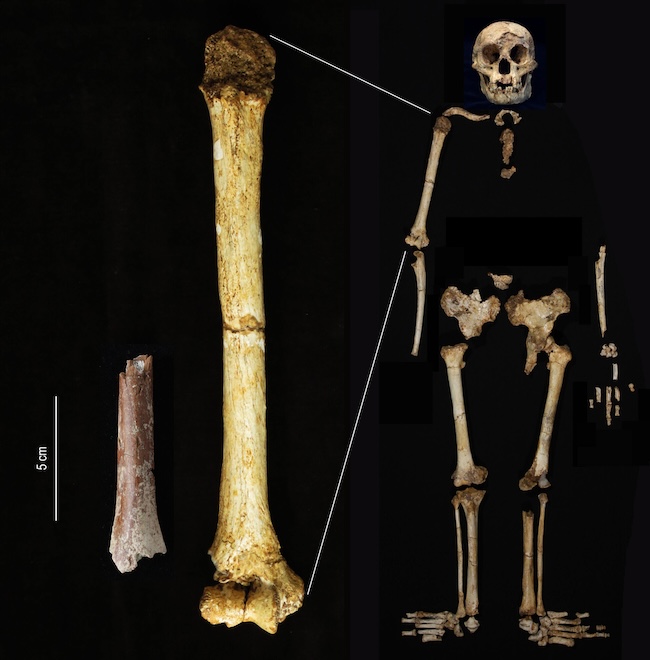
Then, in August 2024, scientists announced they had recovered and reconstructed a section of a humerus or upper arm bone. It’s dated as 700,000 years old. Moreover, a microscopic study of the humerus fossil bone structure determined that it came from an adult.
It was a significant find because scientists could now calculate the size of this individual. And that individual was just 3 feet 3.4 inches (100 cm) tall. That’s 2.4 inches (6 cm) shorter than the estimated height of the 60,000-year-old skeleton from the Liang Bua Cave.
In addition to the humerus fossil, they found two additional teeth. They were also smaller in size compared to the Liang Bua Cave specimens.
Trying to understand the evolution of the “hobbit” hominins
The Mata Menge fossils pre-date the Liang Bua skeleton by about 640,000 years. They are also anatomically similar. Therefore, scientists regard the Mata Menge individuals as ancestors of H. floresiensis from the Liang Bua Cave. However, the dentition of the Mata Menge fossils appears more primitive, according to the scientists.
They also note that the small arm bone indicates that H. floresiensis‘ extreme reduction in body size happened early in the history of this species. Brumm remarked in the statement:
The evolutionary history of the Flores hominins is still largely unknown.
However, the new fossils strongly suggest that the “hobbit” story did indeed begin when a group of the early Asian hominins known as Homo erectus somehow became isolated on this remote Indonesian island, perhaps one million years ago, and underwent a dramatic body size reduction over time.
Bottom line: Ancestors of Homo floresiensis, the “hobbit” humans, were smaller than scientists had previously thought.
Source: Early evolution of small body size in Homo floresiensis
Read more: ‘Hobbits’ among us? An anthropologist says maybe
The post Hobbit human ancestors smaller than thought first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/gVedmEU

- Homo floresiensis, an extinct human species, once lived on the island of Flores, in Indonesia. They were short in stature, just over 3 feet (1 meter) tall.
- These ancient humans were nicknamed “hobbits” because of their diminutive size.
- Fossils indicate Homo floresiensis’ small size likely occurred when their ancestors, possibly Homo erectus, became isolated on Flores and evolved over time.
Small statured ancient humans once lived on the Indonesian island of Flores. This now-extinct species, Homo floresiensis, is nicknamed “hobbit” because of their diminutive size. Now, scientists report finding a fossil arm bone – a section of the humerus – that reveals new details about the evolution of this enigmatic human species. It turns out that H. floresiensis’ ancestors were smaller than scientists had previously thought.
The researchers published their findings in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications on August 6, 2024.
Adam Brumm, of Griffith University, is a paper co-author. He said, in a statement:
This very rare specimen confirms our hypothesis that the ancestors of Homo floresiensis were extremely small in body size; however, it is now apparent from the tiny proportions of this limb bone that the early progenitors of the “hobbit” were even smaller than we had previously thought.
Homo floresiensis, a real human “hobbit”
A 10-minute video introduction to the “hobbit” humans, Homo floresiensis. Via PBS Eons.
In 2003, scientists uncovered the skeleton of an adult female hominin in a cave named Liang Bua, on the island of Flores, Indonesia. (Hominin is a term often used to refer to modern and extinct human species.) She was just 3 feet 5.7 inches tall (106 cm) and they date her remains as 60,000 years old.
Subsequently, they excavated more partial skeletons from individuals of a similar diminutive stature at this cave, along with stone tools.
They named this unique human species, found only in Flores, Homo floresiensis. Because of their small size, their discoverers nicknamed them “hobbits,” after the fictional little beings created by author J. R. R. Tolkien.
H. floresiensis, scientists think, became extinct about 50,000 years ago.

There’s been much controversy over the origins of this enigmatic species. Some scientists think that H. floresiensis descended from an ancient human species called Homo erectus that arrived at Flores about one million years ago. Others wonder if these hominins evolved from another perhaps older human species.
It’s thought their small body size is due to a phenomenon known as insular dwarfism. That’s when large animals confined to a small environment, like an island, evolve to a reduced body size over many generations.
Older fossils discovered on Flores
Since the discoveries of H. floresiensis fossils at Liang Bua Cave, scientists have uncovered even older fossils on the island. They reported, in 2016, that hominin teeth and a jaw fragment, dated 700,000 years old, were unearthed at Mata Menge, a location just 47 miles (75 km) from the Liang Bua Cave.
The researchers were intrigued by these fossils because they are like the Liang Bua Cave individuals but they are a bit smaller in size. However, they needed bones below the head to get a better sense of the size of these hominins.
Then, in August 2024, scientists announced they had recovered and reconstructed a section of a humerus or upper arm bone. It’s dated as 700,000 years old. Moreover, a microscopic study of the humerus fossil bone structure determined that it came from an adult.
It was a significant find because scientists could now calculate the size of this individual. And that individual was just 3 feet 3.4 inches (100 cm) tall. That’s 2.4 inches (6 cm) shorter than the estimated height of the 60,000-year-old skeleton from the Liang Bua Cave.
In addition to the humerus fossil, they found two additional teeth. They were also smaller in size compared to the Liang Bua Cave specimens.

Trying to understand the evolution of the “hobbit” hominins
The Mata Menge fossils pre-date the Liang Bua skeleton by about 640,000 years. They are also anatomically similar. Therefore, scientists regard the Mata Menge individuals as ancestors of H. floresiensis from the Liang Bua Cave. However, the dentition of the Mata Menge fossils appears more primitive, according to the scientists.
They also note that the small arm bone indicates that H. floresiensis‘ extreme reduction in body size happened early in the history of this species. Brumm remarked in the statement:
The evolutionary history of the Flores hominins is still largely unknown.
However, the new fossils strongly suggest that the “hobbit” story did indeed begin when a group of the early Asian hominins known as Homo erectus somehow became isolated on this remote Indonesian island, perhaps one million years ago, and underwent a dramatic body size reduction over time.
Bottom line: Ancestors of Homo floresiensis, the “hobbit” humans, were smaller than scientists had previously thought.
Source: Early evolution of small body size in Homo floresiensis
Read more: ‘Hobbits’ among us? An anthropologist says maybe
The post Hobbit human ancestors smaller than thought first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/gVedmEU

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire