- A famous variable star – T Coronae Borealis, or Blaze Star – should become visible to the unaided eye in 2024.
- It could be a once-in-a-lifetime viewing opportunity, since the star only becomes bright enough to see without optical aid every 80 years.
- This star last erupted in 1946. And astronomers believe it will do so again between now and September 2024. Learn how to spot its constellation now. Then prepare to be amazed when the “new” star, or nova, pops into view.
Do you want to see the most recent reports of T Coronae Borealis’ brightness? Check the AAVSO here.
NASA published this original article on February 27, 2024. Edits by EarthSky.
A nova could trigger a new star soon
T Coronae Borealis, which also has the nickname Blaze Star, lies 3,000 light-years away from Earth. It’s a recurring nova with outbursts about every 80 years. Its last outburst was in 1946, and astronomers believe another will occur sometime between now and September 2024.
The star system, normally magnitude +10, is far too dim to see with the unaided eye. After the nova occurs, it will jump to around magnitude +2. That’s roughly the same brightness as the North Star, Polaris.
Once its brightness peaks, it should be visible to the unaided eye for several days and just over a week with binoculars before it dims again, likely for another 80 years.

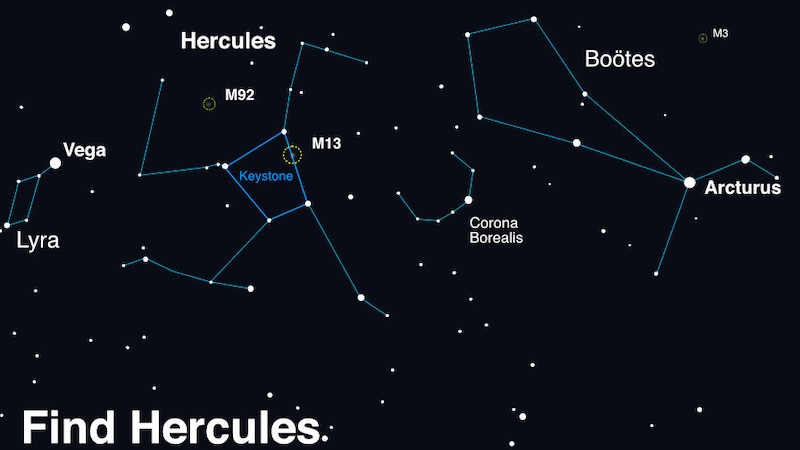
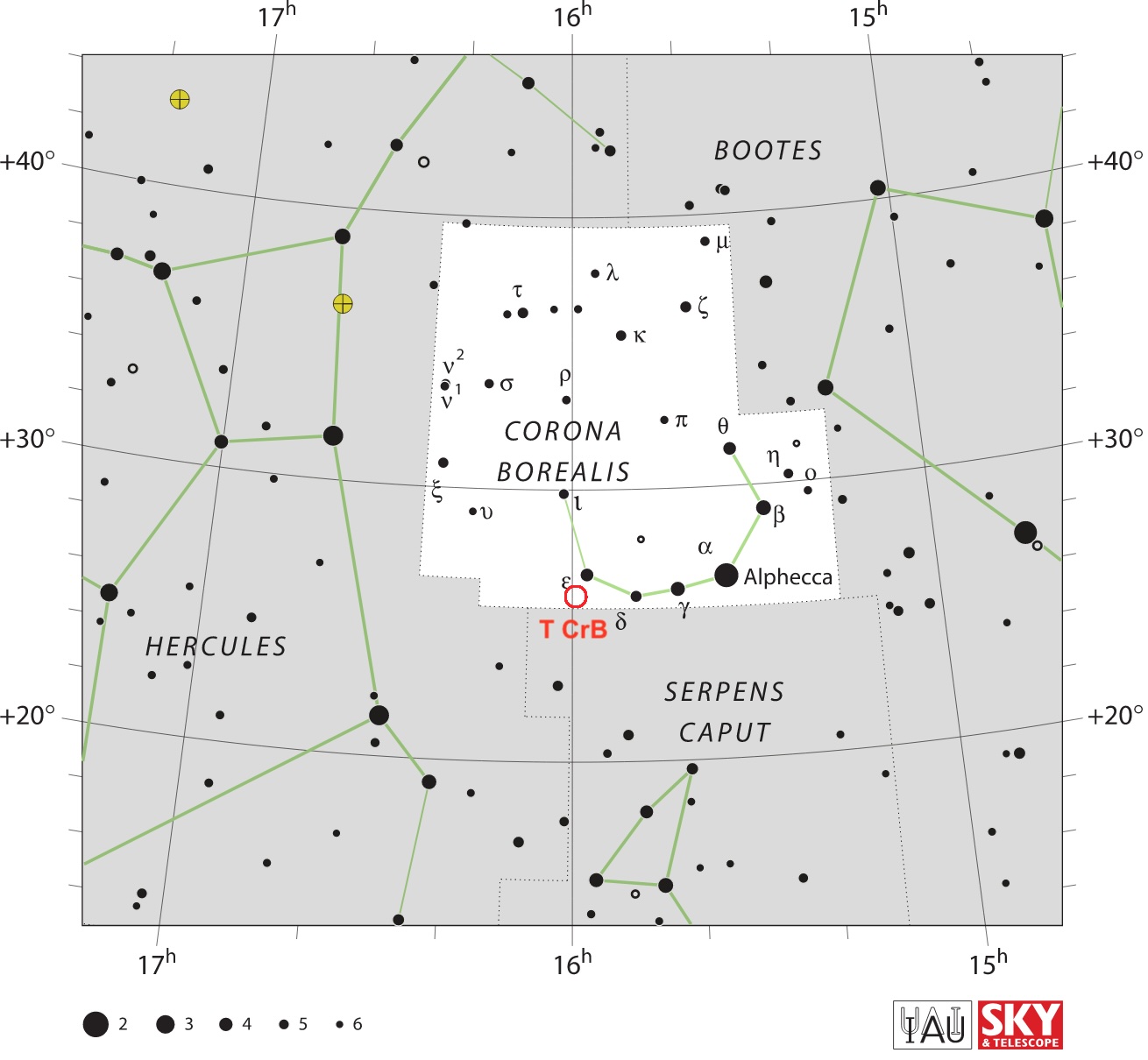
Corona Borealis is easy to see, in a dark sky
As we wait for the nova, become familiar with the constellation Corona Borealis, or the Northern Crown. It’s a small, semicircular arc between Boötes the Herdsman and Hercules the Strongman. This is where the outburst will appear as a new star.
Corona Borealis is visible in the Northern Hemisphere spring and summer (autumn and winter in the Southern Hemisphere). It’s best viewed in the month of July. You’ll find it between two bright stars (Vega and Arcturus) and two larger constellations. You’ll need a dark sky to see it.
Recurring novae are rare
As a matter of fact, this recurring nova is only one of five in our galaxy. This happens because Blaze Star is really two stars. It’s a binary system with a white dwarf and red giant. The stars are close enough that as the red giant becomes unstable from its increasing temperature and pressure and begins ejecting its outer layers, the white dwarf collects that matter onto its surface. The shallow, dense atmosphere of the white dwarf eventually heats enough to cause a runaway thermonuclear reaction, which produces the nova we see from Earth.
Bottom line: A recurring nova in Corona Borealis – Blaze Star – will probably appear as a “new star” and brighten enough to see with the unaided eye sometime in 2024.
The post Blaze Star to go nova soon! Here’s how to see it first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/MJ87LWP
- A famous variable star – T Coronae Borealis, or Blaze Star – should become visible to the unaided eye in 2024.
- It could be a once-in-a-lifetime viewing opportunity, since the star only becomes bright enough to see without optical aid every 80 years.
- This star last erupted in 1946. And astronomers believe it will do so again between now and September 2024. Learn how to spot its constellation now. Then prepare to be amazed when the “new” star, or nova, pops into view.
Do you want to see the most recent reports of T Coronae Borealis’ brightness? Check the AAVSO here.
NASA published this original article on February 27, 2024. Edits by EarthSky.
A nova could trigger a new star soon
T Coronae Borealis, which also has the nickname Blaze Star, lies 3,000 light-years away from Earth. It’s a recurring nova with outbursts about every 80 years. Its last outburst was in 1946, and astronomers believe another will occur sometime between now and September 2024.
The star system, normally magnitude +10, is far too dim to see with the unaided eye. After the nova occurs, it will jump to around magnitude +2. That’s roughly the same brightness as the North Star, Polaris.
Once its brightness peaks, it should be visible to the unaided eye for several days and just over a week with binoculars before it dims again, likely for another 80 years.

Corona Borealis is easy to see, in a dark sky
As we wait for the nova, become familiar with the constellation Corona Borealis, or the Northern Crown. It’s a small, semicircular arc between Boötes the Herdsman and Hercules the Strongman. This is where the outburst will appear as a new star.
Corona Borealis is visible in the Northern Hemisphere spring and summer (autumn and winter in the Southern Hemisphere). It’s best viewed in the month of July. You’ll find it between two bright stars (Vega and Arcturus) and two larger constellations. You’ll need a dark sky to see it.


Recurring novae are rare
As a matter of fact, this recurring nova is only one of five in our galaxy. This happens because Blaze Star is really two stars. It’s a binary system with a white dwarf and red giant. The stars are close enough that as the red giant becomes unstable from its increasing temperature and pressure and begins ejecting its outer layers, the white dwarf collects that matter onto its surface. The shallow, dense atmosphere of the white dwarf eventually heats enough to cause a runaway thermonuclear reaction, which produces the nova we see from Earth.
Bottom line: A recurring nova in Corona Borealis – Blaze Star – will probably appear as a “new star” and brighten enough to see with the unaided eye sometime in 2024.
The post Blaze Star to go nova soon! Here’s how to see it first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/MJ87LWP

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire