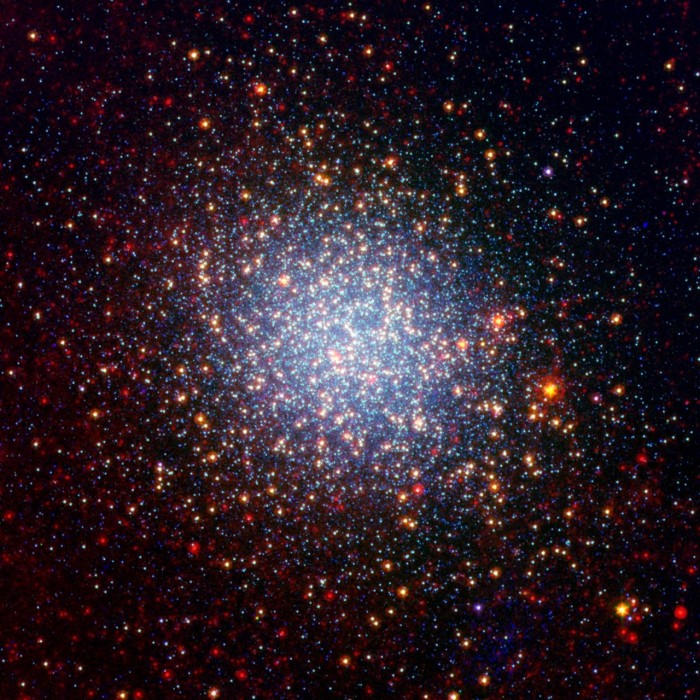

Omega Centauri is a monster globular star cluster
Omega Centauri, the largest globular star cluster of the Milky Way, contains about 10 million stars. This behemoth, also known as NGC 5139, has a diameter of about 150 light-years. And, it’s 10 times more massive than a typical globular cluster. However, despite all these stars, scientists released a study in 2018 that said Omega Centauri probably is not home to life.
Join us in making sure everyone has access to the wonders of astronomy. Donate now!
Stars pack so tightly inside Omega Centauri that the average distance between stars in the cluster’s core is 0.1 light-years. That’s much closer than the sun’s nearest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, at 4.25 light-years. So scientists concluded that stars in Omega Centauri would gravitationally interact with each other too frequently to harbor stable habitable planets.
It’s not only Omega Centauri’s great size that sets it apart from other globular star clusters. Most globular clusters generally have stars of similar age and composition. However, studies of Omega Centauri reveal that it has different stellar populations that formed at varying periods of time. In fact, it may be that Omega Centauri is something other than a globular cluster. It might be a remnant core of a small galaxy absorbed by our Milky Way galaxy in the distant past!
The difference between an open and a globular star cluster
The symmetrical, round appearance of Omega Centauri distinguishes it from star clusters such as the Pleiades and Hyades, which are open star clusters.
An open star cluster is a loose gathering of dozens to hundreds of young stars that formed together within the disk of the Milky Way galaxy. Open clusters are weakly held together by gravity, and tend to disperse after several hundreds of millions of years.
Globular clusters, on the other hand, orbit the Milky Way outside the galactic disk. They harbor tens of thousands to millions of stars. Tightly bound by gravity, globular clusters remain intact after 12 billion years.
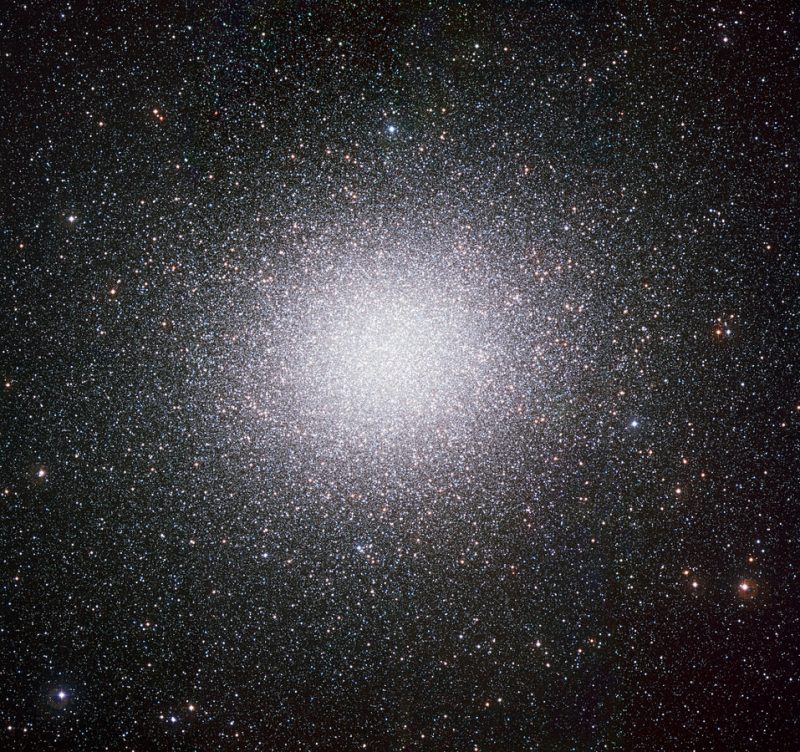

How to see Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri – the most luminous of all globular star clusters – is far to the south on the sky’s dome. It’s visible from the southern half of the United States, or south of 40 degrees north latitude (the latitude of Denver, Colorado and Beijing, China). Canadians hasten to remind us that they can spot Omega Centauri from as far north as Point Pelee in Canada (42 degrees north latitude). When seeing conditions are just right, they say they “… can catch the Omega Centauri star cluster skimming along the surface of Lake Erie.”
From the Southern Hemisphere, Omega Centauri appears much higher in the sky and is a glorious sight.
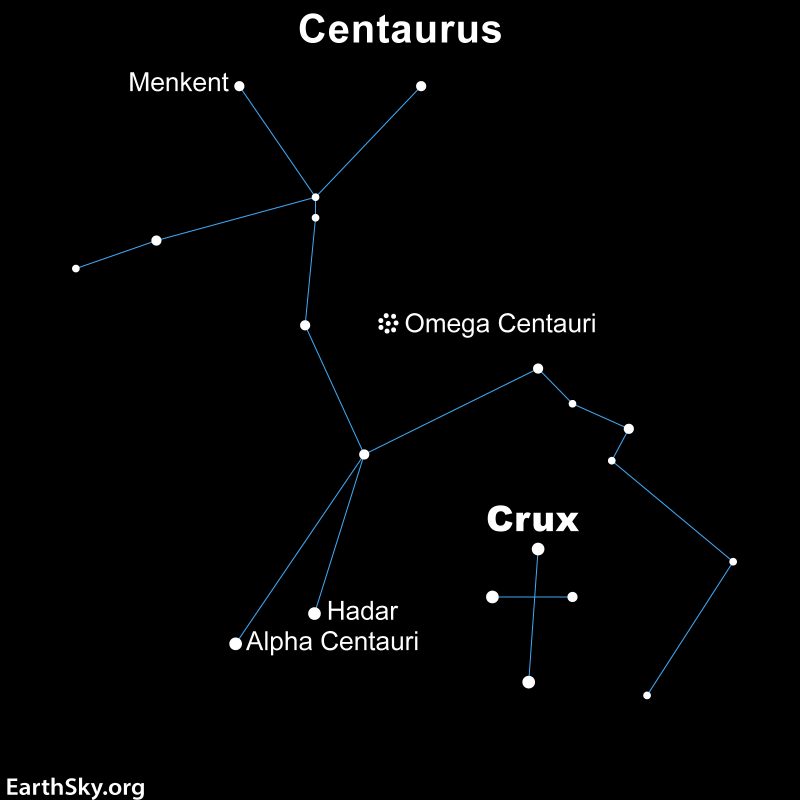
Finding Omega Centauri from the Northern Hemisphere
If you’re in the Northern Hemisphere and want to spot this cluster, know that Omega Centauri can only be seen at certain times of the year. It’s best seen in the evening sky from the Northern Hemisphere late on April, May and June evenings.
So around mid-May, this wondrous star cluster is highest up and due south around 11 p.m. your local daylight saving time.
Then, by mid-June, Omega Centauri is highest up and due south around 10 p.m. your local daylight saving time.
Northern Hemisphere residents can see Omega Centauri from January through April as well, but they must be willing to stay up past midnight or get up before dawn.
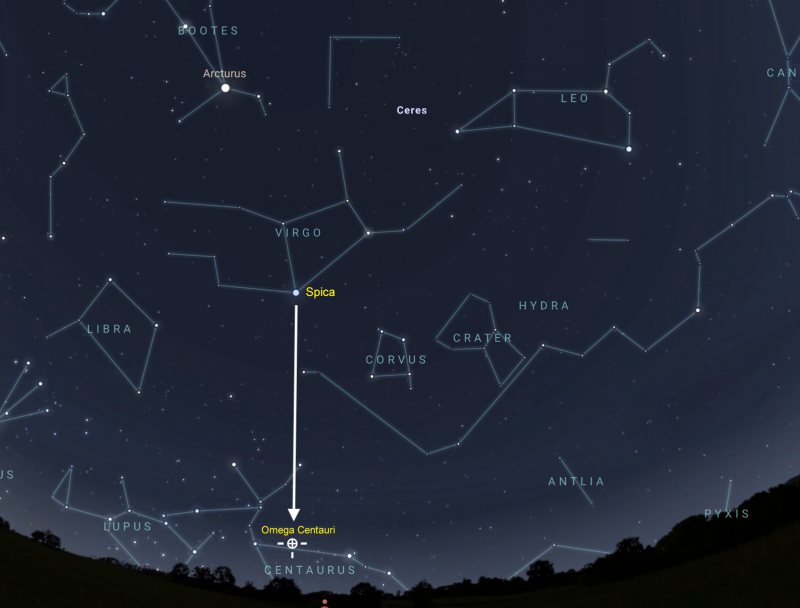
Use the Big Dipper to find Spica
For those in the Northern Hemisphere, Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, serves as your guide star to Omega Centauri. When Spica and Omega Centauri transit – appear due south and reach the highest point in the sky – they do so in unison. However, Omega Centauri transits about 35 degrees south of (or below) sparkling blue-white Spica. For reference, your fist at arm’s length approximates 10 degrees of sky. Find Spica by following the arc in the handle of the Big Dipper.
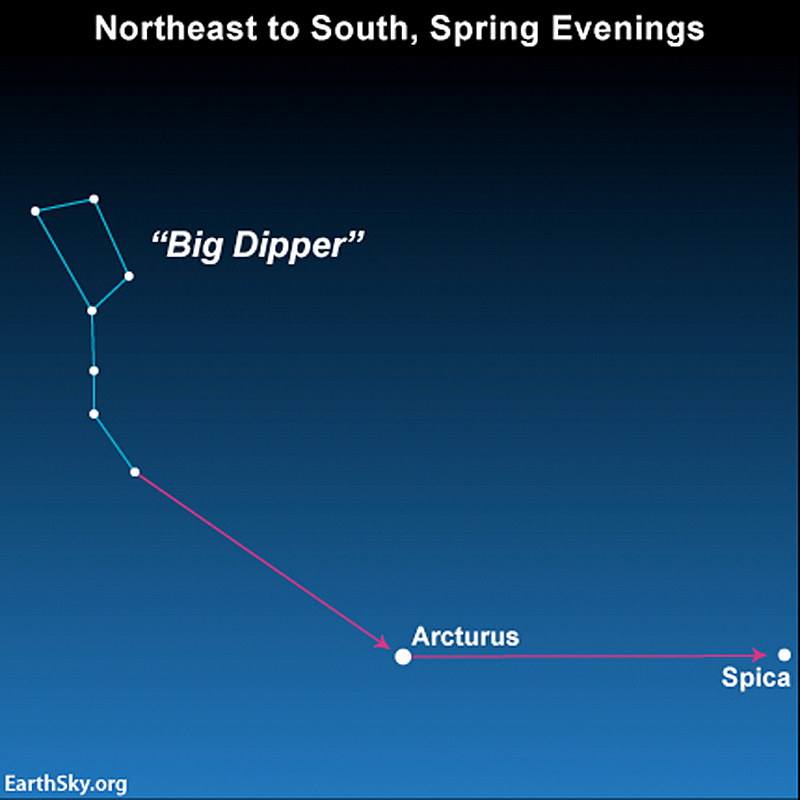
Use the search function in Stellarium-Web.org to locate sky objects as viewed from your location
It’s visible to the unaided eye
Generally, open clusters visible to the unaided eye are hundreds to a few thousand light-years away. In contrast, globular clusters are generally tens of thousands of light-years distant.
At about 16,000 light-years, Omega Centauri is one of the few of our galaxy’s 150 or so globular clusters that is visible to the unaided eye. It shines at +3.9 magnitude. It looks like a faint, fuzzy star, but Omega Centauri’s mere presence testifies to its size and brilliance. Like any globular cluster, Omega Centauri is best viewed with a telescope.
Omega Centauri’s position is at Right Ascension: 13h 26.8m; Declination: 47 degrees 29′ south.
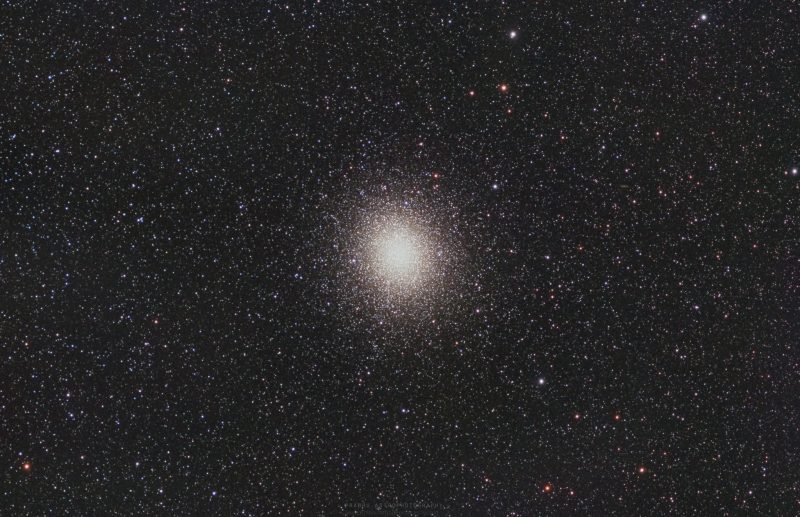

Bottom line: The Milky Way’s largest globular star cluster, Omega Centauri, contains about 10 million stars. It’s visible from the Southern Hemisphere as well as parts of the Northern Hemisphere.
Enjoying EarthSky? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
The post Omega Centauri is the Milky Way’s largest star cluster first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/yzmKr5a

Omega Centauri is a monster globular star cluster
Omega Centauri, the largest globular star cluster of the Milky Way, contains about 10 million stars. This behemoth, also known as NGC 5139, has a diameter of about 150 light-years. And, it’s 10 times more massive than a typical globular cluster. However, despite all these stars, scientists released a study in 2018 that said Omega Centauri probably is not home to life.
Join us in making sure everyone has access to the wonders of astronomy. Donate now!
Stars pack so tightly inside Omega Centauri that the average distance between stars in the cluster’s core is 0.1 light-years. That’s much closer than the sun’s nearest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, at 4.25 light-years. So scientists concluded that stars in Omega Centauri would gravitationally interact with each other too frequently to harbor stable habitable planets.
It’s not only Omega Centauri’s great size that sets it apart from other globular star clusters. Most globular clusters generally have stars of similar age and composition. However, studies of Omega Centauri reveal that it has different stellar populations that formed at varying periods of time. In fact, it may be that Omega Centauri is something other than a globular cluster. It might be a remnant core of a small galaxy absorbed by our Milky Way galaxy in the distant past!
The difference between an open and a globular star cluster
The symmetrical, round appearance of Omega Centauri distinguishes it from star clusters such as the Pleiades and Hyades, which are open star clusters.
An open star cluster is a loose gathering of dozens to hundreds of young stars that formed together within the disk of the Milky Way galaxy. Open clusters are weakly held together by gravity, and tend to disperse after several hundreds of millions of years.
Globular clusters, on the other hand, orbit the Milky Way outside the galactic disk. They harbor tens of thousands to millions of stars. Tightly bound by gravity, globular clusters remain intact after 12 billion years.

How to see Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri – the most luminous of all globular star clusters – is far to the south on the sky’s dome. It’s visible from the southern half of the United States, or south of 40 degrees north latitude (the latitude of Denver, Colorado and Beijing, China). Canadians hasten to remind us that they can spot Omega Centauri from as far north as Point Pelee in Canada (42 degrees north latitude). When seeing conditions are just right, they say they “… can catch the Omega Centauri star cluster skimming along the surface of Lake Erie.”
From the Southern Hemisphere, Omega Centauri appears much higher in the sky and is a glorious sight.

Finding Omega Centauri from the Northern Hemisphere
If you’re in the Northern Hemisphere and want to spot this cluster, know that Omega Centauri can only be seen at certain times of the year. It’s best seen in the evening sky from the Northern Hemisphere late on April, May and June evenings.
So around mid-May, this wondrous star cluster is highest up and due south around 11 p.m. your local daylight saving time.
Then, by mid-June, Omega Centauri is highest up and due south around 10 p.m. your local daylight saving time.
Northern Hemisphere residents can see Omega Centauri from January through April as well, but they must be willing to stay up past midnight or get up before dawn.

Use the Big Dipper to find Spica
For those in the Northern Hemisphere, Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, serves as your guide star to Omega Centauri. When Spica and Omega Centauri transit – appear due south and reach the highest point in the sky – they do so in unison. However, Omega Centauri transits about 35 degrees south of (or below) sparkling blue-white Spica. For reference, your fist at arm’s length approximates 10 degrees of sky. Find Spica by following the arc in the handle of the Big Dipper.

Use the search function in Stellarium-Web.org to locate sky objects as viewed from your location
It’s visible to the unaided eye
Generally, open clusters visible to the unaided eye are hundreds to a few thousand light-years away. In contrast, globular clusters are generally tens of thousands of light-years distant.
At about 16,000 light-years, Omega Centauri is one of the few of our galaxy’s 150 or so globular clusters that is visible to the unaided eye. It shines at +3.9 magnitude. It looks like a faint, fuzzy star, but Omega Centauri’s mere presence testifies to its size and brilliance. Like any globular cluster, Omega Centauri is best viewed with a telescope.
Omega Centauri’s position is at Right Ascension: 13h 26.8m; Declination: 47 degrees 29′ south.

Bottom line: The Milky Way’s largest globular star cluster, Omega Centauri, contains about 10 million stars. It’s visible from the Southern Hemisphere as well as parts of the Northern Hemisphere.
Enjoying EarthSky? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
The post Omega Centauri is the Milky Way’s largest star cluster first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/yzmKr5a

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire