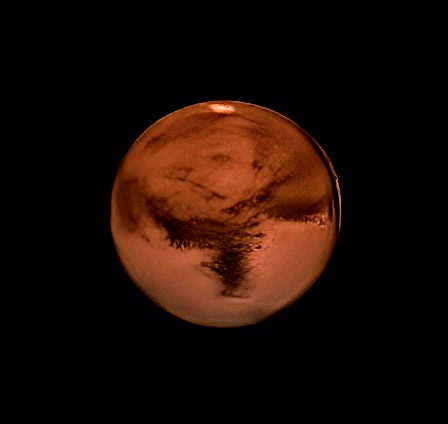

As November begins, Mars is rising in the east around 8 p.m. local time. It’s bright, and it’s red! Throughout northern fall, Mars will rise earlier each evening, edging toward its December 8, 2022, opposition.
Mars in November 2022: Mars is rising in the east around 8 p.m. local time. It’s brighter than most stars. And it’s noticeably red in color. Throughout November, Mars will continue to increase in brightness. And, each night, the red planet will rise earlier.
Opposition for Mars will fall at 6 UTC on December 8, 2022.
Mars closest to Earth: December 1, 2022 (2 UTC). At its closest, Mars will be 4.5 light-minutes from Earth.
Opposition constellation: Taurus the Bull.
Opposition brightness: Magnitude -1.9 (maximum brightness for 2022). At this point, Mars will be brighter than all the stars, but not as bright as Venus or Jupiter.
Through a telescope: At opposition, Mars will appear 17.01 arcseconds across. Major features on Mars will show surface coloration, plus Mars’ white polar cap will be visible.
Note: Opposition marks the middle of the best time to see an outer planet. So start watching Mars now! The red planet reaches opposition only about every 26 months. At opposition – as Earth flies between Mars and the sun, placing Mars opposite the sun in our sky – it’ll rise in the east at sunset, reach its highest point around midnight and set at dawn.
Finder chart

Moon occults Mars on December 7-8
The moon occults, or passes in front of, Mars at 04:21 UTC on December 8. The lunar occultation of Mars is visible from parts of the Americas, Europe and Northern Africa. Mars’ apparent diameter will be 17 arcseconds. And it’ll be shining at magnitude -1.9. So Mars will be big through a telescope and bright to the eye! The moon will be fully illuminated, but you should be able to glimpse Mars near the moon in binoculars.
Mars lunar cccultation map and local times by IOTA
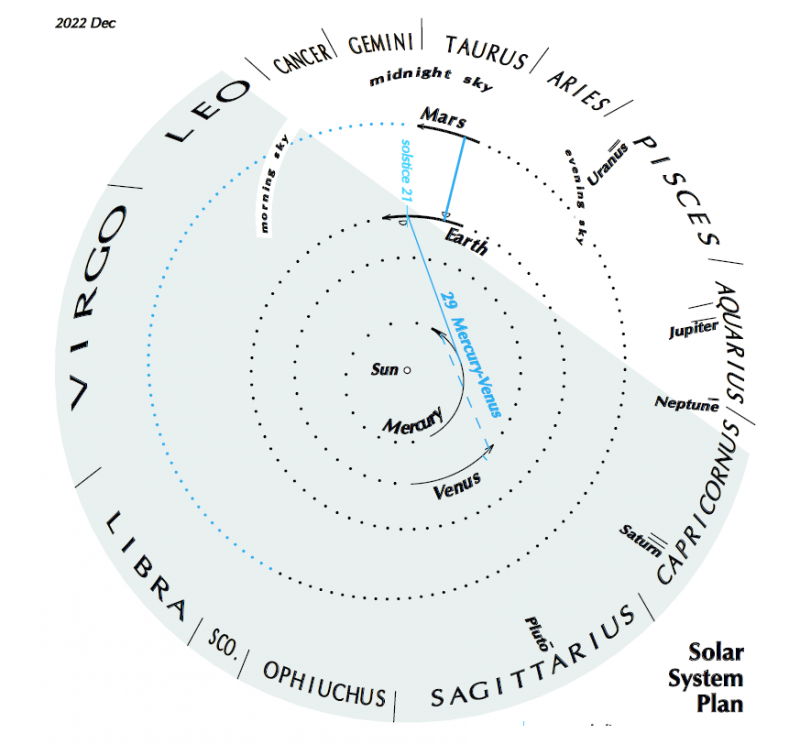
View from above the solar system, December 2022
Sometimes, Mars is faint
Mars was in our evening sky for much of 2021. But, around October, the red planet disappeared from our sky for a time. Its superior conjunction – when it was most directly behind the sun as seen from Earth – was October 8, 2021. Some weeks afterwards – as both Earth and Mars moved in their respective orbits around the sun – Mars returned to our sky as a faint red dot in the east before sunrise. It remained inconspicuous throughout the early months of 2022.

Sometimes, Mars is bright
Mars steadily brightened in the first half of 2022, first as a morning object. During the second half of 2022, Mars shines as a bright red ruby in the evening sky. It’ll reach opposition – when Earth will fly between Mars and the sun – on December 8, 2022.
Mars’ dramatic swings in brightness (and its red color) are why the early stargazers named Mars for their God of War.
Sometimes the war god rests. And sometimes he grows fierce! These changes are part of the reason Mars is so fascinating to watch in the night sky.
Want to follow Mars? Bookmark EarthSky’s monthly night sky guide.

Mars isn’t very big
To understand why Mars varies so much in brightness in Earth’s sky, first realize that Mars isn’t a very big world. It’s only 4,219 miles (6,790 km) in diameter, making it only slightly more than half Earth’s size (7,922 miles or 12,750 km in diameter).
Consider Mars in contrast to Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is 86,881 miles (140,000 km) in diameter. More than 20 planets the size of Mars could be lined up side by side in front of Jupiter. Jupiter always looks bright, because it’s so big.
Not so for little Mars. Its extremes in brightness have to do with its nearness (or lack of nearness) to Earth.

Future Martian oppositions
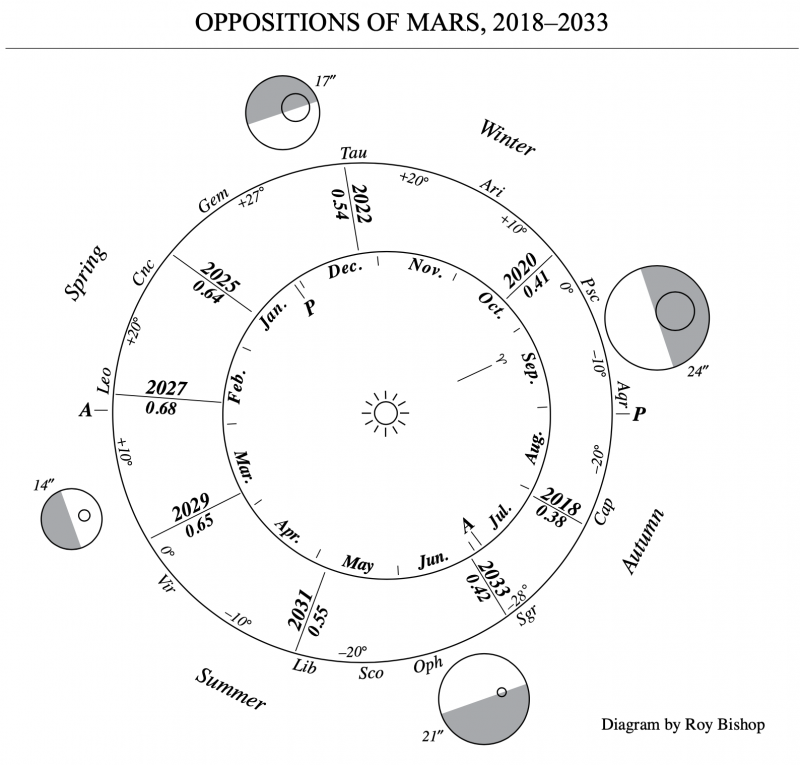
When is the next opposition of Mars? The next time Mars will appear at its brightest for that two-year period in our sky? You guessed it. In January 2025! Check out the chart on this page that lists all oppositions of Mars from 1995 to 2037.

Seeing red
Mars appears as a reddish light in the sky and is often called the red planet. Mars is currently near two obvious red stars in the sky. So, it might be fun to compare their color and intensity of red.
Mars appears red because of iron oxide in the dust that covers Mars. Iron oxide gives rust and blood its red color. Rovers on Mars sampled the Martian dust and determined it contains three colors: reds, browns and oranges. Indeed, those three colors are what you may see when you gaze upon Mars.
On the other hand, the surface temperature determines the color of a star. The hottest stars are blue; the coolest stars are red. In fact, from hottest to coolest, the colors of stars range from blue, white, yellow, orange and red. And while the colors of stars may be hard to detect, some stars are noticeably colorful.
Because Mars is in the constellation Taurus, you will notice reddish-orange Aldebaran nearby in the sky. Then, lower in the sky is mighty Orion with the famous red supergiant star, Betelgeuse.
Do you see red when you look at Mars, Aldebaran and Betelgeuse? Are they the same color? Do you see any other colors of stars?
Bottom line: Mars alternates years in appearing bright and faint in our night sky. Throughout 2021, Mars was faint. But by November 2022, Mars is bright. And it’ll brighten still more by its December 8, 2022, opposition.
Photos of bright Mars in 2018, from the EarthSky community
Photos of bright Mars in 2020, from the EarthSky community
The post Mars in 2022! Now’s the time to start watching first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/7CrpGcn

As November begins, Mars is rising in the east around 8 p.m. local time. It’s bright, and it’s red! Throughout northern fall, Mars will rise earlier each evening, edging toward its December 8, 2022, opposition.
Mars in November 2022: Mars is rising in the east around 8 p.m. local time. It’s brighter than most stars. And it’s noticeably red in color. Throughout November, Mars will continue to increase in brightness. And, each night, the red planet will rise earlier.
Opposition for Mars will fall at 6 UTC on December 8, 2022.
Mars closest to Earth: December 1, 2022 (2 UTC). At its closest, Mars will be 4.5 light-minutes from Earth.
Opposition constellation: Taurus the Bull.
Opposition brightness: Magnitude -1.9 (maximum brightness for 2022). At this point, Mars will be brighter than all the stars, but not as bright as Venus or Jupiter.
Through a telescope: At opposition, Mars will appear 17.01 arcseconds across. Major features on Mars will show surface coloration, plus Mars’ white polar cap will be visible.
Note: Opposition marks the middle of the best time to see an outer planet. So start watching Mars now! The red planet reaches opposition only about every 26 months. At opposition – as Earth flies between Mars and the sun, placing Mars opposite the sun in our sky – it’ll rise in the east at sunset, reach its highest point around midnight and set at dawn.
Finder chart

Moon occults Mars on December 7-8
The moon occults, or passes in front of, Mars at 04:21 UTC on December 8. The lunar occultation of Mars is visible from parts of the Americas, Europe and Northern Africa. Mars’ apparent diameter will be 17 arcseconds. And it’ll be shining at magnitude -1.9. So Mars will be big through a telescope and bright to the eye! The moon will be fully illuminated, but you should be able to glimpse Mars near the moon in binoculars.
Mars lunar cccultation map and local times by IOTA
View from above the solar system, December 2022

Sometimes, Mars is faint
Mars was in our evening sky for much of 2021. But, around October, the red planet disappeared from our sky for a time. Its superior conjunction – when it was most directly behind the sun as seen from Earth – was October 8, 2021. Some weeks afterwards – as both Earth and Mars moved in their respective orbits around the sun – Mars returned to our sky as a faint red dot in the east before sunrise. It remained inconspicuous throughout the early months of 2022.

Sometimes, Mars is bright
Mars steadily brightened in the first half of 2022, first as a morning object. During the second half of 2022, Mars shines as a bright red ruby in the evening sky. It’ll reach opposition – when Earth will fly between Mars and the sun – on December 8, 2022.
Mars’ dramatic swings in brightness (and its red color) are why the early stargazers named Mars for their God of War.
Sometimes the war god rests. And sometimes he grows fierce! These changes are part of the reason Mars is so fascinating to watch in the night sky.
Want to follow Mars? Bookmark EarthSky’s monthly night sky guide.

Mars isn’t very big
To understand why Mars varies so much in brightness in Earth’s sky, first realize that Mars isn’t a very big world. It’s only 4,219 miles (6,790 km) in diameter, making it only slightly more than half Earth’s size (7,922 miles or 12,750 km in diameter).
Consider Mars in contrast to Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is 86,881 miles (140,000 km) in diameter. More than 20 planets the size of Mars could be lined up side by side in front of Jupiter. Jupiter always looks bright, because it’s so big.
Not so for little Mars. Its extremes in brightness have to do with its nearness (or lack of nearness) to Earth.

Future Martian oppositions
When is the next opposition of Mars? The next time Mars will appear at its brightest for that two-year period in our sky? You guessed it. In January 2025! Check out the chart on this page that lists all oppositions of Mars from 1995 to 2037.


Seeing red
Mars appears as a reddish light in the sky and is often called the red planet. Mars is currently near two obvious red stars in the sky. So, it might be fun to compare their color and intensity of red.
Mars appears red because of iron oxide in the dust that covers Mars. Iron oxide gives rust and blood its red color. Rovers on Mars sampled the Martian dust and determined it contains three colors: reds, browns and oranges. Indeed, those three colors are what you may see when you gaze upon Mars.
On the other hand, the surface temperature determines the color of a star. The hottest stars are blue; the coolest stars are red. In fact, from hottest to coolest, the colors of stars range from blue, white, yellow, orange and red. And while the colors of stars may be hard to detect, some stars are noticeably colorful.
Because Mars is in the constellation Taurus, you will notice reddish-orange Aldebaran nearby in the sky. Then, lower in the sky is mighty Orion with the famous red supergiant star, Betelgeuse.
Do you see red when you look at Mars, Aldebaran and Betelgeuse? Are they the same color? Do you see any other colors of stars?
Bottom line: Mars alternates years in appearing bright and faint in our night sky. Throughout 2021, Mars was faint. But by November 2022, Mars is bright. And it’ll brighten still more by its December 8, 2022, opposition.
Photos of bright Mars in 2018, from the EarthSky community
Photos of bright Mars in 2020, from the EarthSky community
The post Mars in 2022! Now’s the time to start watching first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/7CrpGcn

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire