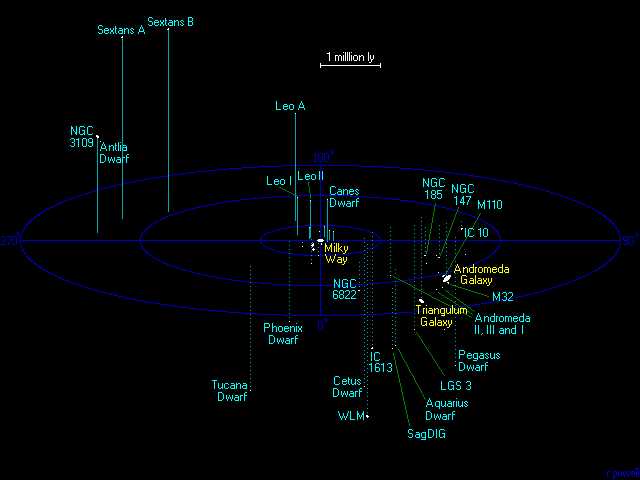
What is the Local Group?
Our universe contains at least hundreds of billions of galaxies, maybe trillions, in all shapes and sizes. Most are very far away from our home galaxy, the Milky Way. At billions of light-years away, most are too far to see without binoculars or a telescope. But our Local Group of galaxies is different. It consists of our neighboring galaxies within the vast universe. The Local Group galaxies are all located within roughly 5 million light-years of space around us. The Local Group’s diameter as a whole is about 10 million light-years. Our Milky Way is just one of three large galaxies in the Local Group. But it’s not the biggest of the Local Group galaxies. That would be the Andromeda galaxy. And the third galaxy, called the Triangulum galaxy, is the smallest of the three large ones. There are also 50 or so dwarf galaxies in the Local Group. So is the Local Group considered a large structure in our universe? Yes and no. Keep reading to learn more.
On the vast astronomical distance scale, the Local Group galaxies are relatively close to us. They’re only millions of light-years away, instead of billions. As a result, some Local Group galaxies are visible to the unaided eye from a dark site.
The illustration above suggests our Milky Way galaxy lies at the center of the Local Group. It doesn’t, of course, but the image is organized that way, honoring our human perspective. On the other hand, the Local Group does have a gravitational center. It’s somewhere between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy.
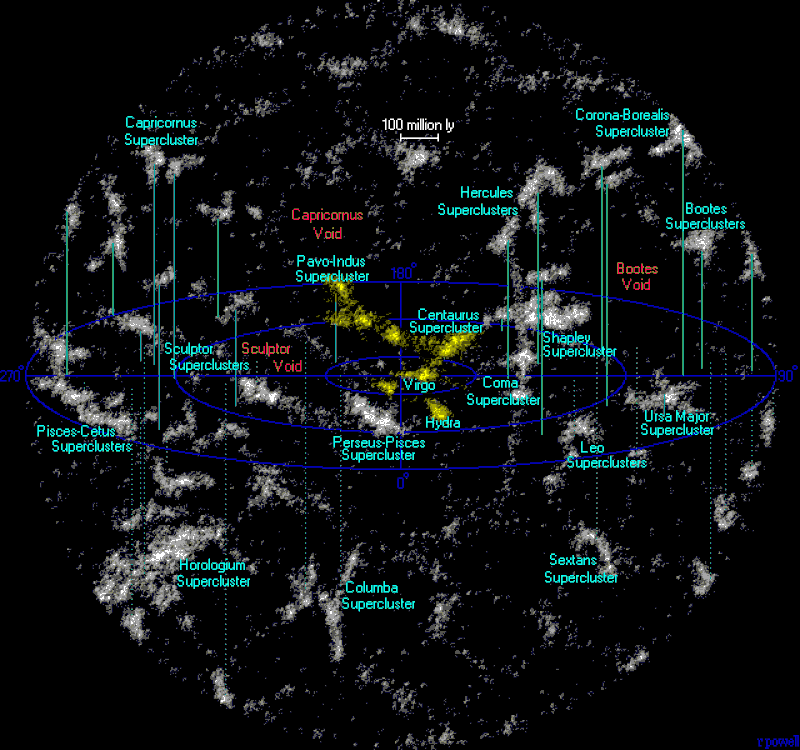
Astronomers have also discovered that our Local Group is on the outskirts of a giant supercluster of galaxies, known as the Virgo Supercluster.
EarthSky 2022 lunar calendars now available! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
Want to get to know the neighbors?
Andromeda Galaxy: All you need to know
Triangulum Galaxy: 2nd-closest large spiral galaxy
The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds
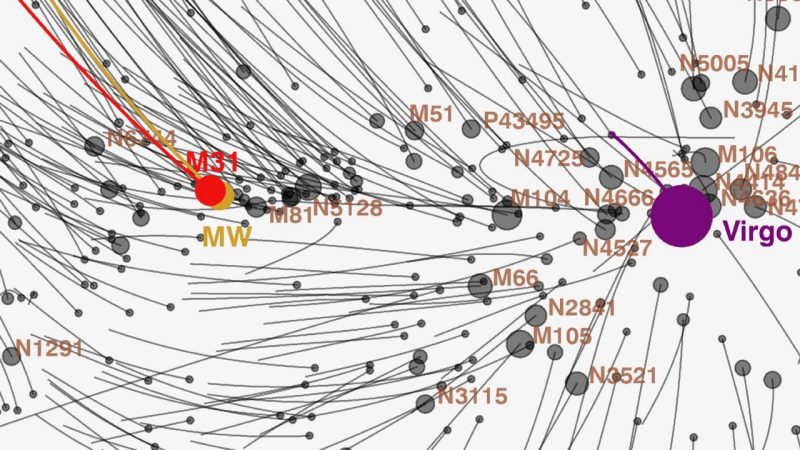
What’s bigger than the Local Group?
The Local Group is a collection of galaxies. It spans some 10 million light-years of space. But, although gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental forces of nature, gravity has an infinite range. So it’s no wonder that – as astronomers look out into space – they see groups of galaxies on both small and large scales. They see groups like the Local Group belonging to even more gigantic structures.
At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters – including our Local Group – are located within the Virgo Supercluster. The diameter of this great supercluster – sometimes called our “local” supercluster – is thought to be about 110 million light-years.
And, in 2014, astronomers announced that the Virgo Supercluster itself might be part of an even-larger structure, which astronomers call the Laniakea Supercluster. They described that greater supercluster as consisting of perhaps 100,000 galaxies stretched out over some 520 million light-years. At that time, astronomers pointed to this vast supercluster as one of many such structures known in space.
But, a few years later, another group of astronomers showed that the galaxies in the Laniakea Supercluster aren’t gravitationally bound. So, they said then, this cluster will disperse over time, rather than maintain itself as a bound object.
Will it? We don’t know for sure yet. What we do know is that gravity works across our universe to form collections of galaxies in space. Our Local Group is just one example – albeit an interesting one to us – of how galaxies like to congregate.
Big, bigger, biggest?
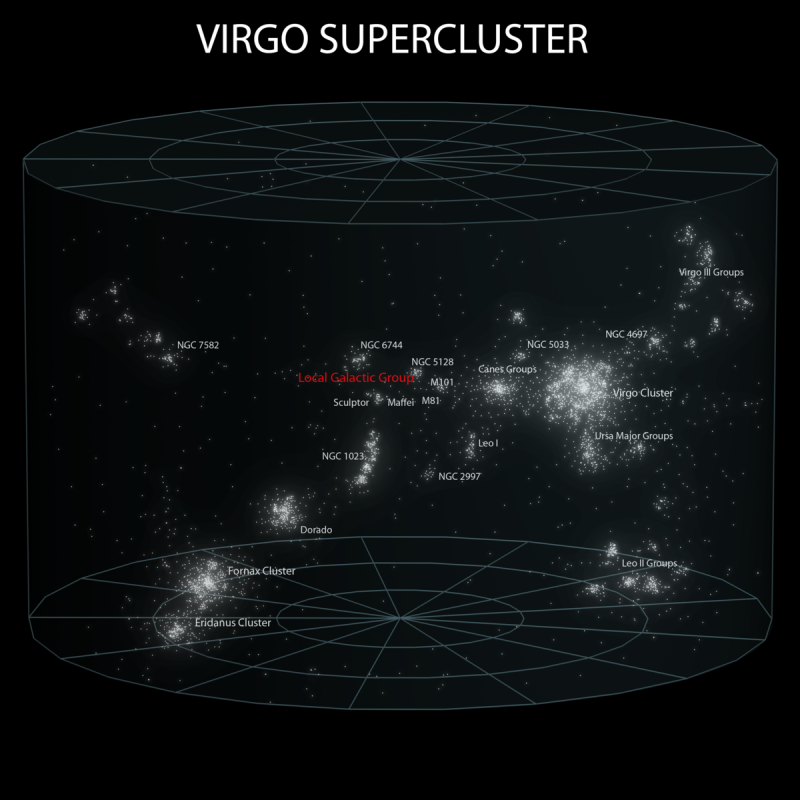
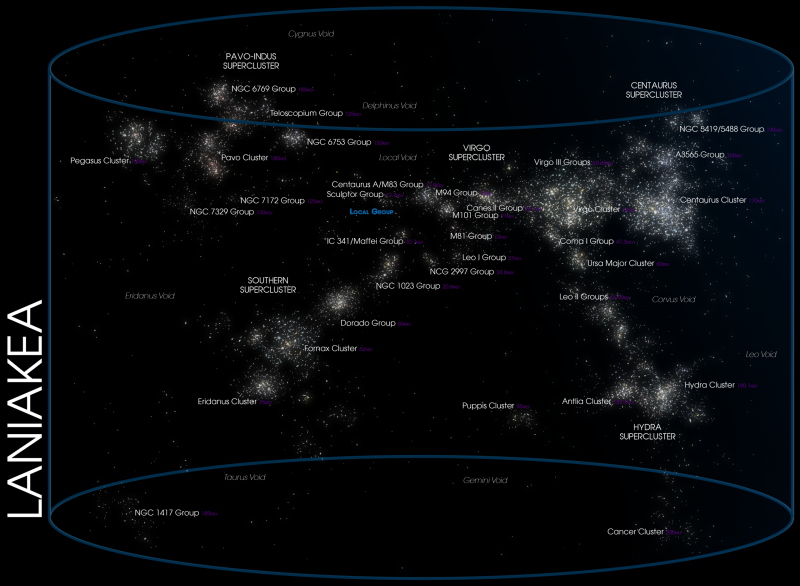
Bottom line: The Local Group of galaxies consists of three large galaxies – the Andromeda Galaxy (biggest), our Milky Way (2nd-biggest) and the Triangulum Galaxy (3rd biggest) – along with 50 or so much-smaller dwarf galaxies.
The post The Local Group is our galactic neighborhood first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3rM6XZX

What is the Local Group?
Our universe contains at least hundreds of billions of galaxies, maybe trillions, in all shapes and sizes. Most are very far away from our home galaxy, the Milky Way. At billions of light-years away, most are too far to see without binoculars or a telescope. But our Local Group of galaxies is different. It consists of our neighboring galaxies within the vast universe. The Local Group galaxies are all located within roughly 5 million light-years of space around us. The Local Group’s diameter as a whole is about 10 million light-years. Our Milky Way is just one of three large galaxies in the Local Group. But it’s not the biggest of the Local Group galaxies. That would be the Andromeda galaxy. And the third galaxy, called the Triangulum galaxy, is the smallest of the three large ones. There are also 50 or so dwarf galaxies in the Local Group. So is the Local Group considered a large structure in our universe? Yes and no. Keep reading to learn more.
On the vast astronomical distance scale, the Local Group galaxies are relatively close to us. They’re only millions of light-years away, instead of billions. As a result, some Local Group galaxies are visible to the unaided eye from a dark site.
The illustration above suggests our Milky Way galaxy lies at the center of the Local Group. It doesn’t, of course, but the image is organized that way, honoring our human perspective. On the other hand, the Local Group does have a gravitational center. It’s somewhere between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy.
Astronomers have also discovered that our Local Group is on the outskirts of a giant supercluster of galaxies, known as the Virgo Supercluster.
EarthSky 2022 lunar calendars now available! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
Want to get to know the neighbors?
Andromeda Galaxy: All you need to know
Triangulum Galaxy: 2nd-closest large spiral galaxy
The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds

What’s bigger than the Local Group?
The Local Group is a collection of galaxies. It spans some 10 million light-years of space. But, although gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental forces of nature, gravity has an infinite range. So it’s no wonder that – as astronomers look out into space – they see groups of galaxies on both small and large scales. They see groups like the Local Group belonging to even more gigantic structures.
At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters – including our Local Group – are located within the Virgo Supercluster. The diameter of this great supercluster – sometimes called our “local” supercluster – is thought to be about 110 million light-years.
And, in 2014, astronomers announced that the Virgo Supercluster itself might be part of an even-larger structure, which astronomers call the Laniakea Supercluster. They described that greater supercluster as consisting of perhaps 100,000 galaxies stretched out over some 520 million light-years. At that time, astronomers pointed to this vast supercluster as one of many such structures known in space.
But, a few years later, another group of astronomers showed that the galaxies in the Laniakea Supercluster aren’t gravitationally bound. So, they said then, this cluster will disperse over time, rather than maintain itself as a bound object.
Will it? We don’t know for sure yet. What we do know is that gravity works across our universe to form collections of galaxies in space. Our Local Group is just one example – albeit an interesting one to us – of how galaxies like to congregate.
Big, bigger, biggest?



Bottom line: The Local Group of galaxies consists of three large galaxies – the Andromeda Galaxy (biggest), our Milky Way (2nd-biggest) and the Triangulum Galaxy (3rd biggest) – along with 50 or so much-smaller dwarf galaxies.
The post The Local Group is our galactic neighborhood first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3rM6XZX

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire