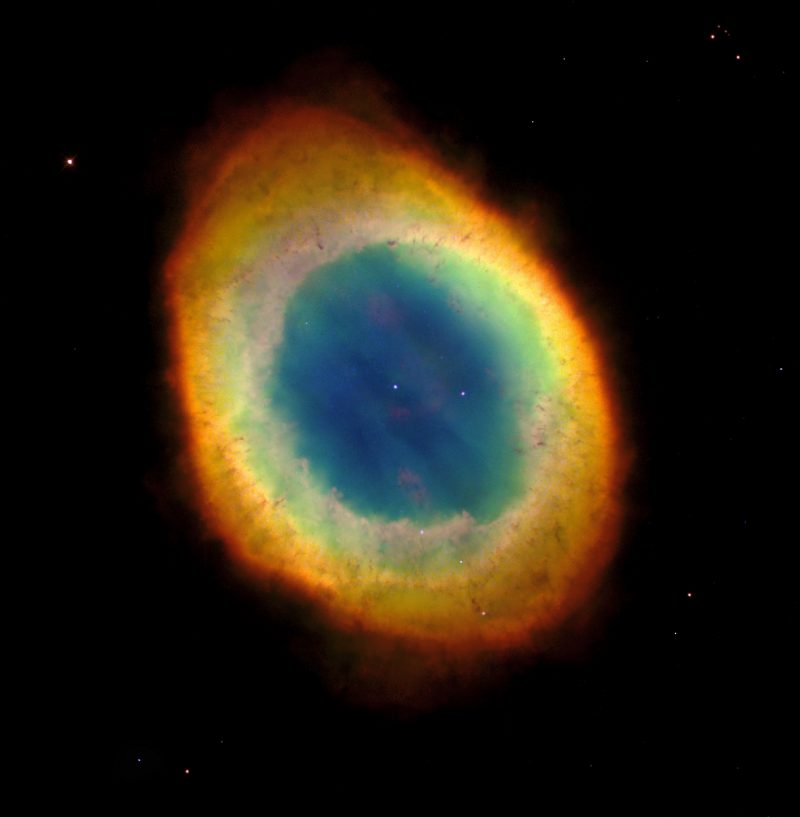
What are deep-sky objects?
Deep-sky objects lie beyond our solar system and make great observing targets for those using optical aid. Amateur stargazers sometimes refer to them as faint fuzzies. Unlike the nearby planets (which look like little disks through a telescope) or stars (which always look like pinpoints), deep-sky objects are hazy spots in the sky that start to take shape when viewed through binoculars or a telescope. Deep-sky objects generally fall into three categories: nebulae, galaxies and star clusters, including open clusters and globular clusters.
Some of the best deep-sky targets are those in the Messier catalog. Charles Messier was a comet hunter who methodically searched the skies for comets. He cataloged all objects that were not comets, but might be confused with them because they looked fuzzy.
He didn’t know it at the time, but he was creating a list of the best and brightest deep-sky objects. These groupings of stars, gas and dust in our Milky Way, plus galaxies beyond our own, are some of the most fun objects to track down with a telescope. So today’s amateur astronomers attempt to join a Messier Club, by observing all 110 Messier objects (or some subset of them). Or they perform Messier marathons, seeing as many of these objects as they can in one night.
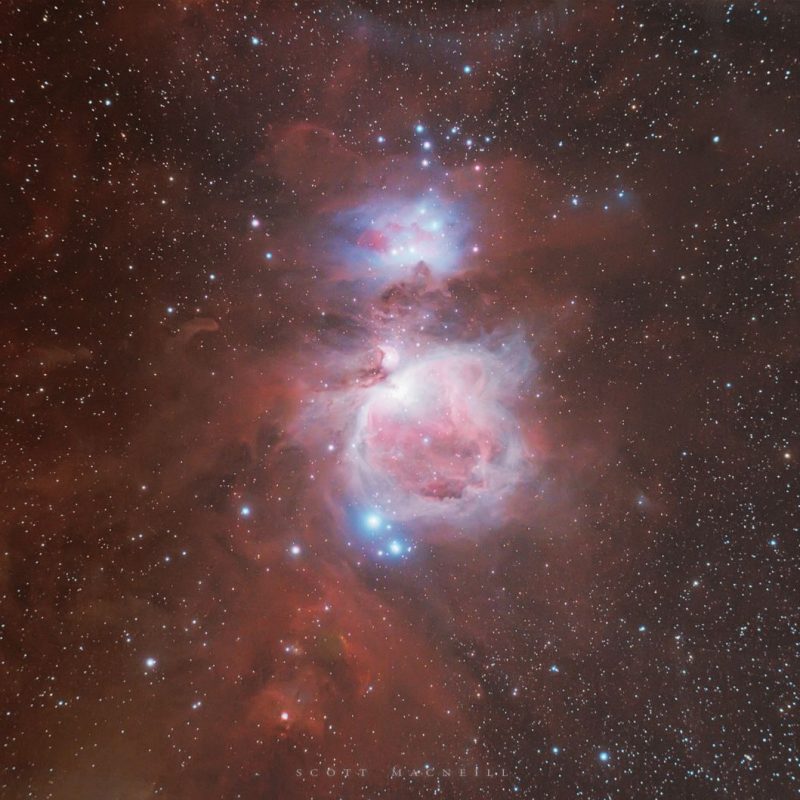

Nebulae: Clouds of gas and dust
There are a few different types of nebulae, or clouds of gas and dust, that you can observe. There are emission nebulae, which include planetary nebulae, that glow because a star late in its life has puffed off a glowing shell of ionized gas. Then there are reflection nebulae, which are clouds of dust that aren’t glowing themselves but reflecting the light of nearby stars. Lastly are the dark nebulae, which are so dense that they block out the light from any background sources. Nebulae are usually found along the plane of the Milky Way where most of the stars in our galaxy reside.
Galaxies: Island universes
Not surprisingly, the best place to look for galaxies in the night sky is away from the direction of our own galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way blocks the view of more distant island universes. The closest large spiral to Earth is also the easiest to spot, M31, or the Andromeda Galaxy. M81 and M82 are handy galactic targets for the Northern Hemisphere, because they’re visible year round.


Star clusters: Open clusters
Open star clusters are young, loosely bound gatherings of stars. One of the most famous open clusters is the Pleiades found in the constellation Taurus. Because this cluster is so close and large, you can view it best with binoculars or even the unaided eye. A telescope gives you too narrow a view and cuts out members of the cluster. The Beehive is another popular open cluster. The view of this deep-sky object improves with magnification.
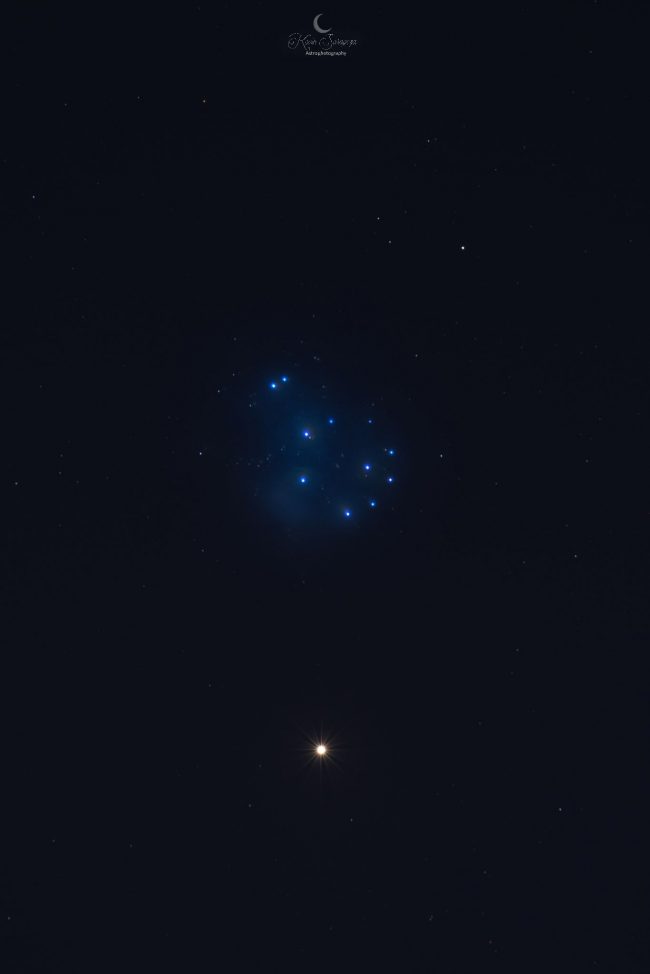
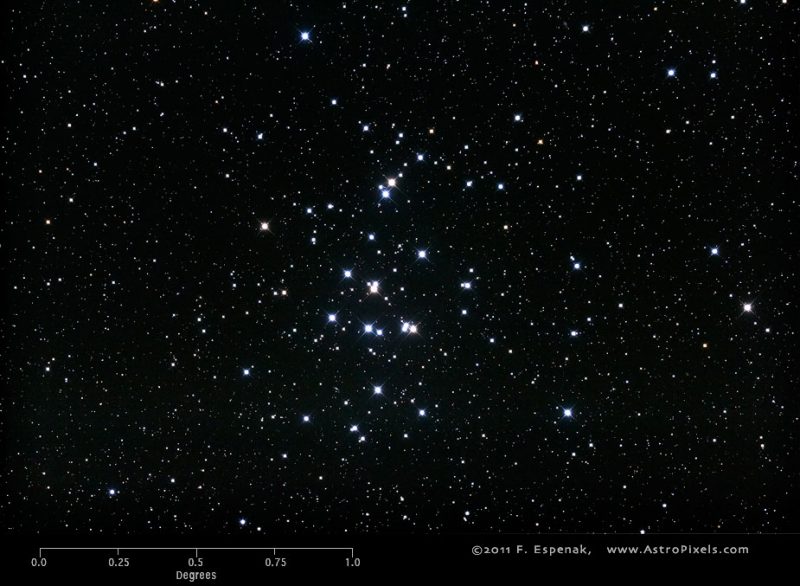


Star clusters: Globular clusters
Globular clusters are huge, ancient conglomerations of tightly packed stars that orbit in the halo of the Milky Way. The big balls of stars lie much farther away than the open clusters we see. The best known globular cluster for Northern Hemisphere observers lies in Hercules. This deep-sky target is easy to spot with a small telescope.
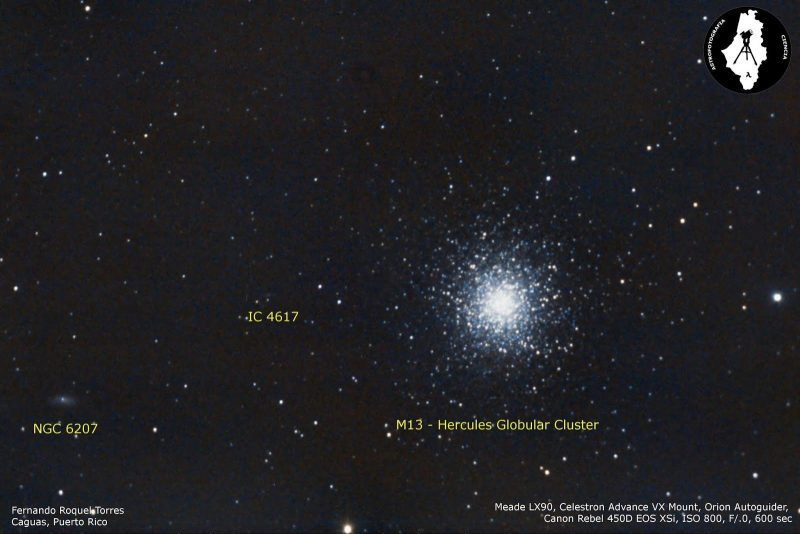


Advice for observing deep-sky objects
To see objects in the deep sky that lie in our Milky Way or even farther, you’ll want a dark sky and binoculars or a telescope. Have patience when tracking down these far-flung gems. Wait for your eyes to grow adapted to the dark. Use averted vision if necessary to pick up the dim fuzzies. A good star chart will help you hop your way across the deep sky and to galaxies beyond our own.
Bottom line: Deep-sky objects are targets in space that amateur astronomers often call faint fuzzies. They lie outside our solar system and don’t resolve into pointlike objects like stars do. Deep-sky objects include nebulae, galaxies and star clusters.
The post Deep-sky objects: Small telescope and binocular targets first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3DyRxel

What are deep-sky objects?
Deep-sky objects lie beyond our solar system and make great observing targets for those using optical aid. Amateur stargazers sometimes refer to them as faint fuzzies. Unlike the nearby planets (which look like little disks through a telescope) or stars (which always look like pinpoints), deep-sky objects are hazy spots in the sky that start to take shape when viewed through binoculars or a telescope. Deep-sky objects generally fall into three categories: nebulae, galaxies and star clusters, including open clusters and globular clusters.
Some of the best deep-sky targets are those in the Messier catalog. Charles Messier was a comet hunter who methodically searched the skies for comets. He cataloged all objects that were not comets, but might be confused with them because they looked fuzzy.
He didn’t know it at the time, but he was creating a list of the best and brightest deep-sky objects. These groupings of stars, gas and dust in our Milky Way, plus galaxies beyond our own, are some of the most fun objects to track down with a telescope. So today’s amateur astronomers attempt to join a Messier Club, by observing all 110 Messier objects (or some subset of them). Or they perform Messier marathons, seeing as many of these objects as they can in one night.

Nebulae: Clouds of gas and dust
There are a few different types of nebulae, or clouds of gas and dust, that you can observe. There are emission nebulae, which include planetary nebulae, that glow because a star late in its life has puffed off a glowing shell of ionized gas. Then there are reflection nebulae, which are clouds of dust that aren’t glowing themselves but reflecting the light of nearby stars. Lastly are the dark nebulae, which are so dense that they block out the light from any background sources. Nebulae are usually found along the plane of the Milky Way where most of the stars in our galaxy reside.
Galaxies: Island universes
Not surprisingly, the best place to look for galaxies in the night sky is away from the direction of our own galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way blocks the view of more distant island universes. The closest large spiral to Earth is also the easiest to spot, M31, or the Andromeda Galaxy. M81 and M82 are handy galactic targets for the Northern Hemisphere, because they’re visible year round.


Star clusters: Open clusters
Open star clusters are young, loosely bound gatherings of stars. One of the most famous open clusters is the Pleiades found in the constellation Taurus. Because this cluster is so close and large, you can view it best with binoculars or even the unaided eye. A telescope gives you too narrow a view and cuts out members of the cluster. The Beehive is another popular open cluster. The view of this deep-sky object improves with magnification.


Star clusters: Globular clusters
Globular clusters are huge, ancient conglomerations of tightly packed stars that orbit in the halo of the Milky Way. The big balls of stars lie much farther away than the open clusters we see. The best known globular cluster for Northern Hemisphere observers lies in Hercules. This deep-sky target is easy to spot with a small telescope.


Advice for observing deep-sky objects
To see objects in the deep sky that lie in our Milky Way or even farther, you’ll want a dark sky and binoculars or a telescope. Have patience when tracking down these far-flung gems. Wait for your eyes to grow adapted to the dark. Use averted vision if necessary to pick up the dim fuzzies. A good star chart will help you hop your way across the deep sky and to galaxies beyond our own.
Bottom line: Deep-sky objects are targets in space that amateur astronomers often call faint fuzzies. They lie outside our solar system and don’t resolve into pointlike objects like stars do. Deep-sky objects include nebulae, galaxies and star clusters.
The post Deep-sky objects: Small telescope and binocular targets first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3DyRxel

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire