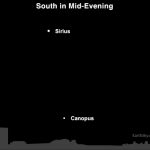
Many know that Sirius is the brightest star visible in Earth’s night sky. But the second-brightest star – Canopus in the constellation Carina the Keel – isn’t nearly as well known. That’s because it’s located so far south on the celestial sphere. Tonight, think about – or look for – a star that northern stargazers rarely see. Because it’s so bright, Canopus is easily visible, even on a moonlit night. Northern stargazers sometimes travel south in winter, just to be able to glimpse this star.
Wait? Easily visible? Well … it is if you live far enough south on Earth’s globe. Canopus never rises above the horizon for locations north of about 37 degrees north latitude. In the United States, that line runs from roughly Richmond, Virginia; westward to Bowling Green, Kentucky; through Trinidad, Colorado; and onward to San Jose, California – just south of San Francisco.
Extend that line of latitude around the world to know who on the globe can see this star.
You must be south of this line of latitude to be able to see Canopus.

If you are far enough south on Earth’s globe, you can see the sky’s second-brightest star, Canopus, below the sky’s brightest star, Sirius. Photo by Jun Lao of the Philippines.
From Northern Hemisphere locations, face southward at around 8 to 9 p.m. this evening. You can’t miss Sirius because it is so bright. Southern Hemisphere? Just wait for darkness to fall, and look approximately overhead for the sky’s two brightest stars.
Sirius makes a wide arc across the southern sky at this time of year. Canopus makes a smaller arc as seen from latitudes like those in the U.S., and – to us – Canopus appears below Sirius in the southern sky.
Sirius is well known for being part of the constellation Canis Major the Greater Dog. Canopus is in the constellation Carina. This southern constellation once was part of Argo Navis, the great Ship that sailed the southern skies, until astronomers officially named the constellations in the 1930s, at which time they divided Argo into three separate constellations. Carina is Latin for the Keel, that large beam along the underside of a ship’s hull from bow to stern, that gives it stability.
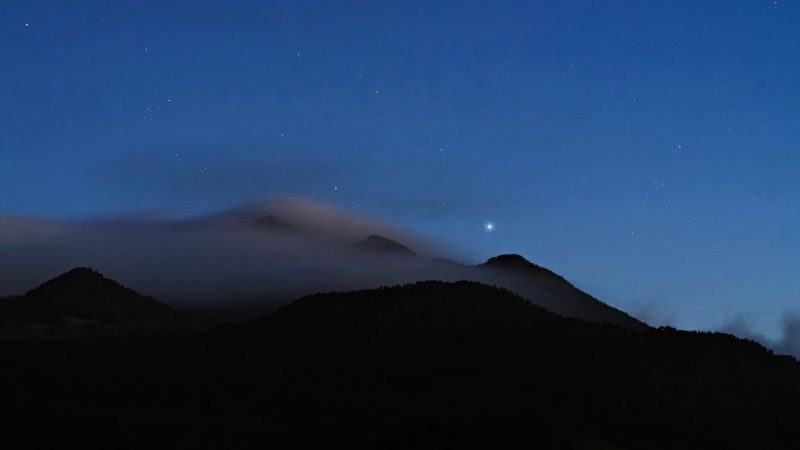

Canopus over Spain’s Canary Islands in 2017. This photo is via Karoline Mrazek and Erwin Matys of Project Nightflight, a Vienna-based astrophotography and education group. Read more about this image.
If we were in the Southern Hemisphere now, our perspective on Sirius and Canopus would be very different. From Australia and New Zealand now, Sirius and Canopus both ride high in the sky. Southern Hemisphere stargazers see them as twin beacons dominating the night.
Bottom line: Sirius is the brightest star visible in Earth’s sky. Canopus is the second-brightest star. You have to be southward on Earth’s globe to see Canopus, at least below 37 degrees north latitude.
Read more: Meet Canopus, the sky’s 2nd-brightest star
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store
Enjoying EarthSky so far? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2Taa6Bp

Many know that Sirius is the brightest star visible in Earth’s night sky. But the second-brightest star – Canopus in the constellation Carina the Keel – isn’t nearly as well known. That’s because it’s located so far south on the celestial sphere. Tonight, think about – or look for – a star that northern stargazers rarely see. Because it’s so bright, Canopus is easily visible, even on a moonlit night. Northern stargazers sometimes travel south in winter, just to be able to glimpse this star.
Wait? Easily visible? Well … it is if you live far enough south on Earth’s globe. Canopus never rises above the horizon for locations north of about 37 degrees north latitude. In the United States, that line runs from roughly Richmond, Virginia; westward to Bowling Green, Kentucky; through Trinidad, Colorado; and onward to San Jose, California – just south of San Francisco.
Extend that line of latitude around the world to know who on the globe can see this star.
You must be south of this line of latitude to be able to see Canopus.

If you are far enough south on Earth’s globe, you can see the sky’s second-brightest star, Canopus, below the sky’s brightest star, Sirius. Photo by Jun Lao of the Philippines.
From Northern Hemisphere locations, face southward at around 8 to 9 p.m. this evening. You can’t miss Sirius because it is so bright. Southern Hemisphere? Just wait for darkness to fall, and look approximately overhead for the sky’s two brightest stars.
Sirius makes a wide arc across the southern sky at this time of year. Canopus makes a smaller arc as seen from latitudes like those in the U.S., and – to us – Canopus appears below Sirius in the southern sky.
Sirius is well known for being part of the constellation Canis Major the Greater Dog. Canopus is in the constellation Carina. This southern constellation once was part of Argo Navis, the great Ship that sailed the southern skies, until astronomers officially named the constellations in the 1930s, at which time they divided Argo into three separate constellations. Carina is Latin for the Keel, that large beam along the underside of a ship’s hull from bow to stern, that gives it stability.

Canopus over Spain’s Canary Islands in 2017. This photo is via Karoline Mrazek and Erwin Matys of Project Nightflight, a Vienna-based astrophotography and education group. Read more about this image.
If we were in the Southern Hemisphere now, our perspective on Sirius and Canopus would be very different. From Australia and New Zealand now, Sirius and Canopus both ride high in the sky. Southern Hemisphere stargazers see them as twin beacons dominating the night.
Bottom line: Sirius is the brightest star visible in Earth’s sky. Canopus is the second-brightest star. You have to be southward on Earth’s globe to see Canopus, at least below 37 degrees north latitude.
Read more: Meet Canopus, the sky’s 2nd-brightest star
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store
Enjoying EarthSky so far? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2Taa6Bp

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire