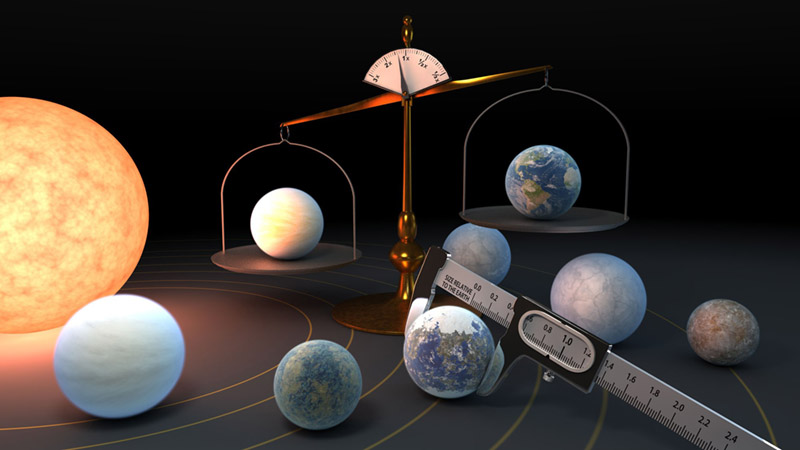
Artist’s concept of TRAPPIST-1 planets, highlighting the measurements of their diameters and masses. The TRAPPIST-1 star system is home to the largest batch of roughly Earth-sized planets ever found outside our solar system. It’s about 40 light-years away. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
An exciting discovery by the Spitzer Space Telescope in 2017 revealed seven Earth-sized planets orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1, less than 40 light-years away. Details about these planets have been hard to come by, but astronomers have wondered, are any like Earth? Are some like Venus? Do any have clouds or even surface water? Late last week (January 22, 2021), astronomers added another piece to the puzzle of Trappist-1’s planets, when they published a paper in the peer-reviewed Planetary Science Journal detailing these worlds’ compositions. The team found them to be made of similar stuff to each other, but quite unlike the planets in our solar system.
Trappist-1 is a red dwarf star, by far the most common type of star in our Milky Way galaxy. Three of the Trappist-1 planets are firmly within the star’s habitable zone – aka the Goldilocks’ Zone – in which liquid water can exist on a planet’s surface. At present, the feeling among astronomers is that it’s unlikely water will be found on the surfaces of Trappist-1’s three innermost planets, and, if the four outermost planets do have surface water, it isn’t much. The discovery contradicts an early belief among astronomers that low-density planets like these must be abundant in water. It also raises questions about just how Earth-like and habitable the seven exoplanets might be.
EarthSky lunar calendars are back in stock! We’re guaranteed to sell out. Get one while you can!
Astrophysicist Martin Turbet of the University of Geneva is a co-author on the new study. He said in a statement:
By combining the planetary interior models from the Universities of Bern and Zürich with the planetary atmosphere models we are developing at the University of Geneva, we were able to evaluate the water content of the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets with a precision literally unprecedented for this category of planet.
Our internal and atmospheric structure models show that the three inner planets of the TRAPPIST-1 system are likely to be waterless, and that the four outer planets have no more than a few percent water, possibly in liquid form, on their surfaces.
Now let’s think a moment about the eight planets in our solar system. They vary widely in density, with the large gas and ice giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) being less dense, and the terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) being more dense. Since the seven bodies in TRAPPIST-1 were known to share a relatively similar density to each other, researchers were met with a quandary when comparing these exoplanets to Earth. If indeed any of them did have surface water, astronomers’ density estimates would need to change.
That’s why, at the outset of the study, researchers worked to determine whether the lower density of the seven exoplanets was the result of water or their interior makeup, both of which would determine whether the planets are very or only somewhat Earth-like in nature. According to a statement about the research, the exoplanets are roughly 8% less dense than Earth. For the lower density of the planets to be the result of surface water, roughly 5% of each planet’s mass would have to exist as surface water.
That’s a lot! In comparison, water represents just 0.1 percent of Earth’s mass. So you can see right away that these worlds are compositionally quite different from Earth.

Martin Turbet is an astronomer at the University of Geneva and a co-author on the study that calculated the densities of the exoplanets in TRAPPIST-1. Image via University of Geneva.

Eric Agol is an astronomer at the University of Washington and the lead author on the study that calculated the densities of the exoplanets in TRAPPIST-1. Image via The Daily at the University of Washington.
But, as it turns out, even the potential for a few percent of water mass is questionable. Astronomer Eric Agol at the University of Washington is lead author on the research. He added in the statement that the planets are likely to have less than a few percent of water mass; otherwise, the similar densities within the group would be an extraordinary coincidence.
To answer this quandary, researchers examined the composition of the seven exoplanets, looking for similarities in the group and between the group and Earth. Most rocky planets are believed to be made of metals like magnesium, iron and nickel, and non-metals like sulfur, oxygen, and silicon. Due to the discrepancy in density between the group and Earth, researchers surmised that the TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets may have a similar makeup to Earth but with significantly different ratios, for example, a lower percentage of iron. While iron represents 32% of Earth’s total mass, the study indicates that iron should represent about 21% of the mass of each TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet.
Agol told EarthSky:
The lower density indicates that these planets have a different make-up, and hence a different history, than our solar system’s terrestrial planets. Perhaps the star + disk started off with less iron? Or perhaps the iron core never formed, and the iron remained oxidized in the mantle?
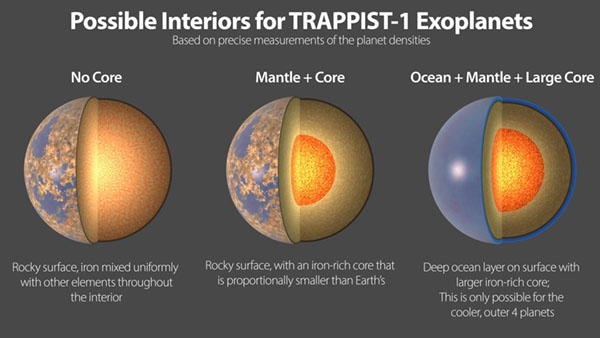
Artist’s concept of the similar densities of the 7 exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 star system. Their similar densities suggests they all have a similar composition. The new study has led scientists to believe that the planets have rocky surfaces and iron-rich cores. Their cores are likely smaller than Earth’s, since the planets each have a mass roughly 8% less than Earth’s. Previous theories considered deep ocean layers on the surface of each planet, or planets with no core. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
To determine the mass of each planet, scientists measured changes in their orbital periods. They measured how long it took for each planet to orbit TRAPPIST-1 and to cross in front of the star as seen from Earth. This process is called transit timing. Combined with radius measurements of each planet, scientists were able to calculate the densities of the planets with more precision. Using a comparison against Earth’s mass, the team was able to calculate the percentage of iron likely to be present in each of the seven exoplanets.
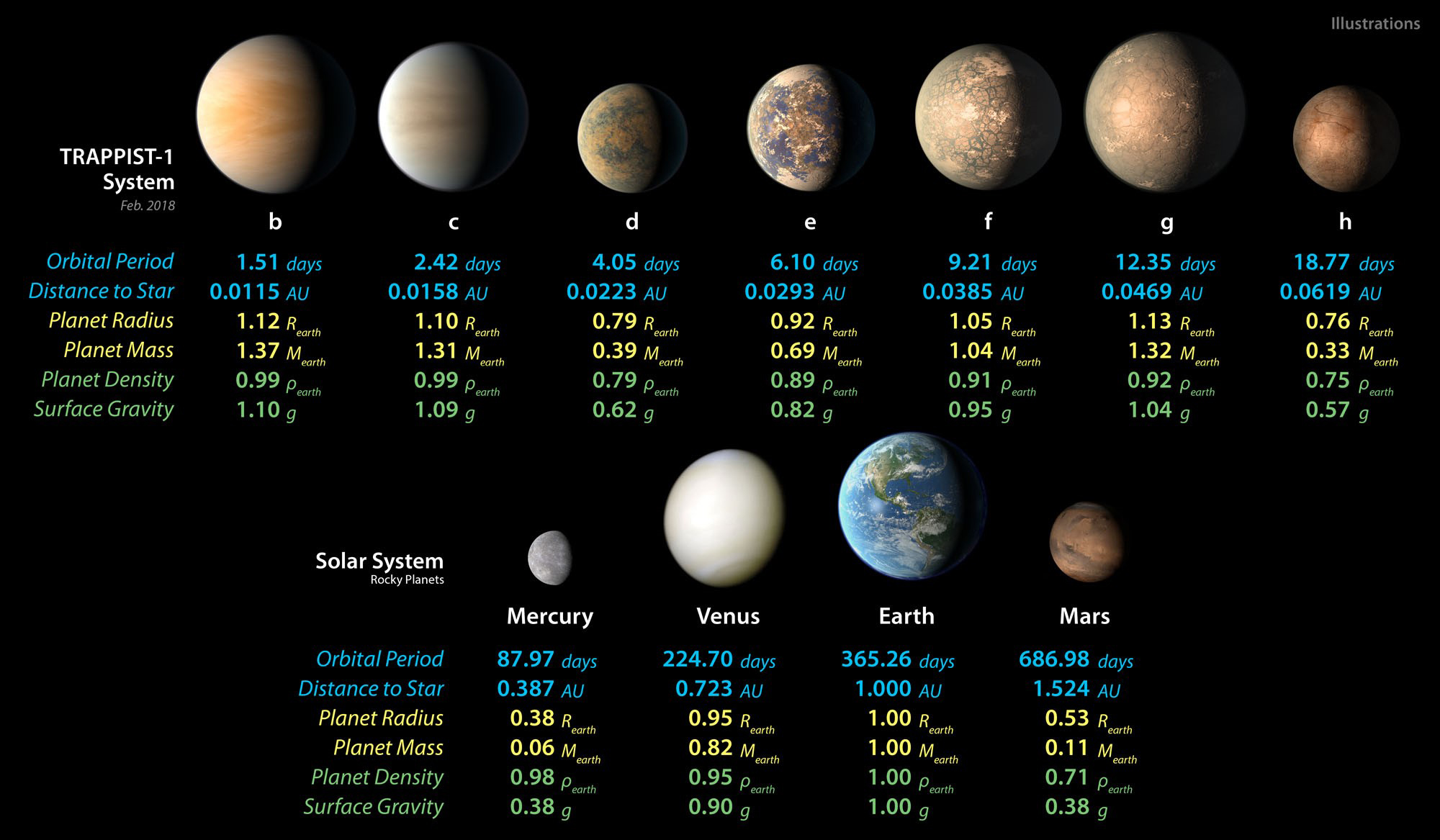

Using data from the now decommissioned Spitzer Space Telescope, astronomers determined that all 7 of the planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1 have similar densities. This finding helped the astronomers characterize the composition of these exoworlds in comparison to Earth. While all 7 planets are considered to be roughly Earth-sized, they are each about 8% less dense than our home planet, meaning their makeup, while potentially similar to Earth, in terms of elements like iron, is significantly different in percentages. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
Combining these data with radius measurements of each planet, scientists calculated the densities of the planets with more precision than before. Using a comparison against Earth’s mass, the team was able to calculate the percentage of iron likely to be present in each of the seven exoplanets.
Agol said:
We found that about 2/3 of the iron is required compared with Earth since these are lower density.
Whether the differences between Earth and the TRAPPIST planets change the potential for life somewhere in the TRAPPIST-1 system is a complicated question. While the presence of liquid water could signal the potential for life, other factors contribute to a planet’s suitability for life to arise, thrive, and survive. On Earth, for example, a strong magnetic field protects our planet and life from high-energy particles from the sun. Our atmosphere is filled with sufficient oxygen and carbon as well as other gases required for animal life, photosynthesis and habitable surface temperatures.
Despite these challenges, Agol is not discounting the potential for life on TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets just yet. He said:
The connection to habitability isn’t clear yet. The structure of the planets might affect their ability to have plate tectonics, to carry a magnetic field, and other possible implications. These aspects of Earth affect the presence and change of life on Earth.
So, lots of questions left to explore.
The study was made possible by data sets taken by the Spitzer Space Telescope since the discovery of the star system more than four years ago. Between 2016 and 2020, when the telescope was decommissioned and stopped collecting data, Spitzer recorded 1,075 hours of observing time for TRAPPIST-1. Although the decommissioning of Spitzer has put a hold on observations, it does not mark a permanent end to TRAPPIST-1 studies.
Agol said:
If the James Webb Space Telescope is successfully launched and commissioned later this year, then we plan to continue monitoring the transits with that telescope to try to detect the atmospheres with transit transmission spectroscopy. Each transit will provide a timing, so we can continue to refine the masses of the planets.

After the discovery of exoplanets orbiting TRAPPIST-1 in 2016, the Spitzer Space Telescope logged 1,075 observing hours on the star system, generating enough data for astronomers to accurately determine the densities and makeup of each planet. The Spitzer Space Telescope was decommissioned in January 2020. Artist’s concept via NASA/JPL-Caltech.
Bottom line: A new study of the seven Earth-sized exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system indicate that all seven planets are extremely similar to each other in makeup, but potentially quite different from Earth.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3qOxySs


Artist’s concept of TRAPPIST-1 planets, highlighting the measurements of their diameters and masses. The TRAPPIST-1 star system is home to the largest batch of roughly Earth-sized planets ever found outside our solar system. It’s about 40 light-years away. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
An exciting discovery by the Spitzer Space Telescope in 2017 revealed seven Earth-sized planets orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1, less than 40 light-years away. Details about these planets have been hard to come by, but astronomers have wondered, are any like Earth? Are some like Venus? Do any have clouds or even surface water? Late last week (January 22, 2021), astronomers added another piece to the puzzle of Trappist-1’s planets, when they published a paper in the peer-reviewed Planetary Science Journal detailing these worlds’ compositions. The team found them to be made of similar stuff to each other, but quite unlike the planets in our solar system.
Trappist-1 is a red dwarf star, by far the most common type of star in our Milky Way galaxy. Three of the Trappist-1 planets are firmly within the star’s habitable zone – aka the Goldilocks’ Zone – in which liquid water can exist on a planet’s surface. At present, the feeling among astronomers is that it’s unlikely water will be found on the surfaces of Trappist-1’s three innermost planets, and, if the four outermost planets do have surface water, it isn’t much. The discovery contradicts an early belief among astronomers that low-density planets like these must be abundant in water. It also raises questions about just how Earth-like and habitable the seven exoplanets might be.
EarthSky lunar calendars are back in stock! We’re guaranteed to sell out. Get one while you can!
Astrophysicist Martin Turbet of the University of Geneva is a co-author on the new study. He said in a statement:
By combining the planetary interior models from the Universities of Bern and Zürich with the planetary atmosphere models we are developing at the University of Geneva, we were able to evaluate the water content of the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets with a precision literally unprecedented for this category of planet.
Our internal and atmospheric structure models show that the three inner planets of the TRAPPIST-1 system are likely to be waterless, and that the four outer planets have no more than a few percent water, possibly in liquid form, on their surfaces.
Now let’s think a moment about the eight planets in our solar system. They vary widely in density, with the large gas and ice giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) being less dense, and the terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) being more dense. Since the seven bodies in TRAPPIST-1 were known to share a relatively similar density to each other, researchers were met with a quandary when comparing these exoplanets to Earth. If indeed any of them did have surface water, astronomers’ density estimates would need to change.
That’s why, at the outset of the study, researchers worked to determine whether the lower density of the seven exoplanets was the result of water or their interior makeup, both of which would determine whether the planets are very or only somewhat Earth-like in nature. According to a statement about the research, the exoplanets are roughly 8% less dense than Earth. For the lower density of the planets to be the result of surface water, roughly 5% of each planet’s mass would have to exist as surface water.
That’s a lot! In comparison, water represents just 0.1 percent of Earth’s mass. So you can see right away that these worlds are compositionally quite different from Earth.

Martin Turbet is an astronomer at the University of Geneva and a co-author on the study that calculated the densities of the exoplanets in TRAPPIST-1. Image via University of Geneva.

Eric Agol is an astronomer at the University of Washington and the lead author on the study that calculated the densities of the exoplanets in TRAPPIST-1. Image via The Daily at the University of Washington.
But, as it turns out, even the potential for a few percent of water mass is questionable. Astronomer Eric Agol at the University of Washington is lead author on the research. He added in the statement that the planets are likely to have less than a few percent of water mass; otherwise, the similar densities within the group would be an extraordinary coincidence.
To answer this quandary, researchers examined the composition of the seven exoplanets, looking for similarities in the group and between the group and Earth. Most rocky planets are believed to be made of metals like magnesium, iron and nickel, and non-metals like sulfur, oxygen, and silicon. Due to the discrepancy in density between the group and Earth, researchers surmised that the TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets may have a similar makeup to Earth but with significantly different ratios, for example, a lower percentage of iron. While iron represents 32% of Earth’s total mass, the study indicates that iron should represent about 21% of the mass of each TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet.
Agol told EarthSky:
The lower density indicates that these planets have a different make-up, and hence a different history, than our solar system’s terrestrial planets. Perhaps the star + disk started off with less iron? Or perhaps the iron core never formed, and the iron remained oxidized in the mantle?

Artist’s concept of the similar densities of the 7 exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 star system. Their similar densities suggests they all have a similar composition. The new study has led scientists to believe that the planets have rocky surfaces and iron-rich cores. Their cores are likely smaller than Earth’s, since the planets each have a mass roughly 8% less than Earth’s. Previous theories considered deep ocean layers on the surface of each planet, or planets with no core. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
To determine the mass of each planet, scientists measured changes in their orbital periods. They measured how long it took for each planet to orbit TRAPPIST-1 and to cross in front of the star as seen from Earth. This process is called transit timing. Combined with radius measurements of each planet, scientists were able to calculate the densities of the planets with more precision. Using a comparison against Earth’s mass, the team was able to calculate the percentage of iron likely to be present in each of the seven exoplanets.

Using data from the now decommissioned Spitzer Space Telescope, astronomers determined that all 7 of the planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1 have similar densities. This finding helped the astronomers characterize the composition of these exoworlds in comparison to Earth. While all 7 planets are considered to be roughly Earth-sized, they are each about 8% less dense than our home planet, meaning their makeup, while potentially similar to Earth, in terms of elements like iron, is significantly different in percentages. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Geneva.
Combining these data with radius measurements of each planet, scientists calculated the densities of the planets with more precision than before. Using a comparison against Earth’s mass, the team was able to calculate the percentage of iron likely to be present in each of the seven exoplanets.
Agol said:
We found that about 2/3 of the iron is required compared with Earth since these are lower density.
Whether the differences between Earth and the TRAPPIST planets change the potential for life somewhere in the TRAPPIST-1 system is a complicated question. While the presence of liquid water could signal the potential for life, other factors contribute to a planet’s suitability for life to arise, thrive, and survive. On Earth, for example, a strong magnetic field protects our planet and life from high-energy particles from the sun. Our atmosphere is filled with sufficient oxygen and carbon as well as other gases required for animal life, photosynthesis and habitable surface temperatures.
Despite these challenges, Agol is not discounting the potential for life on TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets just yet. He said:
The connection to habitability isn’t clear yet. The structure of the planets might affect their ability to have plate tectonics, to carry a magnetic field, and other possible implications. These aspects of Earth affect the presence and change of life on Earth.
So, lots of questions left to explore.
The study was made possible by data sets taken by the Spitzer Space Telescope since the discovery of the star system more than four years ago. Between 2016 and 2020, when the telescope was decommissioned and stopped collecting data, Spitzer recorded 1,075 hours of observing time for TRAPPIST-1. Although the decommissioning of Spitzer has put a hold on observations, it does not mark a permanent end to TRAPPIST-1 studies.
Agol said:
If the James Webb Space Telescope is successfully launched and commissioned later this year, then we plan to continue monitoring the transits with that telescope to try to detect the atmospheres with transit transmission spectroscopy. Each transit will provide a timing, so we can continue to refine the masses of the planets.

After the discovery of exoplanets orbiting TRAPPIST-1 in 2016, the Spitzer Space Telescope logged 1,075 observing hours on the star system, generating enough data for astronomers to accurately determine the densities and makeup of each planet. The Spitzer Space Telescope was decommissioned in January 2020. Artist’s concept via NASA/JPL-Caltech.
Bottom line: A new study of the seven Earth-sized exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system indicate that all seven planets are extremely similar to each other in makeup, but potentially quite different from Earth.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3qOxySs

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire