
For us in North America, the November full moon is the Beaver Moon or Frosty Moon. In the Southern Hemisphere, where it’s the opposite time of year, the November full moon is a fixture of the spring season. For all of us, this November 2020 full moon shines directly in front of the constellation Taurus the Bull. It’s the third and final full moon of this Northern Hemisphere autumn or Southern Hemisphere spring. We in North America are well placed to view a partial penumbral eclipse of this full moon on the night of November 29-30. Greatest eclipse will be November 30 at 09:43 UTC or 4:43 a.m. EST (translate UTC to your time).
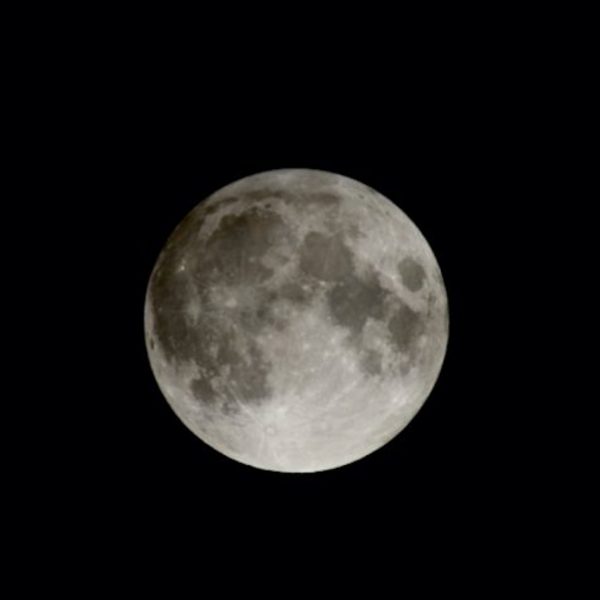

View at EarthSky Community Photos. | Here is the penumbral eclipse of July 4-5, 2020. As you can see, it’s not very noticeable. Greg Redfern in central Virginia commented: “Taken at maximum eclipse for the penumbral lunar eclipse. MAY be some shading in the upper left quadrant.” Thank you, Greg.
It’ll be the faintest of eclipses – nearly imperceptible – so that some of you will swear nothing is happening even while staring straight at it. Then again … observant people may notice a subtle shading on the moon, even without knowing an eclipse is taking place.
A dark rural sky will be best for seeing this very faint eclipse.
The reddish star near the moon during the eclipse will be Aldebaran, Eye of the Bull in Taurus. The tiny dipper-shaped Pleiades star cluster will also be nearby.
You have to be on the nighttime side of the Earth while the eclipse is taking place or you’ll miss it altogether. We refer you to the worldwide map below showing the day and night sides of Earth at the instant of greatest eclipse.
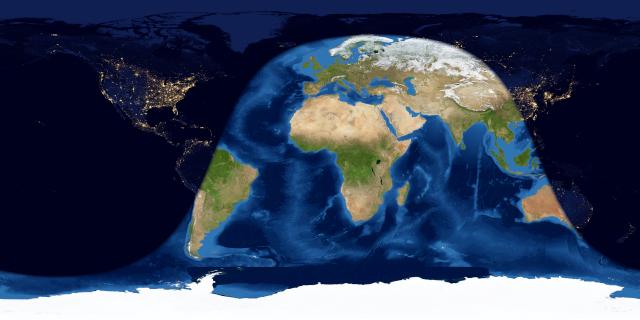
Day and night sides of Earth at the instant of the greatest eclipse (November 30 at 09:43 UTC). The shadow line at left (running through South America) depicts sunrise November 30, while the shadow line at the right (passing through Asia and Australia) depicts sunset November 30. To see this eclipse, you have to be on the nighttime side of the world while the eclipse is taking place. Map via EarthView.
At best, the eclipse might be visible to the eye for roughly an hour, centered on the greatest eclipse (mid-eclipse). We give the time of the greatest eclipse for United States time zones:
Eastern Standard Time (EST): 4:43 a.m. (November 30)
Central Standard Time:(CST): 3:43 a.m. (November 30)
Mountain Standard Time:(MST): 2:43 a.m. (November 30)
Pacific Standard Time (PST): 1:43 a.m. (November 30)
Alaska Standard Time (AKST): 12:43 a.m. (November 30)
Hawaii Standard Time (HST): 11:43 p.m. (November 29)
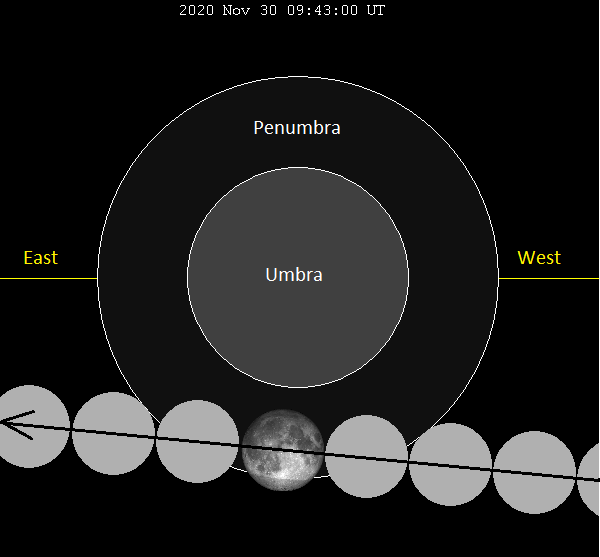
The full moon sweeps through the Earth’s penumbra (light shadow) on the night of November 29-30, 2020. At greatest eclipse, you might note a subtle shading on the moon’s northern hemisphere. Greatest eclipse on November 30 at 09:43 UTC. At U.S. time zones, that translates to November 30, at 4:43 a.m. EST, 3:43 a.m. CST, 2:43 a.m. MST, 1:43 a.m. PST, 12:43 a.m. AKST, and on November 29, at 11:43 p.m. HST.
We give the times for the beginning and ending of the penumbral eclipse in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Be mindful, however, that the eclipse won’t be visible to the eye until the moon’s disk is about 2/3 submerged in the penumbral shadow:
Penumbral eclipse begins: 07:32 UTC (November 30)
First visible?: 09:10 UTC (November 30)
Greatest eclipse: 09:43 UTC (November 30)
Last visible?: 10:10 UTC (November 30)
Penumbral eclipse ends: 11:53 UTC (November 30)Click on TimeandDate.com to find local eclipse times for your sky

A lunar eclipse can only happen at full moon, but more often than not the full moon swings above or below the Earth’s shadow. On the night of November 29-30, 2020, the full moon swings south of the dark umbra, but the moon passes through the faint outer penumbra. At greatest eclipse, nearly 83% of the moon’s diameter is submerged in the penumbral shadow.
Although the moon actually looks full to the eye for two or three days in a row, the moon is astronomically full for only an instant – when it’s 180 degrees opposite the sun in ecliptic longitude. At full moon, the sun-moon elongation equals 180 degrees. Visit Unitarium.com to know the present elongation of the sun and moon, remembering that a positive number means a waxing moon and a negative number a waning moon.
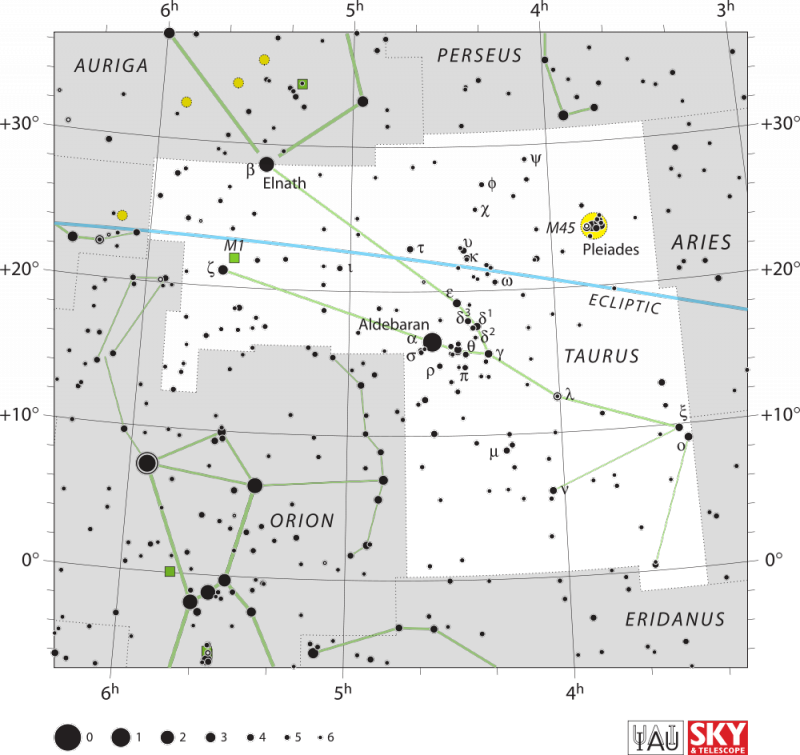
Orion’s Belt, at the lower left, always points in the direction of the constellation Taurus the Bull. The star Aldebaran resides to the south of the ecliptic, or sun’s path across our sky – shown on this chart as a blue line – and the Pleiades star cluster to the north of the ecliptic.
Since the moon stays more or less opposite the sun throughout the night at the vicinity of full moon, look for the moon (and the constellation Taurus) to rise in the east around sunset, climb highest for the night around midnight and set in the west around sunrise.
Because the full moon resides opposite the sun in the northern constellation Taurus the Bull, the full moon’s path across the night sky will resemble that of the sun in the daytime sky for six months hence. In late May, the sun resides in the constellation Taurus, well to the north of the Earth’s equator. For both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, that means this northerly full moon will rise and set considerably north of due east and west. Therefore, for the Northern Hemisphere, this late November full moon will mimic the high path of the late May springtime sun; and in the Southern Hemisphere, it’ll imitate the path of the late May autumn sun.
Bottom line: We in North America are well placed to view a partial penumbral eclipse of the November 2020 full moon on the night of November 29-30. Greatest eclipse will be November 30 at 09:43 UTC or 4:43 a.m. EST (translate UTC to your time).
Read more: Why not an eclipse at every full and new moon?
Read more: What is an eclipse season?
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/36dxeoQ

For us in North America, the November full moon is the Beaver Moon or Frosty Moon. In the Southern Hemisphere, where it’s the opposite time of year, the November full moon is a fixture of the spring season. For all of us, this November 2020 full moon shines directly in front of the constellation Taurus the Bull. It’s the third and final full moon of this Northern Hemisphere autumn or Southern Hemisphere spring. We in North America are well placed to view a partial penumbral eclipse of this full moon on the night of November 29-30. Greatest eclipse will be November 30 at 09:43 UTC or 4:43 a.m. EST (translate UTC to your time).

View at EarthSky Community Photos. | Here is the penumbral eclipse of July 4-5, 2020. As you can see, it’s not very noticeable. Greg Redfern in central Virginia commented: “Taken at maximum eclipse for the penumbral lunar eclipse. MAY be some shading in the upper left quadrant.” Thank you, Greg.
It’ll be the faintest of eclipses – nearly imperceptible – so that some of you will swear nothing is happening even while staring straight at it. Then again … observant people may notice a subtle shading on the moon, even without knowing an eclipse is taking place.
A dark rural sky will be best for seeing this very faint eclipse.
The reddish star near the moon during the eclipse will be Aldebaran, Eye of the Bull in Taurus. The tiny dipper-shaped Pleiades star cluster will also be nearby.
You have to be on the nighttime side of the Earth while the eclipse is taking place or you’ll miss it altogether. We refer you to the worldwide map below showing the day and night sides of Earth at the instant of greatest eclipse.

Day and night sides of Earth at the instant of the greatest eclipse (November 30 at 09:43 UTC). The shadow line at left (running through South America) depicts sunrise November 30, while the shadow line at the right (passing through Asia and Australia) depicts sunset November 30. To see this eclipse, you have to be on the nighttime side of the world while the eclipse is taking place. Map via EarthView.
At best, the eclipse might be visible to the eye for roughly an hour, centered on the greatest eclipse (mid-eclipse). We give the time of the greatest eclipse for United States time zones:
Eastern Standard Time (EST): 4:43 a.m. (November 30)
Central Standard Time:(CST): 3:43 a.m. (November 30)
Mountain Standard Time:(MST): 2:43 a.m. (November 30)
Pacific Standard Time (PST): 1:43 a.m. (November 30)
Alaska Standard Time (AKST): 12:43 a.m. (November 30)
Hawaii Standard Time (HST): 11:43 p.m. (November 29)

The full moon sweeps through the Earth’s penumbra (light shadow) on the night of November 29-30, 2020. At greatest eclipse, you might note a subtle shading on the moon’s northern hemisphere. Greatest eclipse on November 30 at 09:43 UTC. At U.S. time zones, that translates to November 30, at 4:43 a.m. EST, 3:43 a.m. CST, 2:43 a.m. MST, 1:43 a.m. PST, 12:43 a.m. AKST, and on November 29, at 11:43 p.m. HST.
We give the times for the beginning and ending of the penumbral eclipse in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Be mindful, however, that the eclipse won’t be visible to the eye until the moon’s disk is about 2/3 submerged in the penumbral shadow:
Penumbral eclipse begins: 07:32 UTC (November 30)
First visible?: 09:10 UTC (November 30)
Greatest eclipse: 09:43 UTC (November 30)
Last visible?: 10:10 UTC (November 30)
Penumbral eclipse ends: 11:53 UTC (November 30)Click on TimeandDate.com to find local eclipse times for your sky

A lunar eclipse can only happen at full moon, but more often than not the full moon swings above or below the Earth’s shadow. On the night of November 29-30, 2020, the full moon swings south of the dark umbra, but the moon passes through the faint outer penumbra. At greatest eclipse, nearly 83% of the moon’s diameter is submerged in the penumbral shadow.
Although the moon actually looks full to the eye for two or three days in a row, the moon is astronomically full for only an instant – when it’s 180 degrees opposite the sun in ecliptic longitude. At full moon, the sun-moon elongation equals 180 degrees. Visit Unitarium.com to know the present elongation of the sun and moon, remembering that a positive number means a waxing moon and a negative number a waning moon.

Orion’s Belt, at the lower left, always points in the direction of the constellation Taurus the Bull. The star Aldebaran resides to the south of the ecliptic, or sun’s path across our sky – shown on this chart as a blue line – and the Pleiades star cluster to the north of the ecliptic.
Since the moon stays more or less opposite the sun throughout the night at the vicinity of full moon, look for the moon (and the constellation Taurus) to rise in the east around sunset, climb highest for the night around midnight and set in the west around sunrise.
Because the full moon resides opposite the sun in the northern constellation Taurus the Bull, the full moon’s path across the night sky will resemble that of the sun in the daytime sky for six months hence. In late May, the sun resides in the constellation Taurus, well to the north of the Earth’s equator. For both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, that means this northerly full moon will rise and set considerably north of due east and west. Therefore, for the Northern Hemisphere, this late November full moon will mimic the high path of the late May springtime sun; and in the Southern Hemisphere, it’ll imitate the path of the late May autumn sun.
Bottom line: We in North America are well placed to view a partial penumbral eclipse of the November 2020 full moon on the night of November 29-30. Greatest eclipse will be November 30 at 09:43 UTC or 4:43 a.m. EST (translate UTC to your time).
Read more: Why not an eclipse at every full and new moon?
Read more: What is an eclipse season?
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/36dxeoQ

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire