
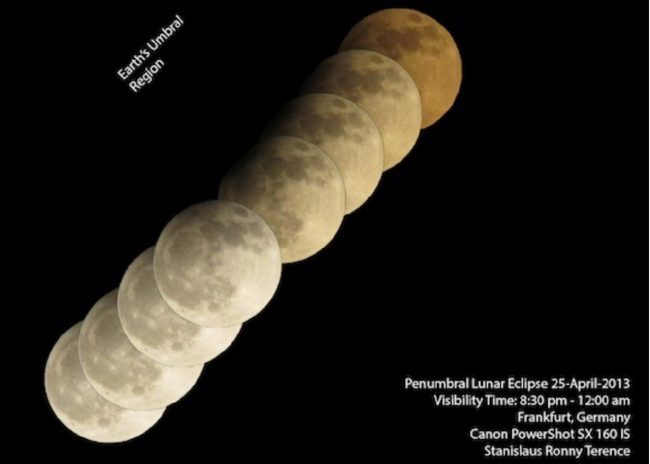
April 2013 penumbral eclipse by Stanislaus Ronny Terrance. See the dark shading on one edge of the moon?
Next penumbral lunar eclipse: July 4-5, 2020
An eclipse of the moon can only happen at full moon, when the sun, Earth and moon line up in space, with Earth in the middle. At such times, Earth’s shadow falls on the moon, creating a lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipses happen a minimum of two times to a maximum of five times a year. There are three kinds of lunar eclipses: total, partial and penumbral.
In a total eclipse of the moon, the inner part of Earth’s shadow, called the umbra, falls on the moon’s face. At mid-eclipse, the entire moon is in shadow, which may appear blood red.
In a partial lunar eclipse, the umbra takes a bite out of only a fraction of the moon. The dark bite grows larger, and then recedes, never reaching the total phase.
In a penumbral lunar eclipse, only the more diffuse outer shadow of Earth – the penumbra – falls on the moon’s face. This third kind of lunar eclipse is much more subtle, and much more difficult to observe, than either a total or partial eclipse of the moon. There is never a dark bite taken out of the moon, as in a partial eclipse. The eclipse never progresses to reach the dramatic minutes of totality. At best, at mid-eclipse, very observant people will notice a dark shading on the moon’s face. Others will look and notice nothing at all.
According to eclipse expert Fred Espenak, about 35% of all eclipses are penumbral. Another 30% are partial eclipses, where it appears as if a dark bite has been taken out of the moon. And the final 35% go all the way to becoming total eclipses of the moon, a beautiful natural event.

View larger. | Left, an ordinary full moon with no eclipse. Right, full moon in penumbral eclipse on November 20, 2002. Master eclipse photographer Fred Espenak took this photo when the moon was 88.9% immersed in Earth’s penumbral shadow. There’s no dark bite taken out of the moon. A penumbral eclipse creates only a dark shading on the moon’s face.
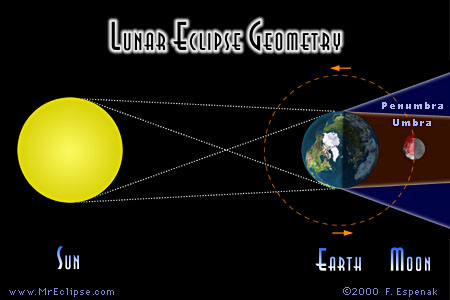
In a lunar eclipse, Earth’s shadow falls on the moon. If the moon passes through the dark central shadow of Earth – the umbra – a partial or total lunar eclipse takes place. If the moon only passes through the outer part of the shadow (the penumbra), a subtle penumbral eclipse occurs. Diagram via Fred Espenak’s Lunar Eclipses for Beginners.

Here’s what a partial lunar eclipse looks like. Astronomer Alan Dyer caught it from his home in southern Alberta, Canada, in June 2012. It was pre-dawn, near moonset. Image copyright Alan Dyer. Used with permission.
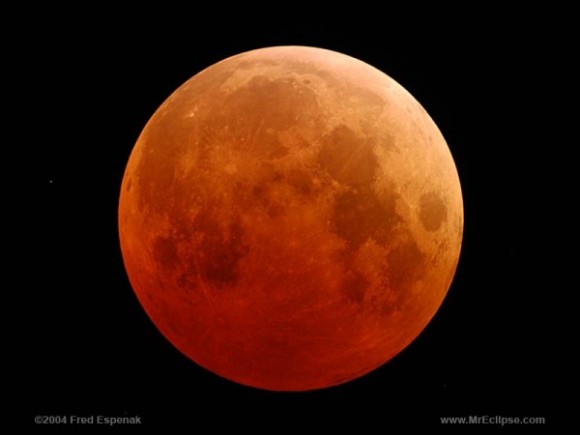

This is what a total eclipse looks like. This is the total eclipse of October 27, 2004, via Fred Espenak of NASA, otherwise known as Mr. Eclipse. Visit Fred’s page here.
Bottom line: There are three kinds of lunar eclipses: total, partial and penumbral. A penumbral eclipse is very subtle. At no time does a dark bite appear to be taken out of the moon. Instead, at mid-eclipse, observant people will notice a shading on the moon’s face.
Next penumbral lunar eclipse: July 4-5, 2020
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2rMqzRl


April 2013 penumbral eclipse by Stanislaus Ronny Terrance. See the dark shading on one edge of the moon?
Next penumbral lunar eclipse: July 4-5, 2020
An eclipse of the moon can only happen at full moon, when the sun, Earth and moon line up in space, with Earth in the middle. At such times, Earth’s shadow falls on the moon, creating a lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipses happen a minimum of two times to a maximum of five times a year. There are three kinds of lunar eclipses: total, partial and penumbral.
In a total eclipse of the moon, the inner part of Earth’s shadow, called the umbra, falls on the moon’s face. At mid-eclipse, the entire moon is in shadow, which may appear blood red.
In a partial lunar eclipse, the umbra takes a bite out of only a fraction of the moon. The dark bite grows larger, and then recedes, never reaching the total phase.
In a penumbral lunar eclipse, only the more diffuse outer shadow of Earth – the penumbra – falls on the moon’s face. This third kind of lunar eclipse is much more subtle, and much more difficult to observe, than either a total or partial eclipse of the moon. There is never a dark bite taken out of the moon, as in a partial eclipse. The eclipse never progresses to reach the dramatic minutes of totality. At best, at mid-eclipse, very observant people will notice a dark shading on the moon’s face. Others will look and notice nothing at all.
According to eclipse expert Fred Espenak, about 35% of all eclipses are penumbral. Another 30% are partial eclipses, where it appears as if a dark bite has been taken out of the moon. And the final 35% go all the way to becoming total eclipses of the moon, a beautiful natural event.

View larger. | Left, an ordinary full moon with no eclipse. Right, full moon in penumbral eclipse on November 20, 2002. Master eclipse photographer Fred Espenak took this photo when the moon was 88.9% immersed in Earth’s penumbral shadow. There’s no dark bite taken out of the moon. A penumbral eclipse creates only a dark shading on the moon’s face.

In a lunar eclipse, Earth’s shadow falls on the moon. If the moon passes through the dark central shadow of Earth – the umbra – a partial or total lunar eclipse takes place. If the moon only passes through the outer part of the shadow (the penumbra), a subtle penumbral eclipse occurs. Diagram via Fred Espenak’s Lunar Eclipses for Beginners.

Here’s what a partial lunar eclipse looks like. Astronomer Alan Dyer caught it from his home in southern Alberta, Canada, in June 2012. It was pre-dawn, near moonset. Image copyright Alan Dyer. Used with permission.

This is what a total eclipse looks like. This is the total eclipse of October 27, 2004, via Fred Espenak of NASA, otherwise known as Mr. Eclipse. Visit Fred’s page here.
Bottom line: There are three kinds of lunar eclipses: total, partial and penumbral. A penumbral eclipse is very subtle. At no time does a dark bite appear to be taken out of the moon. Instead, at mid-eclipse, observant people will notice a shading on the moon’s face.
Next penumbral lunar eclipse: July 4-5, 2020
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2rMqzRl

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire