Tonight, find the Hunting Dogs. The chart above looks directly overhead at nightfall or early evening in May, as seen from a mid-latitude in the Northern Hemisphere. It’s as if we’re viewing the sky from the comfort of a reclining lawn chair, with our feet pointing southward. The constellation Leo the Lion stands high in the southern sky, while the upside-down Big Dipper is high in the north. Notice the Big Dipper and Leo. You can use them to star-hop to to the constellation Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs.
Many people know how to find Polaris, the North Star, by drawing a line through the Big Dipper pointer stars, Dubhe and Merak. You can also find Leo by drawing a line through these same pointer stars, but in the opposite direction.
Extend a line from the star Alkaid in the Big Dipper to the star Denebola in Leo. One-third the way along this line, you’ll see Cor Caroli, Canes Venatici’s brightest star. A telescope reveals that Cor Caroli is a binary star – two stars orbiting a common center of mass.
How a binary star reveals its mass
The two component stars are an estimated 675 astronomical units (AU) apart with an orbital period of around 8,300 years. Given this information, astronomers can figure out the combined mass of Cor Caroli in solar masses with this equation: mass = a3/p2, whereby a = mean distance = 675 AU, and p = orbital period = 8,300 years. If you do the calculations, you’ll find that Cor Caroli has about 4.46 times the mass of our sun.
Cor Caroli (Latin for “Heart of Charles”) is named in honor of England’s King Charles I, who had his head cut off in 1649. The name first appeared on English star maps in the late 1600s as Cor Caroli Regis Martyris (“Heart of Charles the Martyr King”). King Charles II, the son of King Charles I, founded the Royal Greenwich Observatory in 1675.
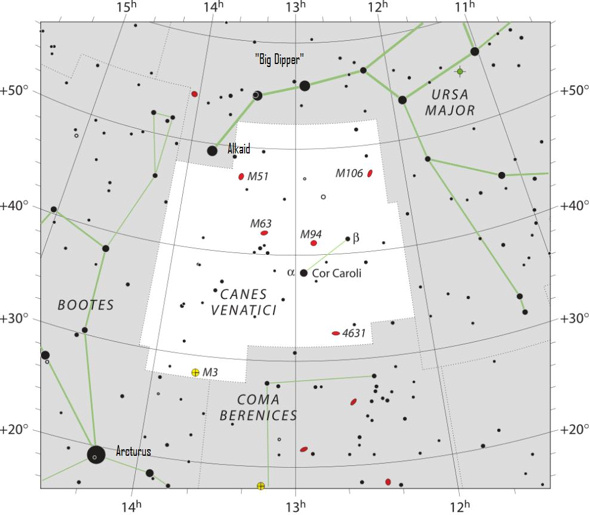
If you’re familiar with the constellation Leo the Lion, you can star-hop to Cor Caroli by drawing an imaginary line from the star Alkaid of the Big Dipper to the Leo star Denebola. This image is via Wikimedia Commons.
Bottom line: Star-hop to Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs, tonight! You can do it, if you can find the constellation Leo and the famous Big Dipper asterism.
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store
Enjoying EarthSky so far? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3d6azvp
Tonight, find the Hunting Dogs. The chart above looks directly overhead at nightfall or early evening in May, as seen from a mid-latitude in the Northern Hemisphere. It’s as if we’re viewing the sky from the comfort of a reclining lawn chair, with our feet pointing southward. The constellation Leo the Lion stands high in the southern sky, while the upside-down Big Dipper is high in the north. Notice the Big Dipper and Leo. You can use them to star-hop to to the constellation Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs.
Many people know how to find Polaris, the North Star, by drawing a line through the Big Dipper pointer stars, Dubhe and Merak. You can also find Leo by drawing a line through these same pointer stars, but in the opposite direction.
Extend a line from the star Alkaid in the Big Dipper to the star Denebola in Leo. One-third the way along this line, you’ll see Cor Caroli, Canes Venatici’s brightest star. A telescope reveals that Cor Caroli is a binary star – two stars orbiting a common center of mass.
How a binary star reveals its mass
The two component stars are an estimated 675 astronomical units (AU) apart with an orbital period of around 8,300 years. Given this information, astronomers can figure out the combined mass of Cor Caroli in solar masses with this equation: mass = a3/p2, whereby a = mean distance = 675 AU, and p = orbital period = 8,300 years. If you do the calculations, you’ll find that Cor Caroli has about 4.46 times the mass of our sun.
Cor Caroli (Latin for “Heart of Charles”) is named in honor of England’s King Charles I, who had his head cut off in 1649. The name first appeared on English star maps in the late 1600s as Cor Caroli Regis Martyris (“Heart of Charles the Martyr King”). King Charles II, the son of King Charles I, founded the Royal Greenwich Observatory in 1675.

If you’re familiar with the constellation Leo the Lion, you can star-hop to Cor Caroli by drawing an imaginary line from the star Alkaid of the Big Dipper to the Leo star Denebola. This image is via Wikimedia Commons.
Bottom line: Star-hop to Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs, tonight! You can do it, if you can find the constellation Leo and the famous Big Dipper asterism.
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store
Enjoying EarthSky so far? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3d6azvp

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire