
Unless you’re a night owl, you probably won’t see the moon and Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo the Maiden, rising up into your eastern sky before your bedtime. The twosome will come up quite late tonight, at or around midnight. That applies to most everywhere worldwide.
EarthSky lunar calendars are cool! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
If you’re not one to stay up late, your best bet is to wake up early to view the moon and Spica before daybreak. The moon will be at or near its half-illuminated last quarter phase, coming on January 17, at 12:58 Universal Time. At time zones in the mainland United States, the moon reaches its last quarter phase on January 17 at 7:58 a.m. Eastern Time, 6:58 a.m. Central Time, 5:58 a.m. Mountain Time and 4:58 a.m.4:58Pacific Time.
Click here to find out when the moon rises into your sky, remembering to check the moonrise and moonset box.
Click here to find out the moon’s present position in front of the constellations of the zodiac.
Spica, a blue-white gem of a star, ranks as the 15th-brightest star to light up the nighttime sky. When you consider that Spica resides some 262 light-years from our solar system, this star must be intrinsically very luminous to shine at 1st-magnitude brightness in Earth’s sky.
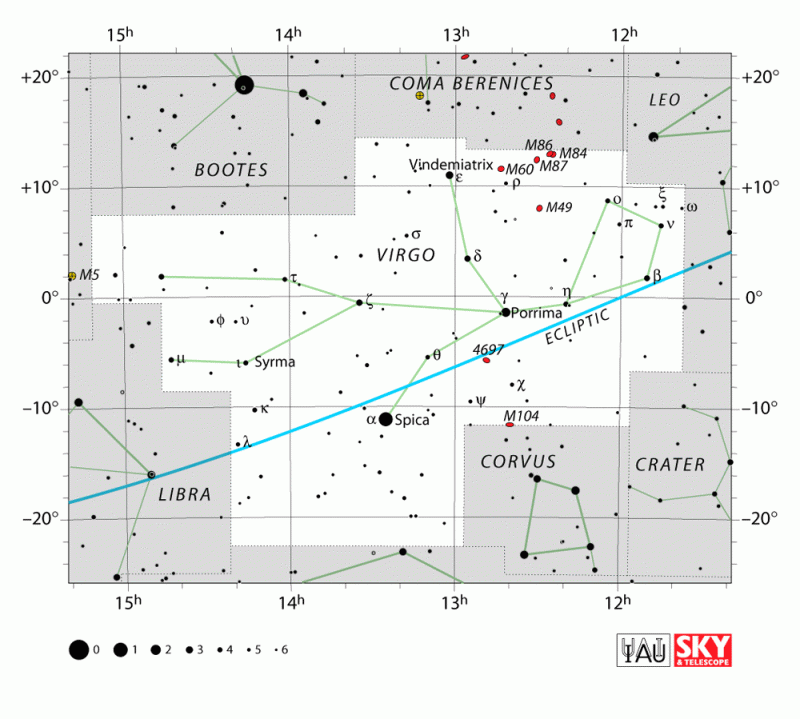
The ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane projected onto the constellations of the zodiac – crosses the celestial equator (declination of Oo) in the constellation Virgo. Because Spica resides so close to the ecliptic, it is considered a major star of the zodiac. Virgo constellation chart via the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
Spica’s blue-white color reveals that this star has an extremely high surface temperature (22,400 Kelvin, 39,860 F, 22,127 C). In contrast, our yellow-colored sun has a surface temperature of nearly 6,000 K (10,340 F, 5,727 C) whereas ruddy Antares sports a rather cool surface temperature of 3,500 K (5,840 F, 3,227 C).
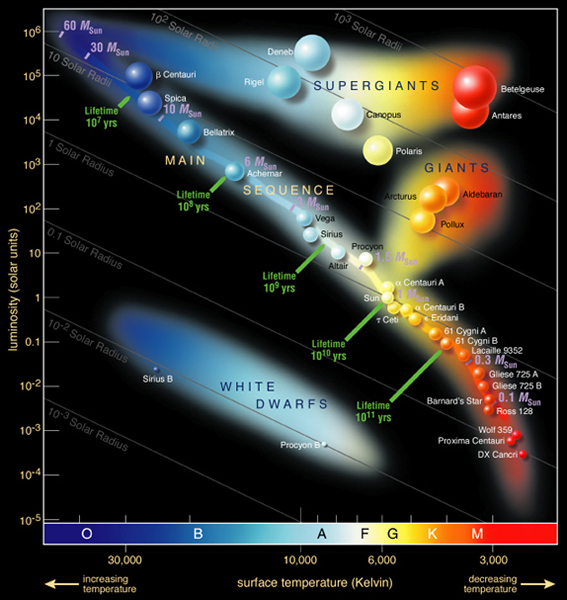
A star that is blue or blue-white in color, such as Spica at the upper left, has a high surface temperature. In contrast, a red-colored star, such as Antares and Betelgeuse at the upper right, has a cool surface temperature. Image of Hertzsprung-Russell diagram via ESO.
Spica, like all the stars, rises some four minutes earlier daily, 1/2 hour earlier weekly and two hours earlier monthly. So, instead of rising around midnight at mid-northern latitudes, as it does in late January, Spica will rise around sunset in early April. Because Spica shines from dusk till dawn in April, we in the Northern Hemisphere often associate this star with the sweet season of spring.
Bottom line: In January, Spica is out from late night until dawn. Use the moon to guide your eye to Spica before daybreak January 17, 2020, and look forward to this star’s all-night appearance in April.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2u0cHUn

Unless you’re a night owl, you probably won’t see the moon and Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo the Maiden, rising up into your eastern sky before your bedtime. The twosome will come up quite late tonight, at or around midnight. That applies to most everywhere worldwide.
EarthSky lunar calendars are cool! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
If you’re not one to stay up late, your best bet is to wake up early to view the moon and Spica before daybreak. The moon will be at or near its half-illuminated last quarter phase, coming on January 17, at 12:58 Universal Time. At time zones in the mainland United States, the moon reaches its last quarter phase on January 17 at 7:58 a.m. Eastern Time, 6:58 a.m. Central Time, 5:58 a.m. Mountain Time and 4:58 a.m.4:58Pacific Time.
Click here to find out when the moon rises into your sky, remembering to check the moonrise and moonset box.
Click here to find out the moon’s present position in front of the constellations of the zodiac.
Spica, a blue-white gem of a star, ranks as the 15th-brightest star to light up the nighttime sky. When you consider that Spica resides some 262 light-years from our solar system, this star must be intrinsically very luminous to shine at 1st-magnitude brightness in Earth’s sky.

The ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane projected onto the constellations of the zodiac – crosses the celestial equator (declination of Oo) in the constellation Virgo. Because Spica resides so close to the ecliptic, it is considered a major star of the zodiac. Virgo constellation chart via the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
Spica’s blue-white color reveals that this star has an extremely high surface temperature (22,400 Kelvin, 39,860 F, 22,127 C). In contrast, our yellow-colored sun has a surface temperature of nearly 6,000 K (10,340 F, 5,727 C) whereas ruddy Antares sports a rather cool surface temperature of 3,500 K (5,840 F, 3,227 C).

A star that is blue or blue-white in color, such as Spica at the upper left, has a high surface temperature. In contrast, a red-colored star, such as Antares and Betelgeuse at the upper right, has a cool surface temperature. Image of Hertzsprung-Russell diagram via ESO.
Spica, like all the stars, rises some four minutes earlier daily, 1/2 hour earlier weekly and two hours earlier monthly. So, instead of rising around midnight at mid-northern latitudes, as it does in late January, Spica will rise around sunset in early April. Because Spica shines from dusk till dawn in April, we in the Northern Hemisphere often associate this star with the sweet season of spring.
Bottom line: In January, Spica is out from late night until dawn. Use the moon to guide your eye to Spica before daybreak January 17, 2020, and look forward to this star’s all-night appearance in April.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2u0cHUn

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire