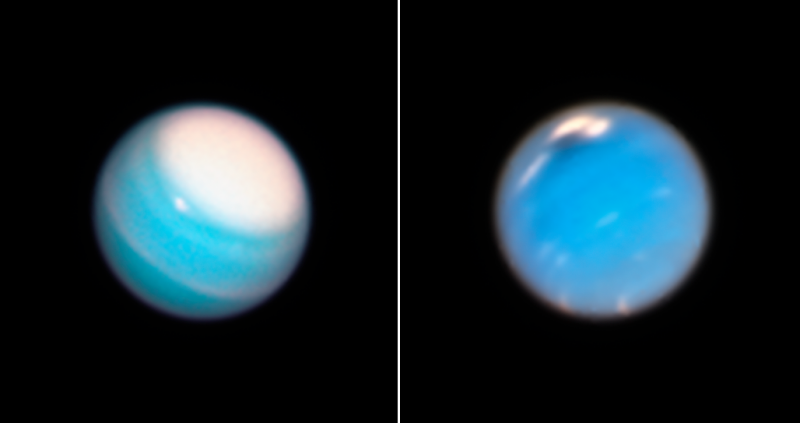


Bright and dark clouds and storms on Uranus (left) and Neptune (right) as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2018. Image via NASA/ ESA/ A. Simon (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center) and M.H. Wong/A. Hsu (University of California, Berkeley)/HubbleSite.
In recent years, the gas giant planets Jupiter and Saturn, along with Pluto, have captured most of the attention in the outer solar system – which is understandable, given the epic missions of Juno, Cassini and New Horizons to these worlds. But the two ice giants – Uranus and Neptune – are still there, too, just waiting to be explored again.
Now the Hubble Space Telescope has taken some beautiful new images of these distant worlds, which were released on February 7, 2019. The images are from the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program, which annually captures global maps of the outer planets when they are closest to Earth in their orbits.
Uranus and Neptune each have been visited only once so far by a spacecraft from Earth – Voyager 2 – in 1986 and 1989 respectively. Voyager 2 sent back some stunning images of both planets and some of their moons, but there’s so much still to learn. No new space missions to these worlds are being planned, although some have been proposed. Until a new future mission can be launched, Hubble is the best resource we have for studying these distant planets.

Larger view of the bright cloud cap over the north pole of Uranus. Image acquired by Hubble in September 3018, via HubbleSite.
The new image of Uranus shows a bright cloud cap across the north pole. Near the edge of that cloud cap is another large, compact methane-ice cloud – sometimes bright enough to be photographed even by amateur astronomers. Another narrow cloud band encircles the planet north of the equator; it is still not known how bands like these are confined to such narrow widths, since both Uranus and Neptune have very broad westward-blowing wind jets.
The northern cloud cap is thought to result from Uranus’ odd rotational axis – the planet rotates “on its side” compared to other planets in the solar system. Seasonal changes in atmospheric flow may create such clouds; right now, Uranus is nearing the middle of the summer season at the north pole, when the sun shines directly on the pole and never sets. In winter seasons, the planet tends to have its typical blander appearance.
The new views of Neptune are also very impressive, showing a huge dark storm – about 6,800 miles (10,943 km) across – near the top of the planet, reminiscent of storms on Jupiter and Saturn. Unlike those storm formations, however, the dark ones on Neptune tend to form and then dissipate fairly quickly after about two years. By comparison, storms on Jupiter, including the Great Red Spot, have been observed to last up to hundreds of years. A previous study led by University of California, Berkeley undergraduate student Andrew Hsu estimated that these storms appear every four to six years at different latitudes.
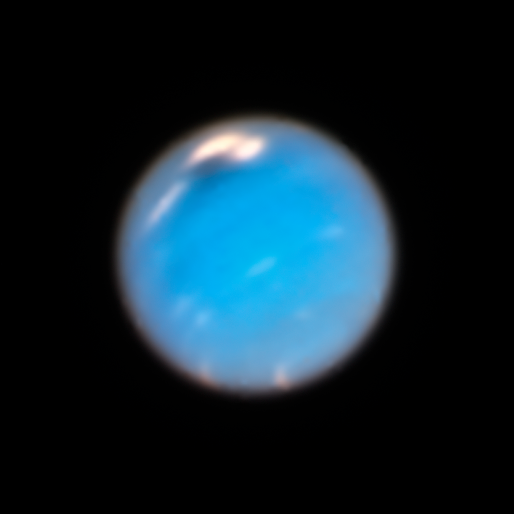
Larger view of the huge dark storm system on Neptune, seen by Hubble in September 2018. Image via HubbleSite.
This new storm on Neptune is only the fourth such one seen by Hubble since 1993, but others were also photographed by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989. As noted in Gizmodo by Amy Simon, a scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center:
The Neptune dark spot is much larger than the one we saw a few years ago, and is comparable in size to the Voyager Great Dark Spot seen in 1989. This is also the first time we could see the region before a storm of that size formed, so that will help us in modeling the formation process.
As on Jupiter, the dark storm vortices swirl in an anti-cyclonic direction, dredging up material from deeper levels in the planet’s atmosphere. This is similar to lenticular or “pancake-shaped” clouds on Earth, which form as air is pushed over the tops of mountains. One cool example is the one that often hangs over the top of Lítla Dímun island, the smallest of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing archipelago, part of the Kingdom of Denmark.

A closer view of one of Neptune’s dark storms, the Great Dark Spot, as seen by Voyager 2 in 1989. Image via NASA/JPL.
There are other storms on Neptune as well – bright white “companion clouds.” These form when the flow of ambient air is disturbed and diverted upward over the darker storm vortices, which causes gases in the atmosphere to freeze into methane ice crystals.
The new dark storm on Neptune was first seen by Hubble in September 2018, but was preceded by other cloud activity as early as 2016. This is possible evidence that such storms first develop deeper in the atmosphere, only becoming visible when the tops of the storms reach a high enough altitude.
The new images are part of a scrapbook of images used by planetary scientists with OPAL to track weather phenomena on these distant worlds; just like on Earth, repeated observations are needed to do this. According to Simon:
The yearly observations are helping us to understand the frequency of storms, as well as their longevity.

An ethereal crescent Uranus as seen by Voyager 2 in 1986, just after the flyby. Image via NASA/JPL.
Uranus and Neptune are both ice giants, with no solid surfaces beneath their atmospheres. Instead, they have mantles of hydrogen and helium surrounding a water-rich interior (the water being in the form of supercritical fluid), which itself is thought to surround a rocky core. Each planet has a bluish hue due to atmospheric methane that absorbs red light but allows blue-green light to be scattered back into space.
Bottom line: Uranus and Neptune are both active, dynamic planets, much like Jupiter and Saturn, with massive storms and other clouds churning in their atmospheres. Although no spacecraft have been able to visit these distant worlds since the late 1980s, the Hubble Space Telescope is still busy observing them, tracking the unique weather phenomena of these icy giants.
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2X0OYgM


Bright and dark clouds and storms on Uranus (left) and Neptune (right) as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2018. Image via NASA/ ESA/ A. Simon (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center) and M.H. Wong/A. Hsu (University of California, Berkeley)/HubbleSite.
In recent years, the gas giant planets Jupiter and Saturn, along with Pluto, have captured most of the attention in the outer solar system – which is understandable, given the epic missions of Juno, Cassini and New Horizons to these worlds. But the two ice giants – Uranus and Neptune – are still there, too, just waiting to be explored again.
Now the Hubble Space Telescope has taken some beautiful new images of these distant worlds, which were released on February 7, 2019. The images are from the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program, which annually captures global maps of the outer planets when they are closest to Earth in their orbits.
Uranus and Neptune each have been visited only once so far by a spacecraft from Earth – Voyager 2 – in 1986 and 1989 respectively. Voyager 2 sent back some stunning images of both planets and some of their moons, but there’s so much still to learn. No new space missions to these worlds are being planned, although some have been proposed. Until a new future mission can be launched, Hubble is the best resource we have for studying these distant planets.

Larger view of the bright cloud cap over the north pole of Uranus. Image acquired by Hubble in September 3018, via HubbleSite.
The new image of Uranus shows a bright cloud cap across the north pole. Near the edge of that cloud cap is another large, compact methane-ice cloud – sometimes bright enough to be photographed even by amateur astronomers. Another narrow cloud band encircles the planet north of the equator; it is still not known how bands like these are confined to such narrow widths, since both Uranus and Neptune have very broad westward-blowing wind jets.
The northern cloud cap is thought to result from Uranus’ odd rotational axis – the planet rotates “on its side” compared to other planets in the solar system. Seasonal changes in atmospheric flow may create such clouds; right now, Uranus is nearing the middle of the summer season at the north pole, when the sun shines directly on the pole and never sets. In winter seasons, the planet tends to have its typical blander appearance.
The new views of Neptune are also very impressive, showing a huge dark storm – about 6,800 miles (10,943 km) across – near the top of the planet, reminiscent of storms on Jupiter and Saturn. Unlike those storm formations, however, the dark ones on Neptune tend to form and then dissipate fairly quickly after about two years. By comparison, storms on Jupiter, including the Great Red Spot, have been observed to last up to hundreds of years. A previous study led by University of California, Berkeley undergraduate student Andrew Hsu estimated that these storms appear every four to six years at different latitudes.

Larger view of the huge dark storm system on Neptune, seen by Hubble in September 2018. Image via HubbleSite.
This new storm on Neptune is only the fourth such one seen by Hubble since 1993, but others were also photographed by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989. As noted in Gizmodo by Amy Simon, a scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center:
The Neptune dark spot is much larger than the one we saw a few years ago, and is comparable in size to the Voyager Great Dark Spot seen in 1989. This is also the first time we could see the region before a storm of that size formed, so that will help us in modeling the formation process.
As on Jupiter, the dark storm vortices swirl in an anti-cyclonic direction, dredging up material from deeper levels in the planet’s atmosphere. This is similar to lenticular or “pancake-shaped” clouds on Earth, which form as air is pushed over the tops of mountains. One cool example is the one that often hangs over the top of Lítla Dímun island, the smallest of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing archipelago, part of the Kingdom of Denmark.

A closer view of one of Neptune’s dark storms, the Great Dark Spot, as seen by Voyager 2 in 1989. Image via NASA/JPL.
There are other storms on Neptune as well – bright white “companion clouds.” These form when the flow of ambient air is disturbed and diverted upward over the darker storm vortices, which causes gases in the atmosphere to freeze into methane ice crystals.
The new dark storm on Neptune was first seen by Hubble in September 2018, but was preceded by other cloud activity as early as 2016. This is possible evidence that such storms first develop deeper in the atmosphere, only becoming visible when the tops of the storms reach a high enough altitude.
The new images are part of a scrapbook of images used by planetary scientists with OPAL to track weather phenomena on these distant worlds; just like on Earth, repeated observations are needed to do this. According to Simon:
The yearly observations are helping us to understand the frequency of storms, as well as their longevity.

An ethereal crescent Uranus as seen by Voyager 2 in 1986, just after the flyby. Image via NASA/JPL.
Uranus and Neptune are both ice giants, with no solid surfaces beneath their atmospheres. Instead, they have mantles of hydrogen and helium surrounding a water-rich interior (the water being in the form of supercritical fluid), which itself is thought to surround a rocky core. Each planet has a bluish hue due to atmospheric methane that absorbs red light but allows blue-green light to be scattered back into space.
Bottom line: Uranus and Neptune are both active, dynamic planets, much like Jupiter and Saturn, with massive storms and other clouds churning in their atmospheres. Although no spacecraft have been able to visit these distant worlds since the late 1980s, the Hubble Space Telescope is still busy observing them, tracking the unique weather phenomena of these icy giants.
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2X0OYgM

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire