

Total lunar eclipse composite image by Fred Espenak.
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth, sun and moon align in space, with Earth between the sun and moon. At such times, Earth’s shadow falls on the full moon, darkening the moon’s face and – at mid-eclipse – usually turning it a coppery red.
A solar eclipse happens at the opposite phase of the moon – new moon – when the moon passes between the sun and Earth.
Why aren’t there eclipses at every full and new moon?
EarthSky lunar calendars are cool! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
The moon takes about a month to orbit around the Earth. If the moon orbited in the same plane as the ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane – we would have a minimum of two eclipses every month. There’d be an eclipse of the moon at every full moon. And, one fortnight (approximately two weeks) later there’d be an eclipse of the sun at new moon for a total of at least 24 eclipses every year.
But the moon’s orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit by about five degrees. Twice a month the moon intersects the ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane – at points called nodes. If the moon is going from south to north in its orbit, it’s called an ascending node. If the moon is going from north to south, it’s a descending node. If the full moon or new moon is appreciably close to one of these nodes, then an eclipse is not only possible – but inevitable.
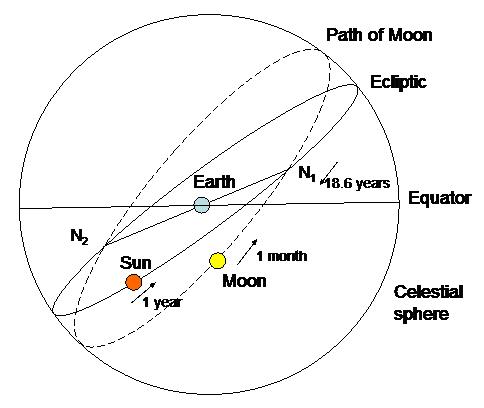
The plane of the moon’s orbit is inclined at 5 degrees to the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane). In this diagram, the ecliptic is portrayed as the sun’s apparent annual path through the constellations of the zodiac. The moon’s orbit intersects the ecliptic at two points called nodes (N1 and N2).
Solar and lunar eclipses always come in pairs, with one following the other in a period of one fortnight (approximately two weeks). For example, in 2019, the upcoming ascending node total lunar eclipse on January 20-21 follows the descending node partial solar eclipse on January 5-6.
Then exactly six lunar months (six new moons) after the descending node partial solar eclipse on January 5-6, there’s an ascending node total solar eclipse on July 2. One fortnight after this ascending node July 2 total solar eclipse, there will be a descending node partial lunar eclipse on July 16.
Then exactly six lunar months (six new moons) after the ascending node partial solar eclipse of July 2, the final eclipse of 2019 will present a descending node annular solar eclipse on December 26. One fortnight later, the first eclipse of 2020 will fall on January 10, 2020, to feature an ascending node penumbral lunar eclipse.
More often than not, two eclipses – one solar and one lunar – occur in one eclipse season, a period lasting approximately 34 to 35 days. Sometimes, though, when the initial eclipse happens sufficiently early in the eclipse season, there can be three eclipses in one eclipse season (two solar and one lunar, or two lunar and one solar).
This year, in 2019, the middle of the eclipse season happens on January 17, July 10 and December 30. At the middle of an eclipse season, which recurs in periods of about 173 days, the lunar nodes are in exact alignment with the Earth and sun.
Is it possible to have three eclipses in one month?
The video below explains why a pair of eclipses happens when the new moon and full moon are closely aligned with the lunar nodes.
There might be some unfamiliar words in this video, including ecliptic and node. The ecliptic is the plane of Earth’s orbit around the sun. The moon’s orbit is inclined to the plane of the ecliptic. The nodes are the two points where the moon’s orbit and the ecliptic intersect.
Relative to the moon’s nodes, the moon’s phases recur about 30 degrees farther eastward (counterclockwise) along the zodiac each month. So the next pair of eclipses won’t be forthcoming for nearly another six calendar months (6 x 30 degrees = 180 degrees), to fall on July 2 and 16, 2019.
Node passages of the moon: 2001 to 2100
Phases of the moon: 2001 to 2100
The following new moon and full moon happen again nearly 30 degrees farther eastward as measured by the constellations of the zodiac in about 29.5 days. But the moon returns to its node a good two days earlier than that, or in about 27.2 days. After the eclipses of January 6 and January 21, 2019, it’ll be a waning crescent moon (not a new moon) that crosses the moon’s descending node on February 3, 2019, and a waxing gibbous moon (not a full moon) that crosses the moon’s ascending node on February 17, 2019.
Even though the moon’s orbit is inclined to that of Earth – and even though there’s not an eclipse with every new and full moon – there are more eclipses than you might think.
There are from four to seven eclipses every year. Some are solar, some are lunar, some are total, and some are partial. All are marvelous to behold – a reminder that we live on a planet – a chance to experience falling in line with great worlds in space!

Photo by pizzodisevo.
Bottom line: There’s no eclipse at every full moon and new moon because the moon’s orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit by about five degrees. Most of the time, the sun, Earth and moon don’t line up precisely enough to cause an eclipse. But sometimes, more often than you might expect, they do!
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2W1JcLa


Total lunar eclipse composite image by Fred Espenak.
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth, sun and moon align in space, with Earth between the sun and moon. At such times, Earth’s shadow falls on the full moon, darkening the moon’s face and – at mid-eclipse – usually turning it a coppery red.
A solar eclipse happens at the opposite phase of the moon – new moon – when the moon passes between the sun and Earth.
Why aren’t there eclipses at every full and new moon?
EarthSky lunar calendars are cool! They make great gifts. Order now. Going fast!
The moon takes about a month to orbit around the Earth. If the moon orbited in the same plane as the ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane – we would have a minimum of two eclipses every month. There’d be an eclipse of the moon at every full moon. And, one fortnight (approximately two weeks) later there’d be an eclipse of the sun at new moon for a total of at least 24 eclipses every year.
But the moon’s orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit by about five degrees. Twice a month the moon intersects the ecliptic – Earth’s orbital plane – at points called nodes. If the moon is going from south to north in its orbit, it’s called an ascending node. If the moon is going from north to south, it’s a descending node. If the full moon or new moon is appreciably close to one of these nodes, then an eclipse is not only possible – but inevitable.

The plane of the moon’s orbit is inclined at 5 degrees to the ecliptic (Earth’s orbital plane). In this diagram, the ecliptic is portrayed as the sun’s apparent annual path through the constellations of the zodiac. The moon’s orbit intersects the ecliptic at two points called nodes (N1 and N2).
Solar and lunar eclipses always come in pairs, with one following the other in a period of one fortnight (approximately two weeks). For example, in 2019, the upcoming ascending node total lunar eclipse on January 20-21 follows the descending node partial solar eclipse on January 5-6.
Then exactly six lunar months (six new moons) after the descending node partial solar eclipse on January 5-6, there’s an ascending node total solar eclipse on July 2. One fortnight after this ascending node July 2 total solar eclipse, there will be a descending node partial lunar eclipse on July 16.
Then exactly six lunar months (six new moons) after the ascending node partial solar eclipse of July 2, the final eclipse of 2019 will present a descending node annular solar eclipse on December 26. One fortnight later, the first eclipse of 2020 will fall on January 10, 2020, to feature an ascending node penumbral lunar eclipse.
More often than not, two eclipses – one solar and one lunar – occur in one eclipse season, a period lasting approximately 34 to 35 days. Sometimes, though, when the initial eclipse happens sufficiently early in the eclipse season, there can be three eclipses in one eclipse season (two solar and one lunar, or two lunar and one solar).
This year, in 2019, the middle of the eclipse season happens on January 17, July 10 and December 30. At the middle of an eclipse season, which recurs in periods of about 173 days, the lunar nodes are in exact alignment with the Earth and sun.
Is it possible to have three eclipses in one month?
The video below explains why a pair of eclipses happens when the new moon and full moon are closely aligned with the lunar nodes.
There might be some unfamiliar words in this video, including ecliptic and node. The ecliptic is the plane of Earth’s orbit around the sun. The moon’s orbit is inclined to the plane of the ecliptic. The nodes are the two points where the moon’s orbit and the ecliptic intersect.
Relative to the moon’s nodes, the moon’s phases recur about 30 degrees farther eastward (counterclockwise) along the zodiac each month. So the next pair of eclipses won’t be forthcoming for nearly another six calendar months (6 x 30 degrees = 180 degrees), to fall on July 2 and 16, 2019.
Node passages of the moon: 2001 to 2100
Phases of the moon: 2001 to 2100
The following new moon and full moon happen again nearly 30 degrees farther eastward as measured by the constellations of the zodiac in about 29.5 days. But the moon returns to its node a good two days earlier than that, or in about 27.2 days. After the eclipses of January 6 and January 21, 2019, it’ll be a waning crescent moon (not a new moon) that crosses the moon’s descending node on February 3, 2019, and a waxing gibbous moon (not a full moon) that crosses the moon’s ascending node on February 17, 2019.
Even though the moon’s orbit is inclined to that of Earth – and even though there’s not an eclipse with every new and full moon – there are more eclipses than you might think.
There are from four to seven eclipses every year. Some are solar, some are lunar, some are total, and some are partial. All are marvelous to behold – a reminder that we live on a planet – a chance to experience falling in line with great worlds in space!

Photo by pizzodisevo.
Bottom line: There’s no eclipse at every full moon and new moon because the moon’s orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit by about five degrees. Most of the time, the sun, Earth and moon don’t line up precisely enough to cause an eclipse. But sometimes, more often than you might expect, they do!
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2W1JcLa

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire