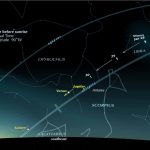
View larger. | The last quarter moon of January 27 will be about as high north of the ecliptic as it can get. You can see why, in this detail from Guy Ottewell’s Zodiac Wavy Chart for 2019.
Originally published at Guy Ottewell’s blog. Reprinted here with permission.
The blue line is the ecliptic, curved in this projection in which the celestial equator – the red line – is straight.
On January 21, 2019 ascending node through the ecliptic coincided with full moon, so there was a total lunar eclipse. Descending node on February 3 will come close to new moon – though not as close as on January 6, when there was a partial solar eclipse.
Halfway between, at last quarter on January 27, the moon is at the top of its arch, about 5° (its orbital inclination) north of the ecliptic.
A result of this is that the libration is at a maximum for the year. This is interesting though, as we’ll explain, of limited observational advantage.
Libration is the moon’s apparent “rocking,” caused by its slightly inclined and elliptical orbit. It’s indicated in our chart by a red tab on the moon’s limb (edge). The tab is at the part of the limb where libration allows us to see farthest into the moon’s usually invisible far side. The libration maximum is at January 27, 17:00 UTC, about 3 hours before the last quarter instant, and the amount of libration is a little over 10°.
The libration point has to be on the part of the moon toward the ecliptic; from the ecliptic plane we are now looking slightly northward toward the moon, so we see more at its southern limb.
Unfortunately the point is on the un-sunlit half of the last quarter moon. So we can’t see past that part of the limb into luna incognita, the “unknown omon.” But it’s not far from the moon’s south pole. Therefore, a little to the left, where the sunlit half begins, it might be possible to see a little way into the mostly hidden South-Pole-Aitken Basin, where China’s Chang’e 4 lander is now exploring.
The libration continues approximately the same for several days, as the tabs show.
To see a last quarter moon, you have to be looking after it rises around midnight. Better to be later than that, in the pre-dawn hours. The moon is then higher, and risen behind it are the stars and planets it is going to pass in the next few dawns – Antares, Jupiter, Venus, Saturn.
View larger. | Monday morning’s moon is just past last quarter, rising around midnight, looking like half a pie. This week, as the moon continues to wane, it will pass the planets in the early morning sky. Read more.
As I was writing this, at about six this morning, I opened the window shutters beside me and saw in a black gap between roofs a light so brilliant that I almost thought the town cinema was on fire again.
It was the moon, a day before last quarter.
Bottom line: Last quarter moon is January 27, 2019 at 21:12 UTC; translate UTC to your time.
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2MACJ5z

View larger. | The last quarter moon of January 27 will be about as high north of the ecliptic as it can get. You can see why, in this detail from Guy Ottewell’s Zodiac Wavy Chart for 2019.
Originally published at Guy Ottewell’s blog. Reprinted here with permission.
The blue line is the ecliptic, curved in this projection in which the celestial equator – the red line – is straight.
On January 21, 2019 ascending node through the ecliptic coincided with full moon, so there was a total lunar eclipse. Descending node on February 3 will come close to new moon – though not as close as on January 6, when there was a partial solar eclipse.
Halfway between, at last quarter on January 27, the moon is at the top of its arch, about 5° (its orbital inclination) north of the ecliptic.
A result of this is that the libration is at a maximum for the year. This is interesting though, as we’ll explain, of limited observational advantage.
Libration is the moon’s apparent “rocking,” caused by its slightly inclined and elliptical orbit. It’s indicated in our chart by a red tab on the moon’s limb (edge). The tab is at the part of the limb where libration allows us to see farthest into the moon’s usually invisible far side. The libration maximum is at January 27, 17:00 UTC, about 3 hours before the last quarter instant, and the amount of libration is a little over 10°.
The libration point has to be on the part of the moon toward the ecliptic; from the ecliptic plane we are now looking slightly northward toward the moon, so we see more at its southern limb.
Unfortunately the point is on the un-sunlit half of the last quarter moon. So we can’t see past that part of the limb into luna incognita, the “unknown omon.” But it’s not far from the moon’s south pole. Therefore, a little to the left, where the sunlit half begins, it might be possible to see a little way into the mostly hidden South-Pole-Aitken Basin, where China’s Chang’e 4 lander is now exploring.
The libration continues approximately the same for several days, as the tabs show.
To see a last quarter moon, you have to be looking after it rises around midnight. Better to be later than that, in the pre-dawn hours. The moon is then higher, and risen behind it are the stars and planets it is going to pass in the next few dawns – Antares, Jupiter, Venus, Saturn.
View larger. | Monday morning’s moon is just past last quarter, rising around midnight, looking like half a pie. This week, as the moon continues to wane, it will pass the planets in the early morning sky. Read more.
As I was writing this, at about six this morning, I opened the window shutters beside me and saw in a black gap between roofs a light so brilliant that I almost thought the town cinema was on fire again.
It was the moon, a day before last quarter.
Bottom line: Last quarter moon is January 27, 2019 at 21:12 UTC; translate UTC to your time.
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2MACJ5z

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire