Arctic sea ice likely reached its minimum extent for the year on September 19 and again on September 23, 2018, according to researchers at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and NASA.
Scientists track sea ice in the Arctic as it grows to a maximum extent through the winter and shrinks back in the summer to its minimum extent in September each year. This year’s minimum sea ice extent – the smallest area of ice for the year – reached 1.77 million square miles (4.59 million square km). That tied with 2008 and 2010as the sixth lowest sea ice minimum since consistent satellite records began 40 years ago.
Researchers at NSIDC noted that the estimate is preliminary, and it is still possible (but not likely) that changing winds could push the ice extent lower.
Image via NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
According to NASA’s Earth Observatory:
Arctic sea ice follows seasonal patterns of growth and decay. It thickens and spreads during the fall and winter and thins and shrinks during the spring and summer. But in recent decades, increasing temperatures have led to significant decreases in summer and winter sea ice extents. The decline in Arctic ice cover will ultimately affect the planet’s weather patterns and the circulation of the oceans.
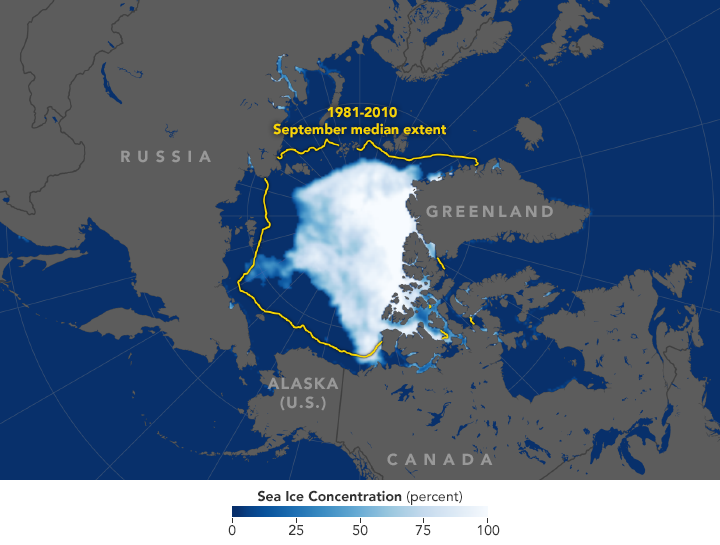
The map above shows the extent of Arctic sea ice as measured by satellites on September 19, 2018. Extent is defined as the total area in which the ice concentration is at least 15 percent. The yellow outline shows the median September sea ice extent from 1981–2010. Image via NASA.
Claire Parkinson is a climate change senior scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. She said in a statement:
This year’s minimum is relatively high compared to the record low extent we saw in 2012, but it is still low compared to what it used to be in the 1970s, 1980s and even the 1990s.
Bottom line: On September 19 and 23, 2018, Arctic sea ice extent dropped to 1.77 million square miles (4.59 million square km) – tied for the 6th lowest minimum in the satellite record.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2ye6WAP
Arctic sea ice likely reached its minimum extent for the year on September 19 and again on September 23, 2018, according to researchers at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and NASA.
Scientists track sea ice in the Arctic as it grows to a maximum extent through the winter and shrinks back in the summer to its minimum extent in September each year. This year’s minimum sea ice extent – the smallest area of ice for the year – reached 1.77 million square miles (4.59 million square km). That tied with 2008 and 2010as the sixth lowest sea ice minimum since consistent satellite records began 40 years ago.
Researchers at NSIDC noted that the estimate is preliminary, and it is still possible (but not likely) that changing winds could push the ice extent lower.
Image via NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
According to NASA’s Earth Observatory:
Arctic sea ice follows seasonal patterns of growth and decay. It thickens and spreads during the fall and winter and thins and shrinks during the spring and summer. But in recent decades, increasing temperatures have led to significant decreases in summer and winter sea ice extents. The decline in Arctic ice cover will ultimately affect the planet’s weather patterns and the circulation of the oceans.

The map above shows the extent of Arctic sea ice as measured by satellites on September 19, 2018. Extent is defined as the total area in which the ice concentration is at least 15 percent. The yellow outline shows the median September sea ice extent from 1981–2010. Image via NASA.
Claire Parkinson is a climate change senior scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. She said in a statement:
This year’s minimum is relatively high compared to the record low extent we saw in 2012, but it is still low compared to what it used to be in the 1970s, 1980s and even the 1990s.
Bottom line: On September 19 and 23, 2018, Arctic sea ice extent dropped to 1.77 million square miles (4.59 million square km) – tied for the 6th lowest minimum in the satellite record.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2ye6WAP

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire