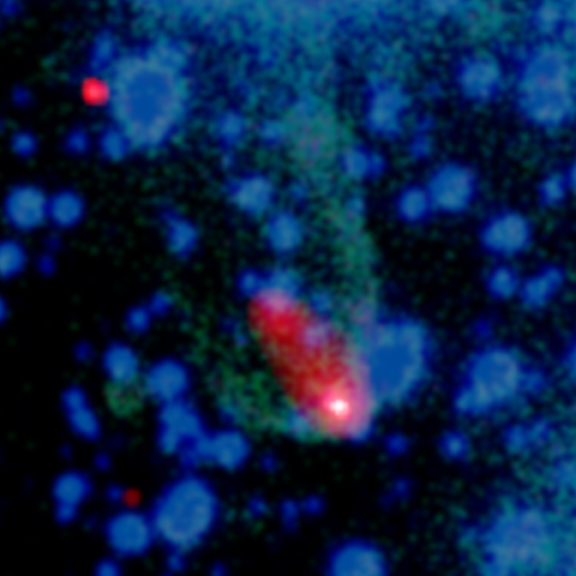
Here’s a composite X-ray (red/white) and optical (green/blue) image of the Black Widow pulsar, aka PSR B1957+20. The image shows an elongated cloud, or cocoon, of high-energy particles flowing behind the rapidly rotating pulsar (the white point-like source). Astronomers have announced a highly detailed observation of this distant pulsar, which they accomplished using the gas in this cloud, or coccon, as a magnifier. This image, from 2001, is via Chandra.
Astronomers in Toronto said today (May 23, 2018) that they’ve performed:
… one of the highest resolution observations in astronomical history by observing two intense regions of radiation, 20 kilometers [12 miles] apart, around a star 6,500 light-years away.
The observation is equivalent to using a telescope on Earth to see a flea on the surface of Pluto.
The work is being published May 24 in the peer-reviewed journal Nature,
Their target object was pulsar PSR B1957+20 – aka the Black Widow pulsar – discovered in 1988. It’s millisecond pulsar, spinning over 600 times per second. As the pulsar spins, it emits beams of radiation from the two hotspots on its surface. The intense regions of radiation observed in this new work are associated with the beams.
The pulsar also has a cool, lightweight brown dwarf companion. The two stars orbit each other about every 9 hours and happen to be aligned with respect to Earth so that – within each orbit – an eclipse occurs, lasting 20 minutes. The brown dwarf is known to have a “wake” or comet-like tail of gas. That’s because it’s moving through space at approximately a million kilometers per hour, in contrast to our own sun’s forward velocity through the Milky Way galaxy of about 72,000 kilometers (45,000 miles) per hour.
Robert Main at the University of Toronto is lead author of the new study. He said this gas around the brown dwarf is what made his observation possible:
The gas is acting like a magnifying glass right in front of the pulsar. We are essentially looking at the pulsar through a naturally occurring magnifier which periodically allows us to see the two regions separately.
The pulsar PSR B1957+20 is seen in the background through the cloud of gas enveloping its brown dwarf star companion. Image: Dr. Mark A. Garlick; Dunlap Institute for Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Toronto
In this unusual star system, the brown dwarf and the pulsar are very close together. The brown dwarf star – which is about a third the diameter of our sun – is roughly 2 million kilometers (1.2 million miles) from the pulsar — in contrast to Earth’s distance from the sun of 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). The dwarf companion star is tidally locked to the pulsar so that one side always faces its pulsating companion, the way the moon is tidally locked to the Earth.
Because it is so close to the pulsar, the brown dwarf star is blasted by the strong radiation coming from its smaller companion. The intense radiation from the pulsar heats one side of the relatively cool dwarf star to the temperature of our sun’s surface, about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit or some 6,000 degrees Celsius.
The blast from the pulsar may ultimately destroy the brown dwarf companion, these astronomers said. Pulsars in these types of binary systems are called black widows because – just as a black widow spider eats its mate – the pulsar, given the right conditions, could gradually erode gas from the dwarf star until the latter is consumed.
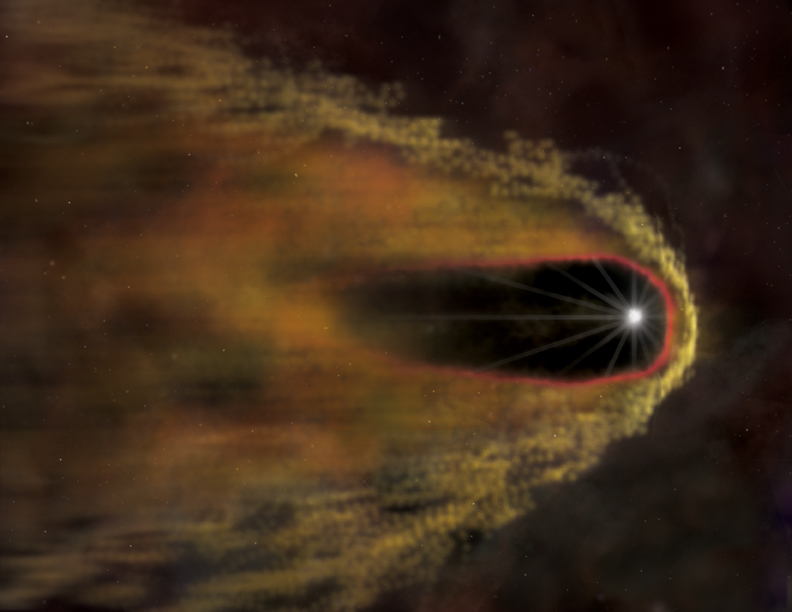
Artist’s concept of the B1957+20 system, moving through space, surrounded by a cloud of gas. The companion star is too close to the pulsar to be visible at this scale. Read more about this image via Wikimedia Commons.
Bottom line: Astronomers observed two intense regions of radiation – 12 miles (20 km) apart – on the rapidly spinning pulsar PSR B1957+20 – aka the Black Widow pulsar. They say it’s “one of the highest resolution observations in astronomical history.”
Source: “Extreme Plasma Lensing of the Black Widow Pulsar,” Robert Main et al., 2018 May 24, Nature
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2sb7u7E

Here’s a composite X-ray (red/white) and optical (green/blue) image of the Black Widow pulsar, aka PSR B1957+20. The image shows an elongated cloud, or cocoon, of high-energy particles flowing behind the rapidly rotating pulsar (the white point-like source). Astronomers have announced a highly detailed observation of this distant pulsar, which they accomplished using the gas in this cloud, or coccon, as a magnifier. This image, from 2001, is via Chandra.
Astronomers in Toronto said today (May 23, 2018) that they’ve performed:
… one of the highest resolution observations in astronomical history by observing two intense regions of radiation, 20 kilometers [12 miles] apart, around a star 6,500 light-years away.
The observation is equivalent to using a telescope on Earth to see a flea on the surface of Pluto.
The work is being published May 24 in the peer-reviewed journal Nature,
Their target object was pulsar PSR B1957+20 – aka the Black Widow pulsar – discovered in 1988. It’s millisecond pulsar, spinning over 600 times per second. As the pulsar spins, it emits beams of radiation from the two hotspots on its surface. The intense regions of radiation observed in this new work are associated with the beams.
The pulsar also has a cool, lightweight brown dwarf companion. The two stars orbit each other about every 9 hours and happen to be aligned with respect to Earth so that – within each orbit – an eclipse occurs, lasting 20 minutes. The brown dwarf is known to have a “wake” or comet-like tail of gas. That’s because it’s moving through space at approximately a million kilometers per hour, in contrast to our own sun’s forward velocity through the Milky Way galaxy of about 72,000 kilometers (45,000 miles) per hour.
Robert Main at the University of Toronto is lead author of the new study. He said this gas around the brown dwarf is what made his observation possible:
The gas is acting like a magnifying glass right in front of the pulsar. We are essentially looking at the pulsar through a naturally occurring magnifier which periodically allows us to see the two regions separately.
The pulsar PSR B1957+20 is seen in the background through the cloud of gas enveloping its brown dwarf star companion. Image: Dr. Mark A. Garlick; Dunlap Institute for Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Toronto
In this unusual star system, the brown dwarf and the pulsar are very close together. The brown dwarf star – which is about a third the diameter of our sun – is roughly 2 million kilometers (1.2 million miles) from the pulsar — in contrast to Earth’s distance from the sun of 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). The dwarf companion star is tidally locked to the pulsar so that one side always faces its pulsating companion, the way the moon is tidally locked to the Earth.
Because it is so close to the pulsar, the brown dwarf star is blasted by the strong radiation coming from its smaller companion. The intense radiation from the pulsar heats one side of the relatively cool dwarf star to the temperature of our sun’s surface, about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit or some 6,000 degrees Celsius.
The blast from the pulsar may ultimately destroy the brown dwarf companion, these astronomers said. Pulsars in these types of binary systems are called black widows because – just as a black widow spider eats its mate – the pulsar, given the right conditions, could gradually erode gas from the dwarf star until the latter is consumed.

Artist’s concept of the B1957+20 system, moving through space, surrounded by a cloud of gas. The companion star is too close to the pulsar to be visible at this scale. Read more about this image via Wikimedia Commons.
Bottom line: Astronomers observed two intense regions of radiation – 12 miles (20 km) apart – on the rapidly spinning pulsar PSR B1957+20 – aka the Black Widow pulsar. They say it’s “one of the highest resolution observations in astronomical history.”
Source: “Extreme Plasma Lensing of the Black Widow Pulsar,” Robert Main et al., 2018 May 24, Nature
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2sb7u7E

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire