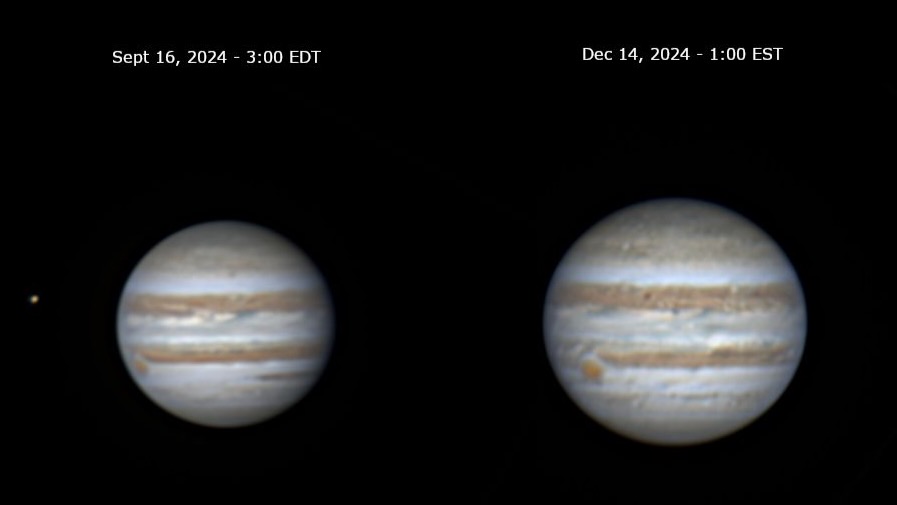

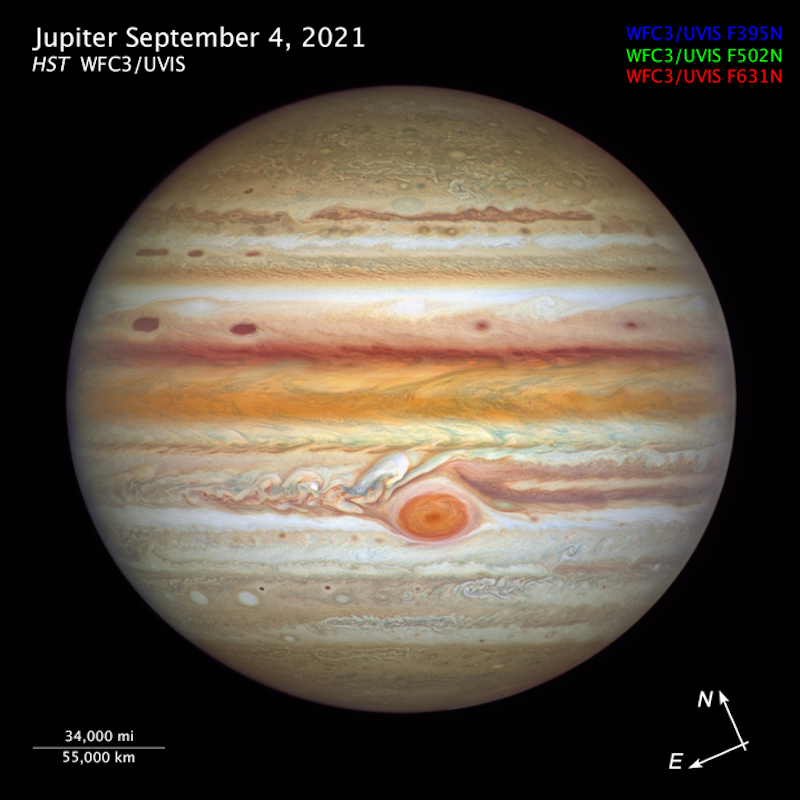
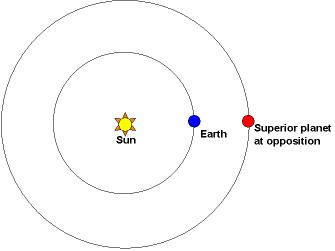
Jupiter in 2025: Earth will fly between the biggest planet in our solar system – Jupiter – and the sun on January 10, 2026. At that time, this mighty world will be most opposite the sun from Earth for this year. It’ll be rising in the east as the sun sets in the west. Astronomers will call it Jupiter’s opposition to the sun. The early months of 2026 will be a great time to observe it!
The exact time of Jupiter’s opposition is 9 UTC (3 a.m. CDT) on January 10, 2026.
Jupiter will be closest to Earth one day before its opposition, on January 9, 2026. At that time, its distance will be 393 million miles/ 633 million km/ 35 light-minutes from Earth. Read: Why is Jupiter closest before opposition?
Opposition constellation in 2026: Gemini the Twins.
Brightness at opposition: Magnitude -2.53. Jupiter shines as the 4th-brightest object in the sky, after the sun, moon and planet Venus. In mid-January 2026, Venus is behind the sun. So Jupiter will be the brightest starlike object visible for most of the night.
Angular size at opposition (as seen through a telescope): 46.58 arcseconds.
Through binoculars (anytime): Jupiter reveals a bright disk. If you look closely, you’ll see several of its four large moons – called the Galilean satellites – appearing as pinpoints of light, arrayed in a line that bisects the giant planet. Read: How to see and enjoy Jupiter’s moons.

How often does Jupiter reach opposition?
Jupiter takes 12 earthly years to orbit the sun once. So, the giant planet comes to opposition roughly every 13 months. It didn’t have an opposition in 2025.
2024 Jupiter opposition – December 7
2026 Jupiter opposition – January 10
2027 Jupiter opposition – February 10
Earth takes 12 months to travel once around the sun relative to Jupiter. So, according to our earthly calendars, Jupiter’s opposition comes about a month later each year. Add to that the fact that we recognize 12 constellations of the zodiac. And there are 12 months in a year. So Jupiter appears in front of a new zodiacal constellation at each year’s opposition. This year, it’s in front of Gemini the Twins.
For the fanciful, the giant planet Jupiter is like a real giant, stepping one by one around the zodiacal constellations, over the period of its 12-year orbit.

Recent Jupiter events
December 7, 2024: Jupiter came to opposition in front of the constellation Taurus.
February 4, 2025: Jupiter ended retrograde motion, a sign that the best time to observe Jupiter had ended. But the planet remained in the night sky through April 2025. In May, it was nearing the sunset glare, becoming increasingly difficult to see.
June 24, 2025: Jupiter was at solar conjunction, or behind the sun as seen from Earth. Afterwards, it emerged in the morning sky in July 2025.
November 11, 2025: Jupiter began retrograde motion, that is, westward motion on the sky’s dome, a sign that opposition lay just ahead.
January 9, 2026: Jupiter at perigee, or closest to Earth for 2026.
January 10, 2026: Jupiter at opposition, or opposite the sun as seen from Earth.
A failed star?
Especially around the time of opposition, it’s fun to think of Jupiter as a failed star. Our sun contains some 99.86% of all the mass in our solar system. Jupiter contains 0.1% of the solar system’s mass. And all the other planets (including Earth), moons, asteroids and comets in our solar system contain 0.04% of the solar system’s mass. So Jupiter is much more massive than all the other planets combined. And, for that reason, we sometimes speak of Jupiter as a failed star.
It’s failed in the sense that it’s not massive enough or hot enough inside to spark thermonuclear fusion reactions, the process that enables stars to shine. Jupiter is big! But, without that thermonuclear reaction it can’t shine as stars do.
Overall, you’d need some 80 Jupiters – rolled into a ball – to be hot enough inside to spark fusion. So, Jupiter isn’t a star. That is, it doesn’t shine with its own light. Instead, it shines by reflected sunlight.
Yet in January 2026 – as bright Jupiter rises in the east opposite the sunset – you can stand on Earth all night and peer toward bright Jupiter in our sky. And indeed, you can imagine that, if the giant planet did have enough mass to shine as stars do, then around Jupiter’s opposition, we’d have no night at all. Instead, Jupiter would shine as a tiny 2nd sun, all night long.
Read more: How to see Jupiter’s moons
For precise sun and Jupiter rising times at your location:
Old Farmer’s Almanac (U.S. and Canada)
timeanddate.com (worldwide)
Stellarium (online planetarium program)
In-the-sky information and finder chart for your location
EarthSky Community Photos


Got a picture of Jupiter? We’d love to see it. Submit them here.
Bottom line: Giant Jupiter is closest to Earth for 2026 on January 9. Then Earth will fly between the sun and Jupiter – bringing Jupiter to opposition – January 10.
Read more: Jupiter’s moons: How to see and enjoy them
Read: Why is Jupiter closest to Earth 1 day before opposition?
The post Earth flies between Jupiter and the sun January 10 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/aAZVyo2

Jupiter in 2025: Earth will fly between the biggest planet in our solar system – Jupiter – and the sun on January 10, 2026. At that time, this mighty world will be most opposite the sun from Earth for this year. It’ll be rising in the east as the sun sets in the west. Astronomers will call it Jupiter’s opposition to the sun. The early months of 2026 will be a great time to observe it!
The exact time of Jupiter’s opposition is 9 UTC (3 a.m. CDT) on January 10, 2026.
Jupiter will be closest to Earth one day before its opposition, on January 9, 2026. At that time, its distance will be 393 million miles/ 633 million km/ 35 light-minutes from Earth. Read: Why is Jupiter closest before opposition?
Opposition constellation in 2026: Gemini the Twins.
Brightness at opposition: Magnitude -2.53. Jupiter shines as the 4th-brightest object in the sky, after the sun, moon and planet Venus. In mid-January 2026, Venus is behind the sun. So Jupiter will be the brightest starlike object visible for most of the night.
Angular size at opposition (as seen through a telescope): 46.58 arcseconds.
Through binoculars (anytime): Jupiter reveals a bright disk. If you look closely, you’ll see several of its four large moons – called the Galilean satellites – appearing as pinpoints of light, arrayed in a line that bisects the giant planet. Read: How to see and enjoy Jupiter’s moons.

How often does Jupiter reach opposition?
Jupiter takes 12 earthly years to orbit the sun once. So, the giant planet comes to opposition roughly every 13 months. It didn’t have an opposition in 2025.
2024 Jupiter opposition – December 7
2026 Jupiter opposition – January 10
2027 Jupiter opposition – February 10
Earth takes 12 months to travel once around the sun relative to Jupiter. So, according to our earthly calendars, Jupiter’s opposition comes about a month later each year. Add to that the fact that we recognize 12 constellations of the zodiac. And there are 12 months in a year. So Jupiter appears in front of a new zodiacal constellation at each year’s opposition. This year, it’s in front of Gemini the Twins.
For the fanciful, the giant planet Jupiter is like a real giant, stepping one by one around the zodiacal constellations, over the period of its 12-year orbit.

Recent Jupiter events
December 7, 2024: Jupiter came to opposition in front of the constellation Taurus.
February 4, 2025: Jupiter ended retrograde motion, a sign that the best time to observe Jupiter had ended. But the planet remained in the night sky through April 2025. In May, it was nearing the sunset glare, becoming increasingly difficult to see.
June 24, 2025: Jupiter was at solar conjunction, or behind the sun as seen from Earth. Afterwards, it emerged in the morning sky in July 2025.
November 11, 2025: Jupiter began retrograde motion, that is, westward motion on the sky’s dome, a sign that opposition lay just ahead.
January 9, 2026: Jupiter at perigee, or closest to Earth for 2026.
January 10, 2026: Jupiter at opposition, or opposite the sun as seen from Earth.
A failed star?
Especially around the time of opposition, it’s fun to think of Jupiter as a failed star. Our sun contains some 99.86% of all the mass in our solar system. Jupiter contains 0.1% of the solar system’s mass. And all the other planets (including Earth), moons, asteroids and comets in our solar system contain 0.04% of the solar system’s mass. So Jupiter is much more massive than all the other planets combined. And, for that reason, we sometimes speak of Jupiter as a failed star.
It’s failed in the sense that it’s not massive enough or hot enough inside to spark thermonuclear fusion reactions, the process that enables stars to shine. Jupiter is big! But, without that thermonuclear reaction it can’t shine as stars do.
Overall, you’d need some 80 Jupiters – rolled into a ball – to be hot enough inside to spark fusion. So, Jupiter isn’t a star. That is, it doesn’t shine with its own light. Instead, it shines by reflected sunlight.
Yet in January 2026 – as bright Jupiter rises in the east opposite the sunset – you can stand on Earth all night and peer toward bright Jupiter in our sky. And indeed, you can imagine that, if the giant planet did have enough mass to shine as stars do, then around Jupiter’s opposition, we’d have no night at all. Instead, Jupiter would shine as a tiny 2nd sun, all night long.
Read more: How to see Jupiter’s moons

For precise sun and Jupiter rising times at your location:
Old Farmer’s Almanac (U.S. and Canada)
timeanddate.com (worldwide)
Stellarium (online planetarium program)
In-the-sky information and finder chart for your location

EarthSky Community Photos


Got a picture of Jupiter? We’d love to see it. Submit them here.
Bottom line: Giant Jupiter is closest to Earth for 2026 on January 9. Then Earth will fly between the sun and Jupiter – bringing Jupiter to opposition – January 10.
Read more: Jupiter’s moons: How to see and enjoy them
Read: Why is Jupiter closest to Earth 1 day before opposition?
The post Earth flies between Jupiter and the sun January 10 first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/aAZVyo2

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire