Mars is bright sometimes, but not now
Mars was in our evening sky for much of 2021. But, around October, the red planet disappeared from our sky for a time. Its superior conjunction – when it was most directly behind the sun as seen from Earth – was October 8. Now Mars has returned to our sky as a faint red dot low in the east before sunrise. It’ll remain inconspicuous throughout the early months of 2022. But the coming year, 2022, will be a good time to observe the red planet. Mars will steadily brighten in the first half of 2021, first as a morning object and then, during the second half of 2022, as a bright red ruby in the evening sky. It’ll reach opposition – when Earth will fly between Mars and the sun – on December 8, 2022.
Mars’ dramatic swings in brightness (and its red color) are why the early stargazers named Mars for their God of War. Sometimes the war god rests. And sometimes he grows fierce!
These changes are part of the reason Mars is so fascinating to watch in the night sky.
Want to follow Mars? Bookmark EarthSky’s monthly planet guide.
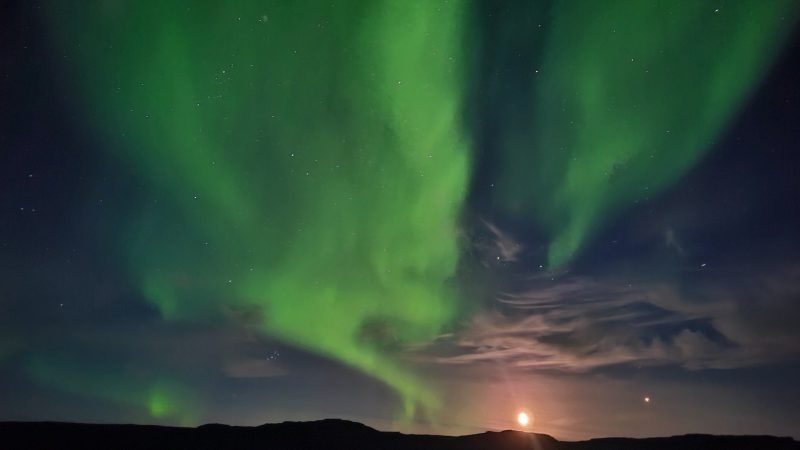
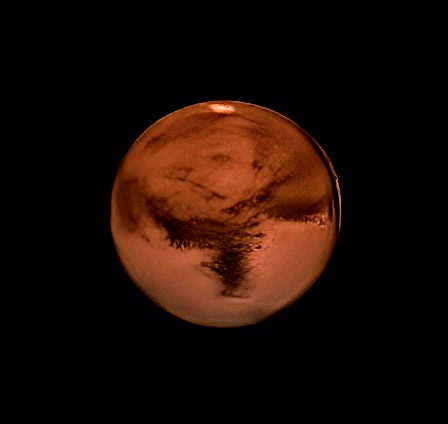


Mars isn’t very big
To understand why Mars varies so much in brightness in Earth’s sky, first realize that Mars isn’t a very big world. It’s only 4,219 miles (6,790 km) in diameter, making it only slightly more than half Earth’s size (7,922 miles or 12,750 km in diameter).
Consider Mars in contrast to Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is 86,881 miles (140,000 km) in diameter. More than 20 planets the size of Mars could be lined up side by side in front of Jupiter. Jupiter always looks bright, because it’s so big.
Not so for little Mars. Its extremes in brightness have to do with its nearness (or lack of nearness) to Earth.
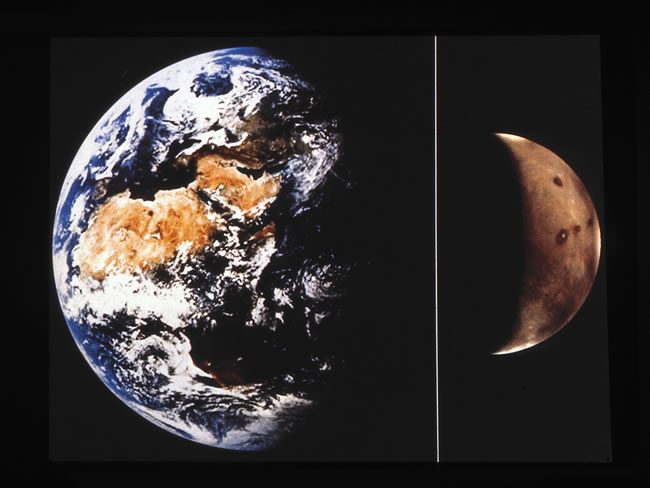


Mars orbits one step outward
Mars orbits the sun one step outward from Earth. The distances between Earth and Mars change as both worlds orbit around the sun. Sometimes Earth and Mars are on the same side of the solar system and near one another. Sometimes, as was the case for much of 2021, Mars and Earth are on nearly opposite sides of the sun from each other, and so Mars appears faint.
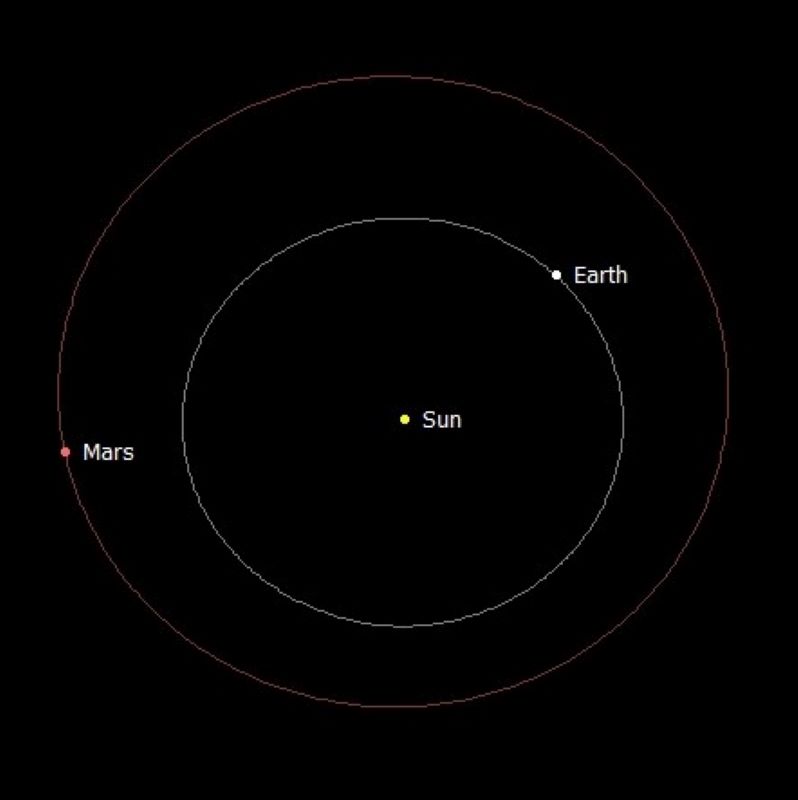
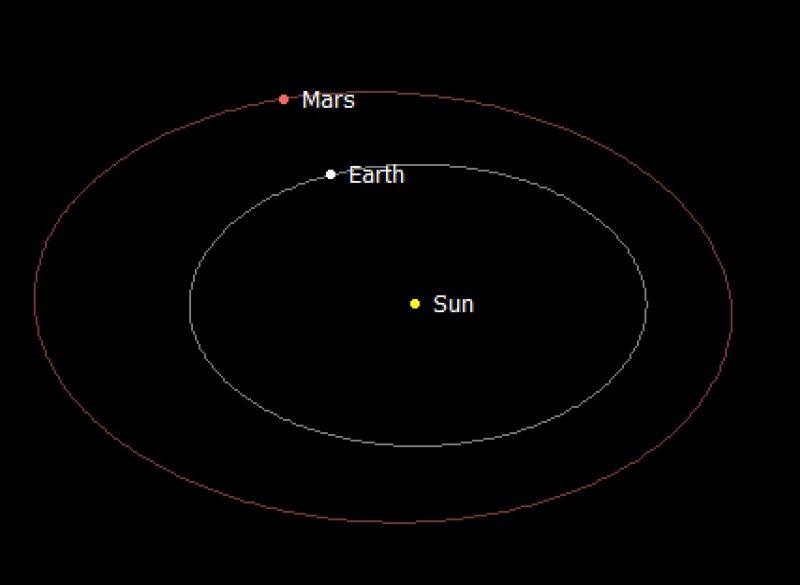
Look at the illustration below, which views the solar system from above. On December 8, 2022, Mars will be at opposition, or opposite the sun from Earth’s viewpoint. This marks the point when Mars is at its brightest and closest for 2022. Compare this view to the one at top, which shows the positions of Mars and Earth in their orbits nearly a year earlier, in December 2021. Mars had recently come out from behind the sun, when it was at conjunction, and started appearing in the morning sky for viewers on Earth.
Why is the red planet sometimes bright?
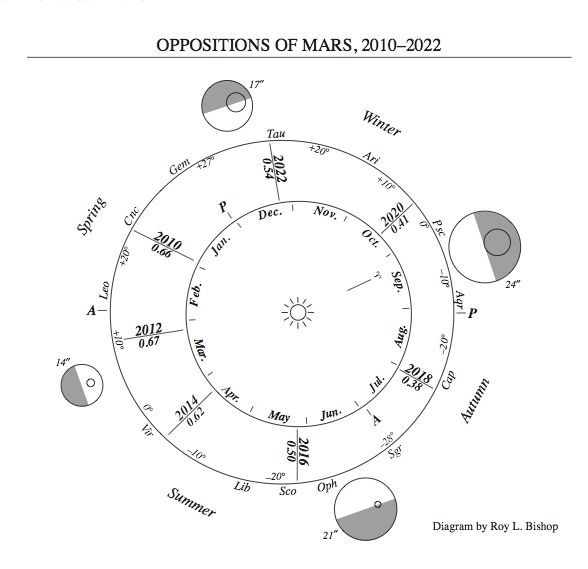
Earth takes a year to orbit the sun once. Mars takes about two years to orbit once. Opposition for Mars – when Earth passes between Mars and the sun – happens every two years and 50 days.
So Mars’ brightness waxes and wanes in our sky about every two years. But that’s not the only cycle of Mars that affects its brightness. There’s also a 15-year cycle of bright and faint oppositions.
Due to that 15-year cycle, 2018 was a very, very special year for Mars, when the planet was brighter than it had been since 2003. Astronomers called it a perihelic opposition (or perihelic apparition) of Mars. In other words, in 2018, we went between Mars and the sun – bringing Mars to opposition in our sky – around the same time Mars came closest to the sun. The word perihelion refers to Mars’ closest point to the sun in orbit.
So, in years when we pass between Mars and the sun, when Mars is also closest to the sun, Earth and Mars are closest.
2003 was the previous perihelic opposition for Mars. The red planet came within 34.6 million miles (55.7 million km) of Earth, closer than at any time in nearly 60,000 years! That was really something.
In 2020, Mars was still very bright at opposition. But it wasn’t as bright as it had been in 2018, or in 2003.
Future Martian oppositions
When is the next opposition of Mars? The next time Mars will appear at its brightest for that two-year period in our sky? You guessed it. 2022!

Bottom line: Mars alternates years in appearing bright and faint in our night sky. In 2021, Mars was faint, but it will brighten for 2022.
Photos of bright Mars in 2018, from the EarthSky community
Photos of bright Mars in 2020, from the EarthSky community
The post Mars in 2022! What to expect from the red planet first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3BekbRi

Mars is bright sometimes, but not now
Mars was in our evening sky for much of 2021. But, around October, the red planet disappeared from our sky for a time. Its superior conjunction – when it was most directly behind the sun as seen from Earth – was October 8. Now Mars has returned to our sky as a faint red dot low in the east before sunrise. It’ll remain inconspicuous throughout the early months of 2022. But the coming year, 2022, will be a good time to observe the red planet. Mars will steadily brighten in the first half of 2021, first as a morning object and then, during the second half of 2022, as a bright red ruby in the evening sky. It’ll reach opposition – when Earth will fly between Mars and the sun – on December 8, 2022.
Mars’ dramatic swings in brightness (and its red color) are why the early stargazers named Mars for their God of War. Sometimes the war god rests. And sometimes he grows fierce!
These changes are part of the reason Mars is so fascinating to watch in the night sky.
Want to follow Mars? Bookmark EarthSky’s monthly planet guide.



Mars isn’t very big
To understand why Mars varies so much in brightness in Earth’s sky, first realize that Mars isn’t a very big world. It’s only 4,219 miles (6,790 km) in diameter, making it only slightly more than half Earth’s size (7,922 miles or 12,750 km in diameter).
Consider Mars in contrast to Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is 86,881 miles (140,000 km) in diameter. More than 20 planets the size of Mars could be lined up side by side in front of Jupiter. Jupiter always looks bright, because it’s so big.
Not so for little Mars. Its extremes in brightness have to do with its nearness (or lack of nearness) to Earth.


Mars orbits one step outward
Mars orbits the sun one step outward from Earth. The distances between Earth and Mars change as both worlds orbit around the sun. Sometimes Earth and Mars are on the same side of the solar system and near one another. Sometimes, as was the case for much of 2021, Mars and Earth are on nearly opposite sides of the sun from each other, and so Mars appears faint.
Look at the illustration below, which views the solar system from above. On December 8, 2022, Mars will be at opposition, or opposite the sun from Earth’s viewpoint. This marks the point when Mars is at its brightest and closest for 2022. Compare this view to the one at top, which shows the positions of Mars and Earth in their orbits nearly a year earlier, in December 2021. Mars had recently come out from behind the sun, when it was at conjunction, and started appearing in the morning sky for viewers on Earth.

Why is the red planet sometimes bright?
Earth takes a year to orbit the sun once. Mars takes about two years to orbit once. Opposition for Mars – when Earth passes between Mars and the sun – happens every two years and 50 days.
So Mars’ brightness waxes and wanes in our sky about every two years. But that’s not the only cycle of Mars that affects its brightness. There’s also a 15-year cycle of bright and faint oppositions.
Due to that 15-year cycle, 2018 was a very, very special year for Mars, when the planet was brighter than it had been since 2003. Astronomers called it a perihelic opposition (or perihelic apparition) of Mars. In other words, in 2018, we went between Mars and the sun – bringing Mars to opposition in our sky – around the same time Mars came closest to the sun. The word perihelion refers to Mars’ closest point to the sun in orbit.
So, in years when we pass between Mars and the sun, when Mars is also closest to the sun, Earth and Mars are closest.
2003 was the previous perihelic opposition for Mars. The red planet came within 34.6 million miles (55.7 million km) of Earth, closer than at any time in nearly 60,000 years! That was really something.
In 2020, Mars was still very bright at opposition. But it wasn’t as bright as it had been in 2018, or in 2003.
Future Martian oppositions
When is the next opposition of Mars? The next time Mars will appear at its brightest for that two-year period in our sky? You guessed it. 2022!


Bottom line: Mars alternates years in appearing bright and faint in our night sky. In 2021, Mars was faint, but it will brighten for 2022.
Photos of bright Mars in 2018, from the EarthSky community
Photos of bright Mars in 2020, from the EarthSky community
The post Mars in 2022! What to expect from the red planet first appeared on EarthSky.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/3BekbRi

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire