
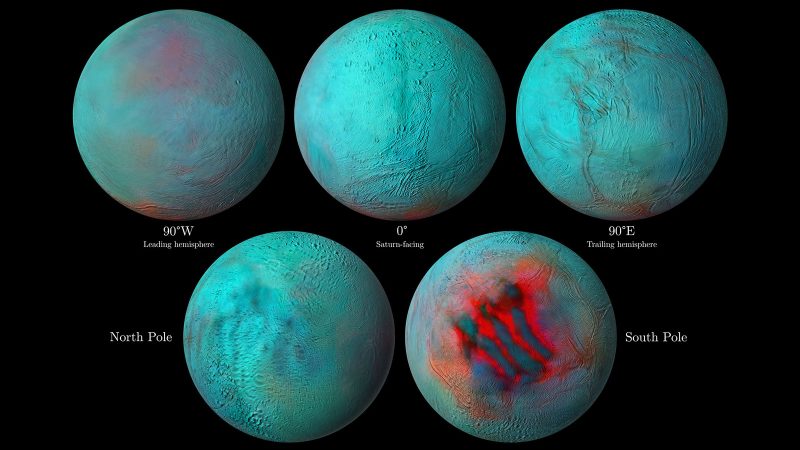
Infrared images of Saturn’s moon Enceladus – as seen by the Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn, weaving in among its moons from 2004 to 2017. A new analysis of Cassini date shows that Enceladus’ north pole might be resurfaced by fresh ice deposits. In this image, the famous tiger stripes fissures – from which water erupts in strange alien geysers – can also be seen at the moon’s south pole. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Arizona/ LPG/ CNRS/ University of Nantes/ Space Science Institute.
Saturn’s moon Enceladus is famous for the huge water-vapor geysers at its south pole, which are thought to originate from a global ocean deep beneath the moon’s outer ice crust. At this moon’s south pole, water is seen to comes up to the surface through giant cracks in the ice called tiger stripes. As the water vapor re-freezes in Enceladus’ extremely tenuous atmosphere, it forms ice particles that fall back down and coat the moon’s south polar region with fresh ice. Until now, this kind of activity was seen only at the moon’s south pole. Now that has changed.
Now, scientists studying new global mosaic infrared images of Enceladus, taken by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, have announced that they’ve found the first evidence that the moon’s north pole has also been painted with a fresh coat of ice fairly recently, geologically-speaking.
Weak geysers at this pole could be the reason. Or the fresh ice might be due to water forced up from the subsurface ocean through cracks in the moon’s icy crust.
The new peer-reviewed study was published in the October 2020 issue of Icarus.
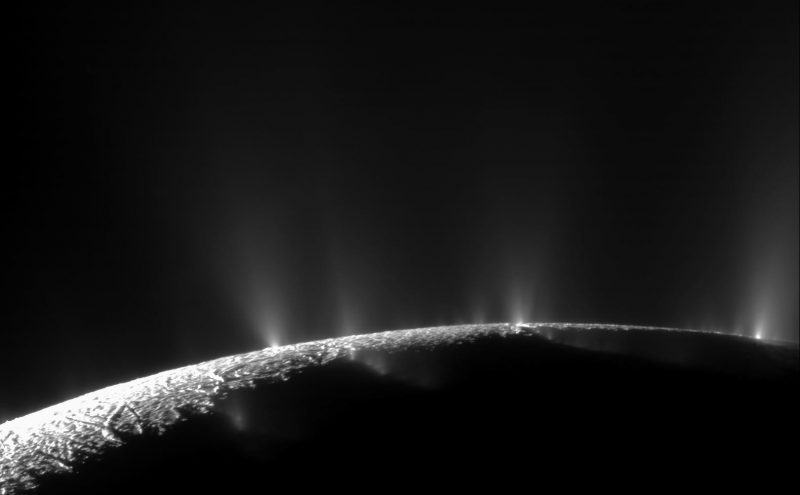

The famous geysers of water vapor at Enceladus’ south pole, which erupt through huge cracks in the icy surface. Now scientists have evidence that the moon’s north polar region is also geologically active, although on a smaller scale. The plumes contain water vapor, ice particles, salts, methane, silica, molecular hydrogen and a variety of simple and complex organic molecules. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ Space Science Institute.
The new infrared images, from Cassini’s Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS), are the most detailed ever made of Enceladus’ surface, from data sent back by the Cassini mission, which ended in September 2017. The researchers found that, surprisingly, the moon’s north polar region also showed evidence of resurfacing by ice, even though it lacks any known geysers or tiger stripe-like fissures. This may be caused by as-yet unseen geysers or a more gradual movement of ice through fractures in the crust, from the subsurface ocean to the surface. Gabriel Tobie, VIMS scientist with the University of Nantes in France and co-author of the new paper, said in a statement:
The infrared shows us that the surface of the south pole is young, which is not a surprise because we knew about the jets that blast icy material there.
Now, thanks to these infrared eyes, you can go back in time and say that one large region in the northern hemisphere appears also young and was probably active not that long ago, in geologic timelines.
VIMS collected light reflected off Saturn, its rings and its ten largest icy moons. This was both visible light that can be seen by human eyes as well as infrared light, which tells scientists more about the makeup of the material reflecting it.
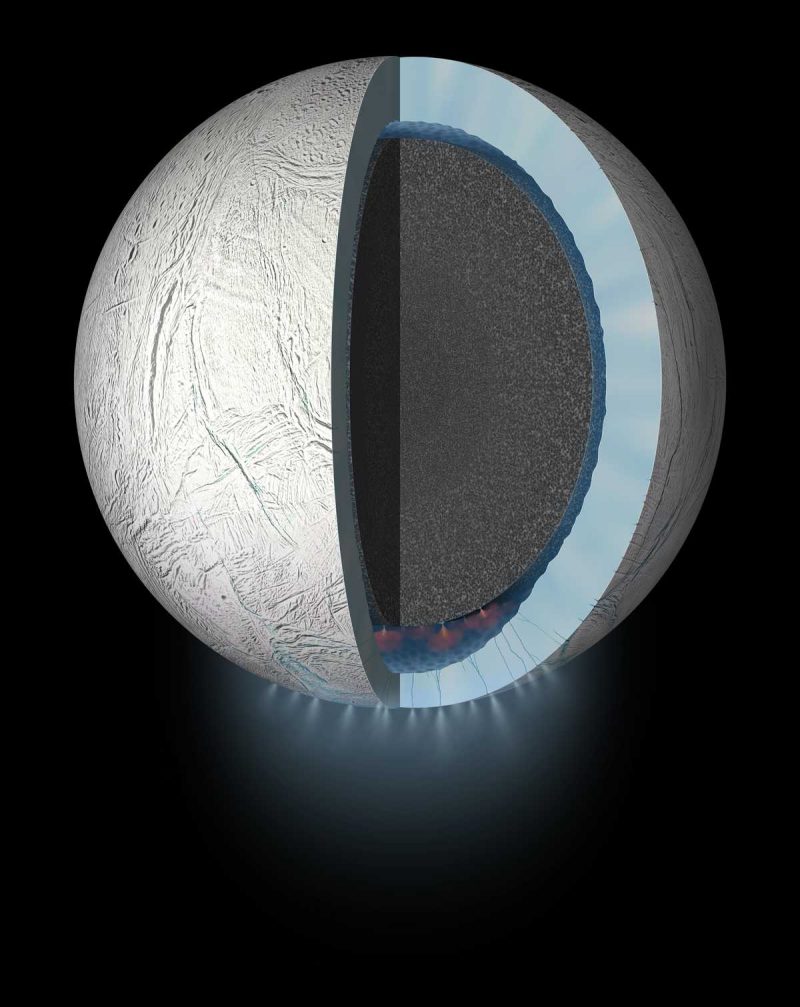

Enceladus’ geysers originate from the subsurface ocean, venting through cracks in the icy surface at the south pole. They coat the surface with fresh layers of ice. Are there as-yet unseen plumes at the moon’s north pole as well? Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ SwRI.
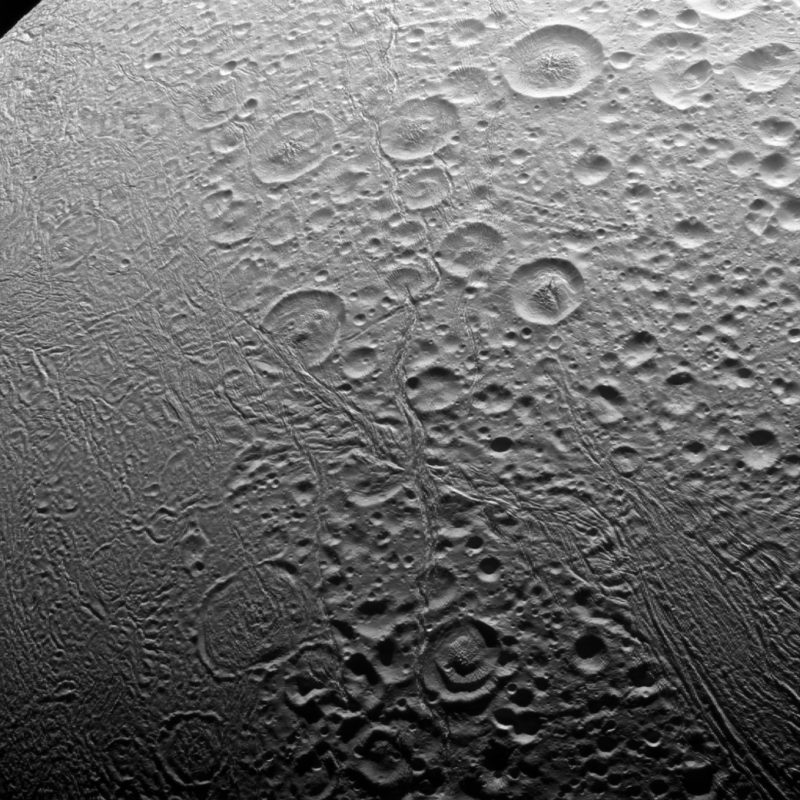

A closer visible light image of Enceladus’ north pole, taken by Cassini on November 27, 2016. The terrain is much more cratered than in the south, but the infrared images in the new study – and the cracks in the surface seen here – show that there has been at least some geological activity in the region. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
Enceladus’ geysers were first spotted by Cassini back in 2005, and ever since then the moon has fascinated scientists and the public alike as to its potentially for being a habitable world. This was especially true after Cassini later confirmed that the water was originating from a global salty ocean beneath the icy surface, similar to Europa.
Additional studies have shown that the ocean is similar to Earth’s oceans in terms of salinity, and there is even evidence for active geothermal vents on the ocean floor. On Earth, such such vents – like “black smokers” – are oases for a diverse population of life forms in the otherwise very dark and cold ocean depths.
Last January, scientists at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) announced that they had developed a new geochemical model of Enceladus that showed the interior of the small moon is more complex than previously thought, including carbon dioxide being controlled by chemical reactions on the seafloor of the ocean. Those findings open up intriguing new possibilities for life in Enceladus’ subsurface watery abyss.
Lead author Christopher Glein of SwRI said in a statement:
By understanding the composition of the plume, we can learn about what the ocean is like, how it got to be this way and whether it provides environments where life as we know it could survive. We came up with a new technique for analyzing the plume composition to estimate the concentration of dissolved CO2 in the ocean. This enabled modeling to probe deeper interior processes.

Gabriel Tobie, VIMS scientist at the University of Nantes and co-author of the new study. Image via LPG.
During its mission, Cassini flew through through the water vapor plumes several times, analyzing what is in them. The spacecraft found water vapor, ice particles, salts, methane, silica (SiO2), molecular hydrogen (H2) and a variety of simple and complex organic molecules. Since this is basically seawater being spewn out into space, this provides important clues as to what conditions are like in the ocean. So far, all signs point to an ocean that is quite habitable by earthly standards. This doesn’t prove there is life there yet, but the evidence indicates there well could be.
The infrared images from Cassini are providing new clues about how geologically active Enceladus is, not only at its south pole with the dramatic watery plumes, but elsewhere on the this little icy world as well.
Bottom line: A new study of infrared images of Saturn’s moon Enceladus shows that the moon’s north pole is geologically active. Could
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/337bEAY


Infrared images of Saturn’s moon Enceladus – as seen by the Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn, weaving in among its moons from 2004 to 2017. A new analysis of Cassini date shows that Enceladus’ north pole might be resurfaced by fresh ice deposits. In this image, the famous tiger stripes fissures – from which water erupts in strange alien geysers – can also be seen at the moon’s south pole. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ University of Arizona/ LPG/ CNRS/ University of Nantes/ Space Science Institute.
Saturn’s moon Enceladus is famous for the huge water-vapor geysers at its south pole, which are thought to originate from a global ocean deep beneath the moon’s outer ice crust. At this moon’s south pole, water is seen to comes up to the surface through giant cracks in the ice called tiger stripes. As the water vapor re-freezes in Enceladus’ extremely tenuous atmosphere, it forms ice particles that fall back down and coat the moon’s south polar region with fresh ice. Until now, this kind of activity was seen only at the moon’s south pole. Now that has changed.
Now, scientists studying new global mosaic infrared images of Enceladus, taken by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, have announced that they’ve found the first evidence that the moon’s north pole has also been painted with a fresh coat of ice fairly recently, geologically-speaking.
Weak geysers at this pole could be the reason. Or the fresh ice might be due to water forced up from the subsurface ocean through cracks in the moon’s icy crust.
The new peer-reviewed study was published in the October 2020 issue of Icarus.

The famous geysers of water vapor at Enceladus’ south pole, which erupt through huge cracks in the icy surface. Now scientists have evidence that the moon’s north polar region is also geologically active, although on a smaller scale. The plumes contain water vapor, ice particles, salts, methane, silica, molecular hydrogen and a variety of simple and complex organic molecules. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ Space Science Institute.
The new infrared images, from Cassini’s Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS), are the most detailed ever made of Enceladus’ surface, from data sent back by the Cassini mission, which ended in September 2017. The researchers found that, surprisingly, the moon’s north polar region also showed evidence of resurfacing by ice, even though it lacks any known geysers or tiger stripe-like fissures. This may be caused by as-yet unseen geysers or a more gradual movement of ice through fractures in the crust, from the subsurface ocean to the surface. Gabriel Tobie, VIMS scientist with the University of Nantes in France and co-author of the new paper, said in a statement:
The infrared shows us that the surface of the south pole is young, which is not a surprise because we knew about the jets that blast icy material there.
Now, thanks to these infrared eyes, you can go back in time and say that one large region in the northern hemisphere appears also young and was probably active not that long ago, in geologic timelines.
VIMS collected light reflected off Saturn, its rings and its ten largest icy moons. This was both visible light that can be seen by human eyes as well as infrared light, which tells scientists more about the makeup of the material reflecting it.

Enceladus’ geysers originate from the subsurface ocean, venting through cracks in the icy surface at the south pole. They coat the surface with fresh layers of ice. Are there as-yet unseen plumes at the moon’s north pole as well? Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ SwRI.

A closer visible light image of Enceladus’ north pole, taken by Cassini on November 27, 2016. The terrain is much more cratered than in the south, but the infrared images in the new study – and the cracks in the surface seen here – show that there has been at least some geological activity in the region. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
Enceladus’ geysers were first spotted by Cassini back in 2005, and ever since then the moon has fascinated scientists and the public alike as to its potentially for being a habitable world. This was especially true after Cassini later confirmed that the water was originating from a global salty ocean beneath the icy surface, similar to Europa.
Additional studies have shown that the ocean is similar to Earth’s oceans in terms of salinity, and there is even evidence for active geothermal vents on the ocean floor. On Earth, such such vents – like “black smokers” – are oases for a diverse population of life forms in the otherwise very dark and cold ocean depths.
Last January, scientists at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) announced that they had developed a new geochemical model of Enceladus that showed the interior of the small moon is more complex than previously thought, including carbon dioxide being controlled by chemical reactions on the seafloor of the ocean. Those findings open up intriguing new possibilities for life in Enceladus’ subsurface watery abyss.
Lead author Christopher Glein of SwRI said in a statement:
By understanding the composition of the plume, we can learn about what the ocean is like, how it got to be this way and whether it provides environments where life as we know it could survive. We came up with a new technique for analyzing the plume composition to estimate the concentration of dissolved CO2 in the ocean. This enabled modeling to probe deeper interior processes.

Gabriel Tobie, VIMS scientist at the University of Nantes and co-author of the new study. Image via LPG.
During its mission, Cassini flew through through the water vapor plumes several times, analyzing what is in them. The spacecraft found water vapor, ice particles, salts, methane, silica (SiO2), molecular hydrogen (H2) and a variety of simple and complex organic molecules. Since this is basically seawater being spewn out into space, this provides important clues as to what conditions are like in the ocean. So far, all signs point to an ocean that is quite habitable by earthly standards. This doesn’t prove there is life there yet, but the evidence indicates there well could be.
The infrared images from Cassini are providing new clues about how geologically active Enceladus is, not only at its south pole with the dramatic watery plumes, but elsewhere on the this little icy world as well.
Bottom line: A new study of infrared images of Saturn’s moon Enceladus shows that the moon’s north pole is geologically active. Could
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/337bEAY

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire