
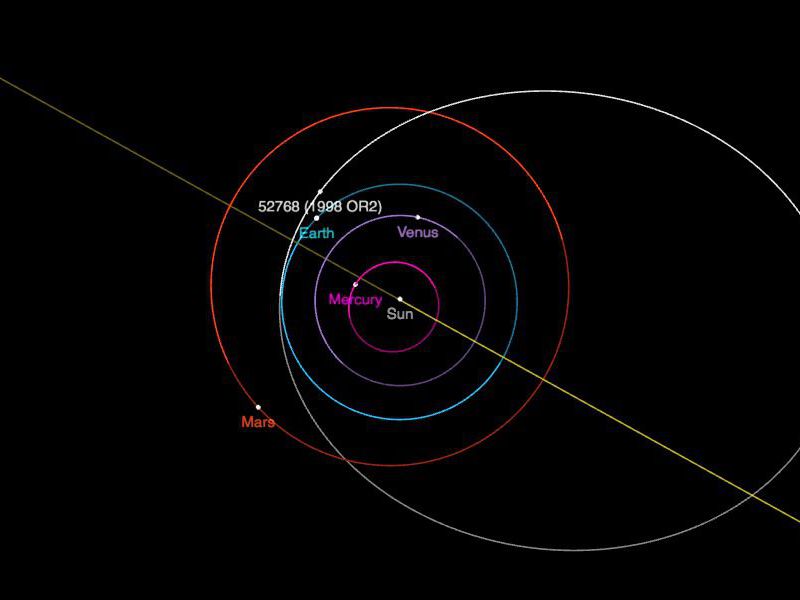
Orbit of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. It requires 3 years and 8 months to orbit the sun onc. It gets nearly as far from the sun as Jupiter (about 5 times Earth’s distance from the sun). Image via NASA/ JPL.
Have you heard the buzz about a big – very big – asteroid that’ll pass close in April? We have! No, it won’t hit our planet. In fact, it won’t have any effects on Earth. Still, excitement is building among both professional and amateur astronomers about the upcoming flyby of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 – the biggest asteroid due to fly by Earth this year – coming closest on April 29, 2020. This space rock is probably at least a mile wide (1.8 km) and maybe 2 1/2 times that big (4.1 km). Closest approach is April 29 around 5:56 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (09:56 UTC; translate UTC to your time). Professional observatories are already pointing their telescopes at the huge space rock. Amateur astronomers with smaller telescopes will have an opportunity to see it as a slow-moving “star” very soon; if that’s you, we give charts and tips for observers at the bottom of this post that should help.
No access to a telescope? No problem. The Virtual Telescope Project in Rome will host a free, online public viewing of the asteroid on April 28, 2020.
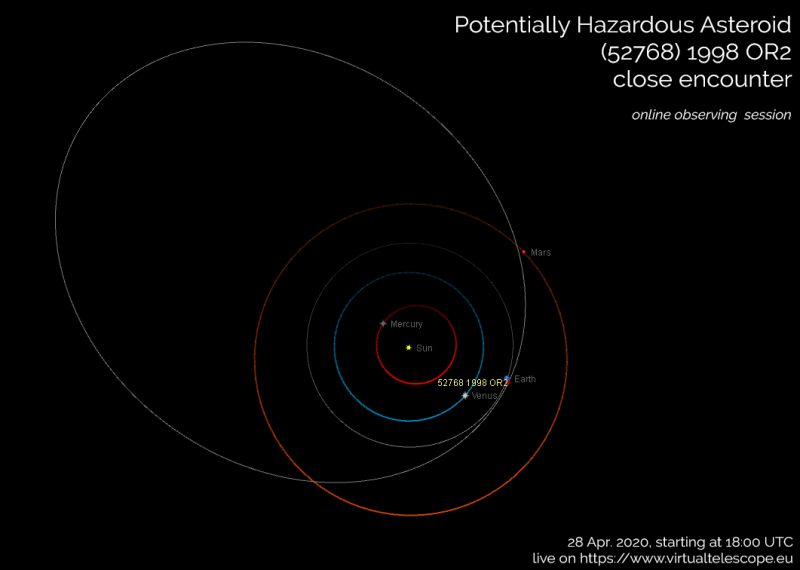
The Virtual Telescope Project will present an online viewing of Potentially Hazardous Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on April 28, 2020. As the time approaches, check this page for more details. Image via Gianluca Masi/ Virtual Telescope Project.
Let’s make absolutely clear that there’s no chance of a collision between this asteroid and Earth. Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass at some 4 million miles (6 million km), or about 16 times the Earth-moon distance. It’s true the object is classified as a Potentially Hazardous Asteroid. The Center for Near Earth Objects defines such an object as one that comes as close to Earth as:
… 0.05 AU or less [about 19.5 lunar distances] and an absolute magnitude of 22.0 or less …
In other words, such objects are reasonably close and reasonably big. And do we need to say there are a bunch of objects like this? Wikipedia lists 22 of the largest here. Recent decades have revealed more and more asteroids orbiting the sun, as the video below from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory shows:
None of the 22 Potentially Hazardous Asteroids listed by Wikipedia is known to be on a collision course with Earth in the foreseeble future. In fact, none of the asteroids in the video above is known to be on a collision course. Likewise, asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 isn’t on a collision course with Earth, not anytime soon. The orbit of this asteroid is well known for at least the next 200 years. Its closest approach to Earth in this century and the next will happen in 2079, when it’ll swoop to within about a million miles of Earth (still about four times farther away than the moon). That 2079 sweep past Earth will still be a big deal. Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is the largest known of all large Near-Earth Objects that’ll pass less than five times the Earth-moon distance over the next two centuries!
Astronomers at Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico will study asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 from April 8 to 24, 2020, as the space rock travels through space at 19,461 miles per hour (31,320 km/h).
The high resolution radar images that will be obtained from Arecibo should provide scientists a better estimate of the space rock’s size and shape.

Astronomers with reasonably sized telescopes are already capturing images of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. This March 6, 2020, image of the asteroid comes from a single 30-second exposure, remotely taken with Elena, a 17-inch robotic telescope. At the imaging time, (52768) 1998 OR2 was at about 22 million miles (36 million km) from Earth. At its closest in late April, it’ll be about 4 million miles (6.4 million km) away. Image via Gianluca Masi/ Virtual Telescope Project.
How to see asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 with a small telescope
During its April 2020 pass, this asteroid will at no time be bright enough to view with the unaided eye. However, it’s estimated to reach a visual magnitude of around 10 to 11, which means observers with at least 6-inch or 8-inch telescopes (the number indicates the size of the primary mirror) will see the asteroid (very slowly) moving in front of the stars!
Sky enthusiasts can initially use a wide-angle (32mm or 35mm) eyepiece to point the telescope to a reference star in the asteroid’s path (charts below). After being assured that the instrument is pointing at the correct patch of the sky, a 26mm or 27mm eyepiece is recommended to detect the asteroid’s slow motion. You will want to note the star field, and watch for the object that moves over a period of about 10 to 15 minutes. Yes, that’ll be the space rock.
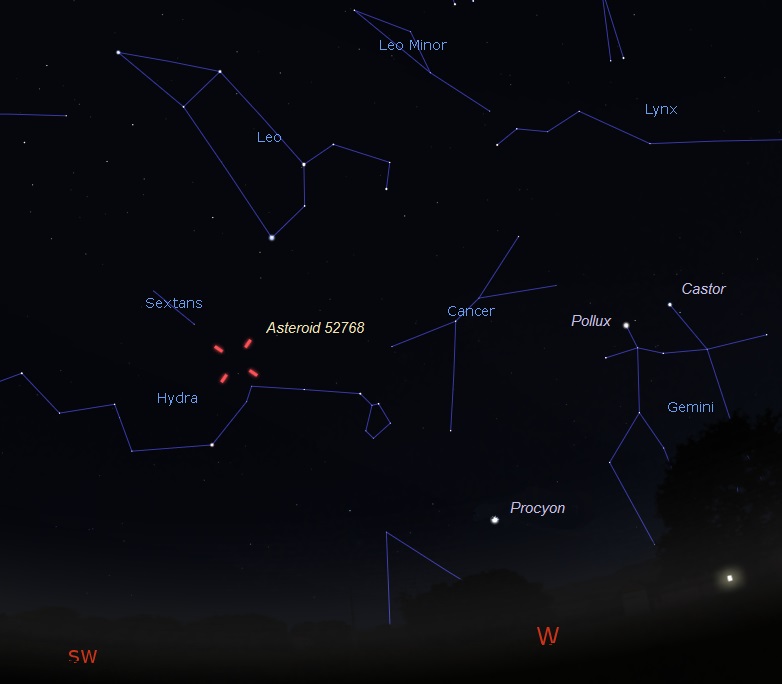
This illustration shows the location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on the night of April 24, 2020 around 11:45 p.m. central time. As seen from central U.S., facing west, southwest. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
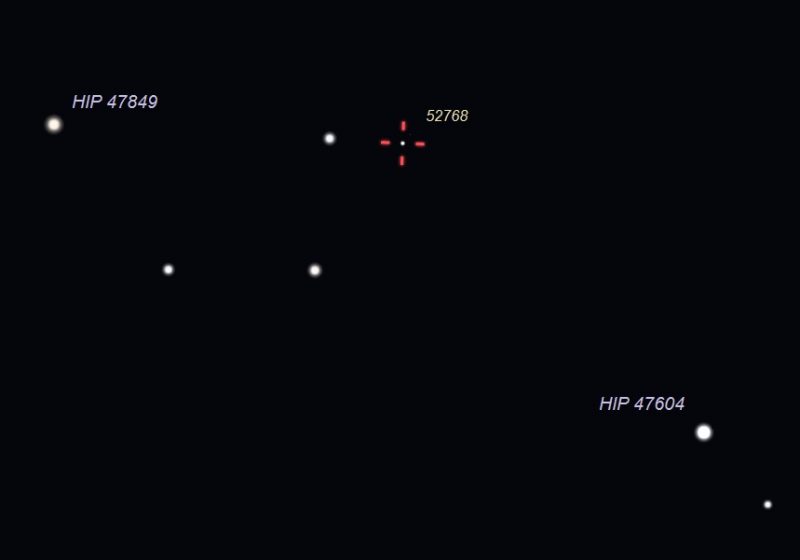
On April 24, 2020 at 11:45 p.m. central time, observers using small computerized telescopes can point their instruments at these reference stars, to observe asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. Compare the views 10 or 15 minutes later to detect an apparent star that has changed position. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
There will be closer approaches of asteroids in the future, including Apophis, which – although smaller – will pass very close to Earth in 2029. Another, larger space rock – 2 miles (3 km) wide – designated as asteroid (415029) 2011 UL21 will pass slightly farther than (52768) 1998 OR2 in June 2024.
But the upcoming flyby in April 2020 of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is the most significant close approach of an asteroid until 2027, as another huge asteroid known as (4953) 1990 MU will safely pass by Earth at 12 lunar distances.
Astronomers first discovered asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on July 24, 1998, from Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii.
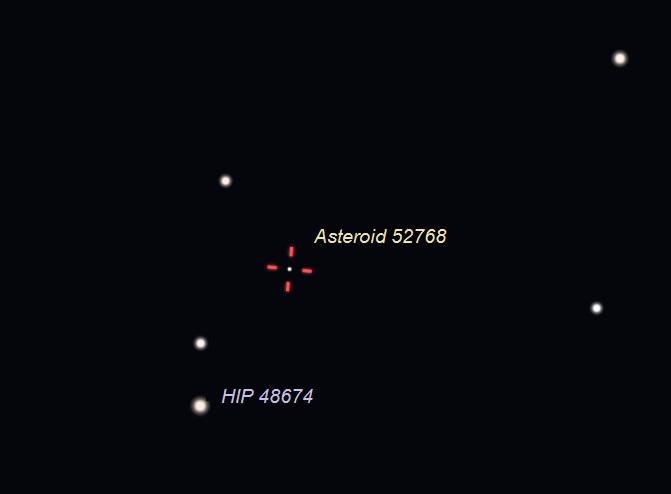
Have a Go-To Telescope? Point your instrument at star HIP 48674 on April 25, 2020 at 10 p.m. central time to find the huge asteroid, which will appear as a slow-moving star. To see its movement, compare the views over about 10 to 15 minutes. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
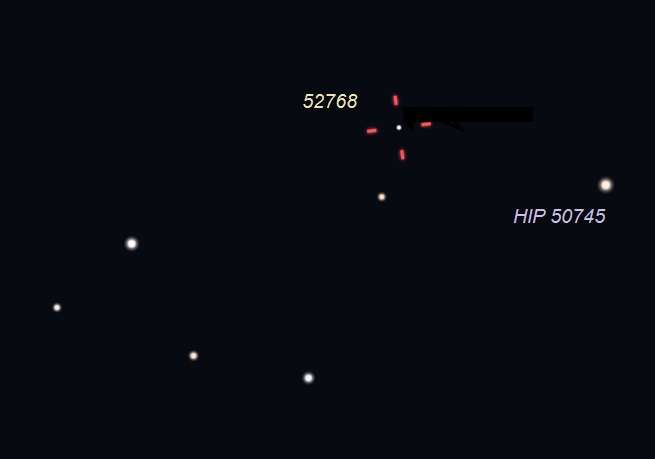
Location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on the night of April 27, 2020. The space rock passes close to star HIP 50745 around 9:15 p.m. central time. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
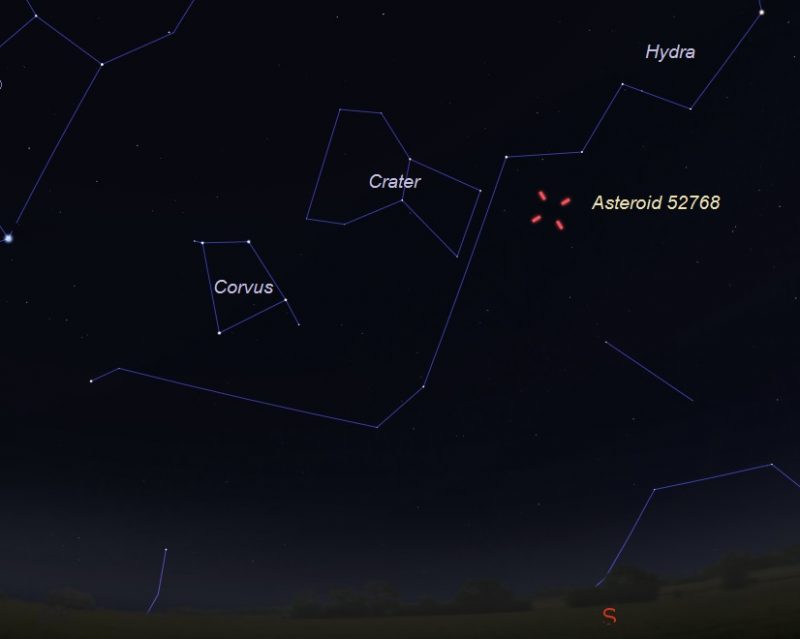
Location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 around the nights of closest approach (April 28-29, 2020). Facing south, as seen from the central U.S. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
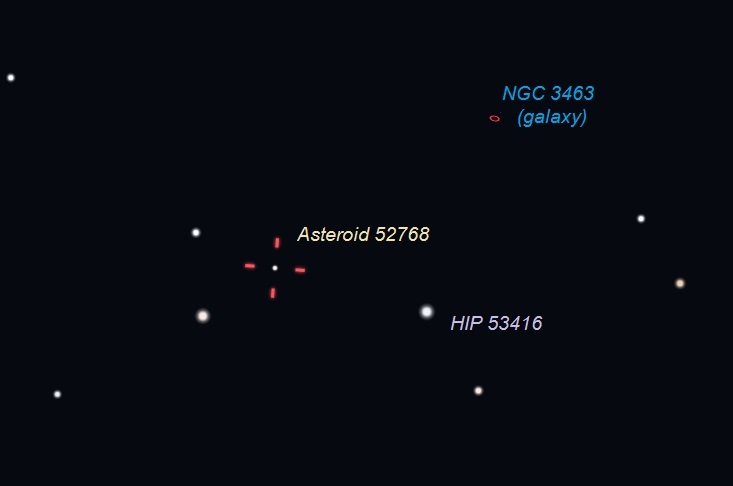
Showtime! On April 29, 2020, around its closest approach to Earth, asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass close to galaxy NGC 3463 and star HIP 53416. Around 9:30 p.m. CT, point your small computerized telescope to these reference objects. Compare the views 10 to 15 minutes later to detect the apparent “star” that changed position. That’s the asteroid. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
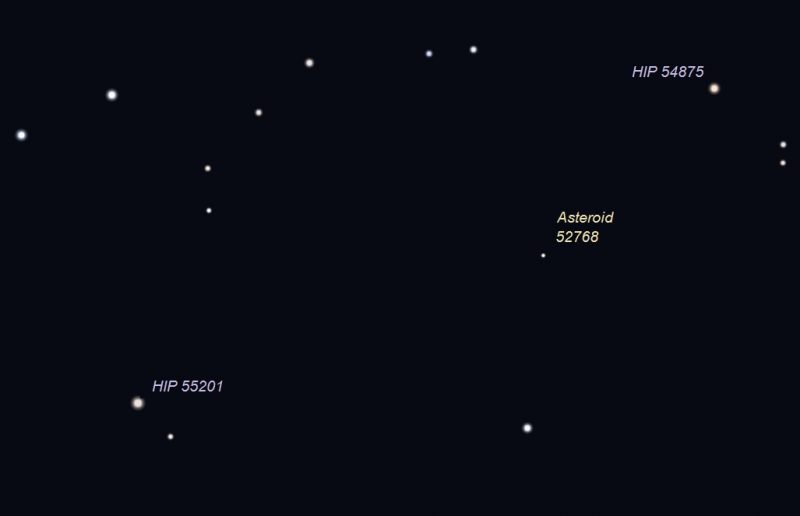
On April 30, 2020 at 9:30 p.m. asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is located close to stars HIP 54875 and 55201. Use a GoTo telescope to locate these reference stars to be able to locate the slow moving asteroid. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
Bottom line: The huge asteroid known as (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass closest to Earth on April 29, 2020. Observers peering through telescopes will see it as a slow-moving “star.” Charts, tips – plus how to watch online – here.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2IxUZeI


Orbit of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. It requires 3 years and 8 months to orbit the sun onc. It gets nearly as far from the sun as Jupiter (about 5 times Earth’s distance from the sun). Image via NASA/ JPL.
Have you heard the buzz about a big – very big – asteroid that’ll pass close in April? We have! No, it won’t hit our planet. In fact, it won’t have any effects on Earth. Still, excitement is building among both professional and amateur astronomers about the upcoming flyby of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 – the biggest asteroid due to fly by Earth this year – coming closest on April 29, 2020. This space rock is probably at least a mile wide (1.8 km) and maybe 2 1/2 times that big (4.1 km). Closest approach is April 29 around 5:56 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (09:56 UTC; translate UTC to your time). Professional observatories are already pointing their telescopes at the huge space rock. Amateur astronomers with smaller telescopes will have an opportunity to see it as a slow-moving “star” very soon; if that’s you, we give charts and tips for observers at the bottom of this post that should help.
No access to a telescope? No problem. The Virtual Telescope Project in Rome will host a free, online public viewing of the asteroid on April 28, 2020.

The Virtual Telescope Project will present an online viewing of Potentially Hazardous Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on April 28, 2020. As the time approaches, check this page for more details. Image via Gianluca Masi/ Virtual Telescope Project.
Let’s make absolutely clear that there’s no chance of a collision between this asteroid and Earth. Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass at some 4 million miles (6 million km), or about 16 times the Earth-moon distance. It’s true the object is classified as a Potentially Hazardous Asteroid. The Center for Near Earth Objects defines such an object as one that comes as close to Earth as:
… 0.05 AU or less [about 19.5 lunar distances] and an absolute magnitude of 22.0 or less …
In other words, such objects are reasonably close and reasonably big. And do we need to say there are a bunch of objects like this? Wikipedia lists 22 of the largest here. Recent decades have revealed more and more asteroids orbiting the sun, as the video below from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory shows:
None of the 22 Potentially Hazardous Asteroids listed by Wikipedia is known to be on a collision course with Earth in the foreseeble future. In fact, none of the asteroids in the video above is known to be on a collision course. Likewise, asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 isn’t on a collision course with Earth, not anytime soon. The orbit of this asteroid is well known for at least the next 200 years. Its closest approach to Earth in this century and the next will happen in 2079, when it’ll swoop to within about a million miles of Earth (still about four times farther away than the moon). That 2079 sweep past Earth will still be a big deal. Asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is the largest known of all large Near-Earth Objects that’ll pass less than five times the Earth-moon distance over the next two centuries!
Astronomers at Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico will study asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 from April 8 to 24, 2020, as the space rock travels through space at 19,461 miles per hour (31,320 km/h).
The high resolution radar images that will be obtained from Arecibo should provide scientists a better estimate of the space rock’s size and shape.

Astronomers with reasonably sized telescopes are already capturing images of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. This March 6, 2020, image of the asteroid comes from a single 30-second exposure, remotely taken with Elena, a 17-inch robotic telescope. At the imaging time, (52768) 1998 OR2 was at about 22 million miles (36 million km) from Earth. At its closest in late April, it’ll be about 4 million miles (6.4 million km) away. Image via Gianluca Masi/ Virtual Telescope Project.
How to see asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 with a small telescope
During its April 2020 pass, this asteroid will at no time be bright enough to view with the unaided eye. However, it’s estimated to reach a visual magnitude of around 10 to 11, which means observers with at least 6-inch or 8-inch telescopes (the number indicates the size of the primary mirror) will see the asteroid (very slowly) moving in front of the stars!
Sky enthusiasts can initially use a wide-angle (32mm or 35mm) eyepiece to point the telescope to a reference star in the asteroid’s path (charts below). After being assured that the instrument is pointing at the correct patch of the sky, a 26mm or 27mm eyepiece is recommended to detect the asteroid’s slow motion. You will want to note the star field, and watch for the object that moves over a period of about 10 to 15 minutes. Yes, that’ll be the space rock.

This illustration shows the location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on the night of April 24, 2020 around 11:45 p.m. central time. As seen from central U.S., facing west, southwest. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.

On April 24, 2020 at 11:45 p.m. central time, observers using small computerized telescopes can point their instruments at these reference stars, to observe asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2. Compare the views 10 or 15 minutes later to detect an apparent star that has changed position. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
There will be closer approaches of asteroids in the future, including Apophis, which – although smaller – will pass very close to Earth in 2029. Another, larger space rock – 2 miles (3 km) wide – designated as asteroid (415029) 2011 UL21 will pass slightly farther than (52768) 1998 OR2 in June 2024.
But the upcoming flyby in April 2020 of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is the most significant close approach of an asteroid until 2027, as another huge asteroid known as (4953) 1990 MU will safely pass by Earth at 12 lunar distances.
Astronomers first discovered asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on July 24, 1998, from Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii.

Have a Go-To Telescope? Point your instrument at star HIP 48674 on April 25, 2020 at 10 p.m. central time to find the huge asteroid, which will appear as a slow-moving star. To see its movement, compare the views over about 10 to 15 minutes. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.

Location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 on the night of April 27, 2020. The space rock passes close to star HIP 50745 around 9:15 p.m. central time. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.

Location of asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 around the nights of closest approach (April 28-29, 2020). Facing south, as seen from the central U.S. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.

Showtime! On April 29, 2020, around its closest approach to Earth, asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass close to galaxy NGC 3463 and star HIP 53416. Around 9:30 p.m. CT, point your small computerized telescope to these reference objects. Compare the views 10 to 15 minutes later to detect the apparent “star” that changed position. That’s the asteroid. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.

On April 30, 2020 at 9:30 p.m. asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 is located close to stars HIP 54875 and 55201. Use a GoTo telescope to locate these reference stars to be able to locate the slow moving asteroid. Illustration by Eddie Irizarry using Stellarium.
Bottom line: The huge asteroid known as (52768) 1998 OR2 will pass closest to Earth on April 29, 2020. Observers peering through telescopes will see it as a slow-moving “star.” Charts, tips – plus how to watch online – here.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2IxUZeI

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire