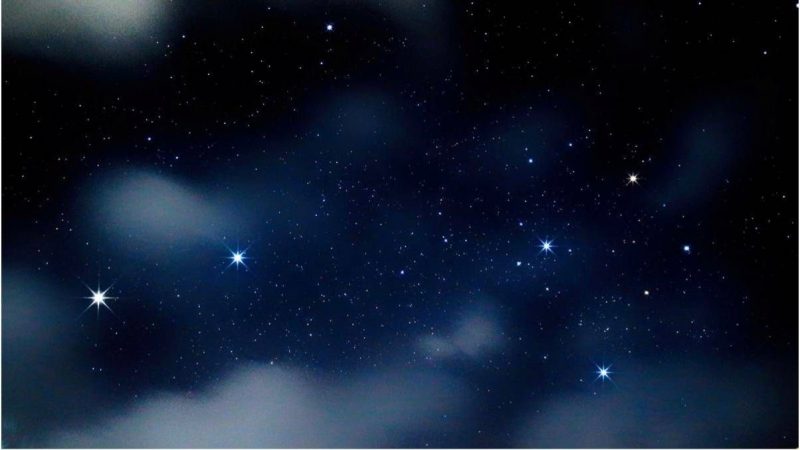


View at EarthSky Community Photos. | Dr Ski in Valencia, Philippines captured the Southern Pointer Stars – Alpha Centauri (far left) and Beta Centauri – aimed at Crux, aka the Southern Cross. Thanks, Dr Ski!
When to see the Southern Cross from the N. Hemisphere At 35o south latitude and all latitudes farther south, you can see the constellation Crux – otherwise known as the Southern Cross – at any hour of the night all year around. In that part of the Southern Hemisphere, the Southern Cross is circumpolar – always above the horizon.
However, for much of the Northern Hemisphere – including most of the United States – the Southern Cross never rises above the horizon, so it can never been seen from our middle and far northern skies.
You can see see all of Crux from the U.S. state of Hawaii. In the contiguous U.S., you need to be in southern Florida or Texas (about 26o north latitude or farther south). Even from the far-southern contiguous U.S., you have a limited viewing window for catching the Southern Cross. It has to be the right season of the year. It has to be the right time of night. And you have to look in the right direction: SOUTH!
For the Northern Hemisphere’s tropical and subtropical regions, the month of May is a good time for finding Crux in the evening sky. You can see the Southern Cross at other times of the year, but not at such a convenient time. In middle March, for instance, you have to wait till about 1 a.m. to catch the Southern Cross at its highest point in the sky. In December and January you have to catch Crux before dawn.
No matter the hour or date, the Southern Cross climbs to its highest point in the sky when it’s due south. The Cross is fairly easy to visualize, because it stands upright over the horizon.
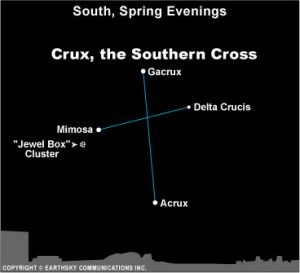
If you live far enough south in the Northern Hemisphere, you’ll find the Southern Cross in the south on spring evenings.
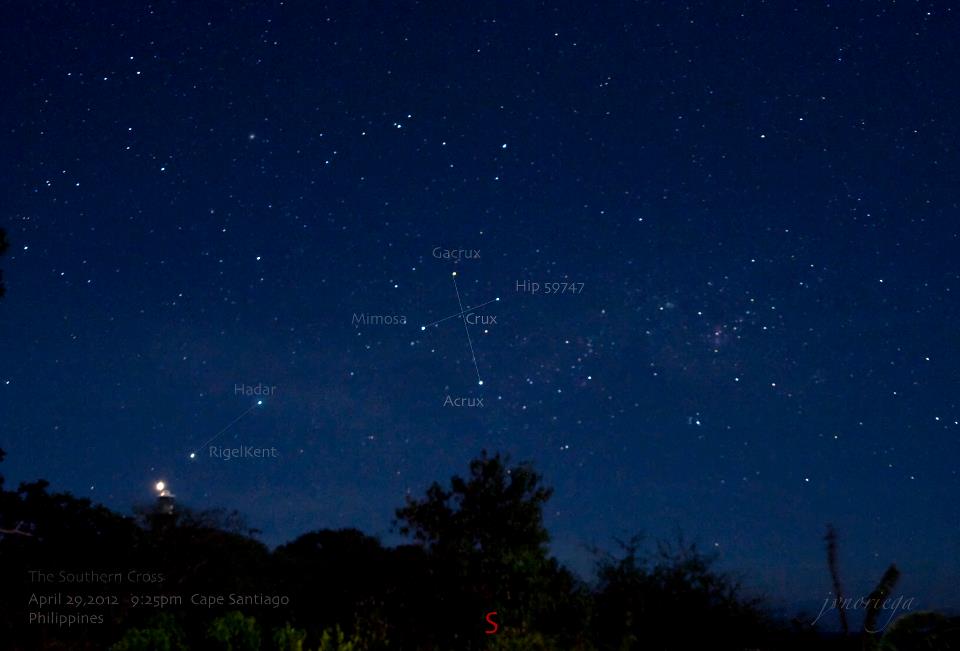

View larger. | Here is the Southern Cross as seen from Manila – latitude 14 degrees N. of the equator – on an April evening. Image via our friend Jv Noriega.
How to use the Big Dipper as a guide Although the Big Dipper is a fixture of the Northern Hemisphere skies, this star formation has a close kinship with the Southern Cross. Both the Big Dipper and the Southern Cross reach their highest point in the sky in unison. Remember spring up and fall down. That’s Northern Hemisphere spring we’re talking about.
The Big Dipper soars highest in the sky on late northern spring evenings. When the Big Dipper is seen above Polaris, the North Star, the Southern Cross is seen standing over the southern horizon in the southern Florida and Texas.
For the Southern Hemisphere, by the way, it works the same way – but in reverse. The Big Dipper can actually be seen in the Southern Hemisphere at opportune times from about 26o south latitude and all latitudes farther north. But to spot it, the Big Dipper has to be viewed at the right season of the year and the right hour of the night. When the Southern Cross sails highest up in the Southern Hemisphere sky, the “upside-down” Big Dipper is seen just above the northern horizon at latitudes near the tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees south latitude).
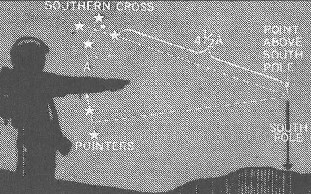
Southern Cross in navigation. When European sailors journeyed south of the equator, they found that the North Star had disappeared below the horizon. As they sailed even farther south, the Big Dipper dropped out of sight as well. Unlike the Northern Hemisphere, the Southern Hemisphere has no bright pole star to highlight the celestial pole. Fortunately, the Southern Cross acts as a navigational aid.
There are various ways to find the direction due south, using the Southern Cross as a guide. For example, a line drawn from the star Gacrux through the star Acrux points in the general direction of the south celestial pole – the point in the sky directly above the Earth’s south pole.
Read more: How to use the Southern Cross to locate the direction south.
Bottom line: We’ve all heard of the legendary Southern Cross. It’s possible to view it from the Northern Hemisphere if you’re in Hawaii, or south Florida, or south Texas.
Rising and setting time for the Southern Cross star Mimosa into your sky
Mimosa is second-brightest star in Southern Cross
Acrux is brightest star in Southern Cross
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2vlmamt


View at EarthSky Community Photos. | Dr Ski in Valencia, Philippines captured the Southern Pointer Stars – Alpha Centauri (far left) and Beta Centauri – aimed at Crux, aka the Southern Cross. Thanks, Dr Ski!
When to see the Southern Cross from the N. Hemisphere At 35o south latitude and all latitudes farther south, you can see the constellation Crux – otherwise known as the Southern Cross – at any hour of the night all year around. In that part of the Southern Hemisphere, the Southern Cross is circumpolar – always above the horizon.
However, for much of the Northern Hemisphere – including most of the United States – the Southern Cross never rises above the horizon, so it can never been seen from our middle and far northern skies.
You can see see all of Crux from the U.S. state of Hawaii. In the contiguous U.S., you need to be in southern Florida or Texas (about 26o north latitude or farther south). Even from the far-southern contiguous U.S., you have a limited viewing window for catching the Southern Cross. It has to be the right season of the year. It has to be the right time of night. And you have to look in the right direction: SOUTH!
For the Northern Hemisphere’s tropical and subtropical regions, the month of May is a good time for finding Crux in the evening sky. You can see the Southern Cross at other times of the year, but not at such a convenient time. In middle March, for instance, you have to wait till about 1 a.m. to catch the Southern Cross at its highest point in the sky. In December and January you have to catch Crux before dawn.
No matter the hour or date, the Southern Cross climbs to its highest point in the sky when it’s due south. The Cross is fairly easy to visualize, because it stands upright over the horizon.

If you live far enough south in the Northern Hemisphere, you’ll find the Southern Cross in the south on spring evenings.

View larger. | Here is the Southern Cross as seen from Manila – latitude 14 degrees N. of the equator – on an April evening. Image via our friend Jv Noriega.
How to use the Big Dipper as a guide Although the Big Dipper is a fixture of the Northern Hemisphere skies, this star formation has a close kinship with the Southern Cross. Both the Big Dipper and the Southern Cross reach their highest point in the sky in unison. Remember spring up and fall down. That’s Northern Hemisphere spring we’re talking about.
The Big Dipper soars highest in the sky on late northern spring evenings. When the Big Dipper is seen above Polaris, the North Star, the Southern Cross is seen standing over the southern horizon in the southern Florida and Texas.
For the Southern Hemisphere, by the way, it works the same way – but in reverse. The Big Dipper can actually be seen in the Southern Hemisphere at opportune times from about 26o south latitude and all latitudes farther north. But to spot it, the Big Dipper has to be viewed at the right season of the year and the right hour of the night. When the Southern Cross sails highest up in the Southern Hemisphere sky, the “upside-down” Big Dipper is seen just above the northern horizon at latitudes near the tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees south latitude).
Southern Cross in navigation. When European sailors journeyed south of the equator, they found that the North Star had disappeared below the horizon. As they sailed even farther south, the Big Dipper dropped out of sight as well. Unlike the Northern Hemisphere, the Southern Hemisphere has no bright pole star to highlight the celestial pole. Fortunately, the Southern Cross acts as a navigational aid.
There are various ways to find the direction due south, using the Southern Cross as a guide. For example, a line drawn from the star Gacrux through the star Acrux points in the general direction of the south celestial pole – the point in the sky directly above the Earth’s south pole.
Read more: How to use the Southern Cross to locate the direction south.
Bottom line: We’ve all heard of the legendary Southern Cross. It’s possible to view it from the Northern Hemisphere if you’re in Hawaii, or south Florida, or south Texas.
Rising and setting time for the Southern Cross star Mimosa into your sky
Mimosa is second-brightest star in Southern Cross
Acrux is brightest star in Southern Cross
from EarthSky http://bit.ly/2vlmamt

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire