

Where does the celestial equator intersect your horizon? No matter what you latitude is, it intersects your horizon at points due east and due west. Read more about how an observer’s latitude affects your visible sky.
The September 2018 equinox happens on September 23 at 1:54 UTC (or September 22 at 8:54 p.m. CDT); translate to your time zone. So as you read this, the due-east equinox sunrise might have already have happened for you. But maybe it’s not too late for you to catch the due-west equinox sunset?
It’s often said that – at each equinox – the sun rises due east and sets due west. And that’s true, no matter where you live on the globe. But why? And how can you visualize it?

The ecliptic and celestial equator intersect at the spring and autumn equinox points. The ecliptic represents the sun’s apparent yearly path in front of the constellations of the zodiac. The celestial equator is the imaginary great circle above Earth’s equator.
First you need to know this. An equinox occurs when the sun crosses the celestial equator. No matter where you are on Earth, the celestial equator intersects your horizon at due east and due west. See the diagram above to try to visualize that.
At its highest point in your sky, the celestial equator appears high or low, depending on your latitude. The imaginary celestial equator is a great circle dividing the imaginary celestial sphere into its northern and southern hemispheres, so, from the equator, it’s directly overhead, for example, wrapping the sky directly above Earth’s equator.
For purposes of today’s visualization, though, the height of the celestial equator in your sky doesn’t matter. What matters are these two things. One, the sun is on the celestial equator at the equinox. Two, the celestial equator intersects your horizon at points due east and due west.
Voila. The sun rises due east and sets due west on the day of the equinox, as seen from around the globe.
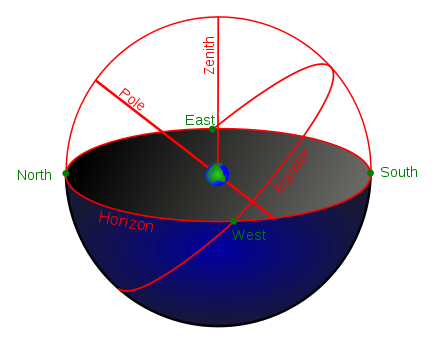
Where does the celestial equator intersect your horizon? No matter where you are on Earth (unless you’re at a pole), the celestial equator meets your horizon at points due east and due west.

Why does the sun rises due east and set due west at the equinoxes? The blue line is the celestial equator (always at your due east and due west points). The purple line is the ecliptic, or sun’s path. At the equinox, these two lines intersect. Illustration via JCCC Astronomy.
This fact – the sun rising and setting due east and west at every equinox – makes the day of an equinox a good day for finding due east and due west from your yard or other favorite site for watching the sky.
Just go outside around sunset or sunrise and notice the location of the sun on the horizon with respect to familiar landmarks. If you do this, you’ll be able to use those landmarks to find those cardinal directions in the weeks and months ahead, long after Earth has moved on in its orbit around the sun, carrying the sunrise and sunset points southward or northward.

Equatorial sundial by Tom Laidlaw. The north face of an equatorial sundial receives sunshine in spring and summer, and the south face receives it in autumn and winter. On the equinoxes, sunshine should hit neither side of the sundial, but only the edge.
Now let’s think about what an equinox really is. It’s an event that happens on the imaginary dome of Earth’s sky, but each equinox also represents a real point on Earth’s orbit. What happens at every equinox is very real – as real as the sun’s passage across the sky each day and as real as the change of the seasons.
Our ancestors didn’t understand the equinoxes as events that occur in the course of Earth’s yearly orbit around the sun. But if they were observant – and many were very observant indeed – they surely marked today as being midway between the sun’s lowest path across the sky in winter and highest path across the sky in summer.
And that’s where we are, in orbit, at this equinox.
We’re midway between the two extremes of the sun’s path in your sky.
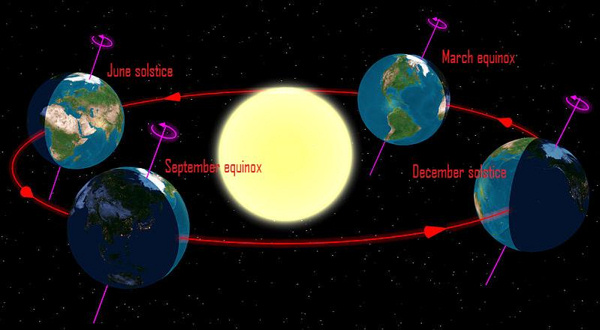
The seasons result from the Earth's rotational axis tilting 23.5 degrees out of perpendicular to the ecliptic - or Earth's orbital plane.
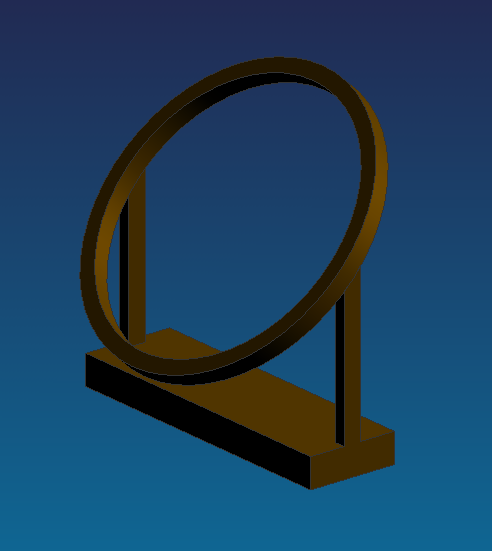

An equatorial ring was used in ancient times in an attempt to determine the equinoxes. The ring plane is set parallel to the plane of the Earth’s equator. If the equinox happened during the daylight hours, the inside of the ring was expected to be completely in shade at the equinox. Image via Wikipedia
Bottom line: The 2018 September equinox comes on September 23 at 1:54 UTC – or September 22 at 8:54 p.m. Central Daylight Time for us in the central U.S. At each equinox, the sun rises due east and sets due west. The diagrams and explanations in this post are meant to help you visualize that.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2OHjveT


Where does the celestial equator intersect your horizon? No matter what you latitude is, it intersects your horizon at points due east and due west. Read more about how an observer’s latitude affects your visible sky.
The September 2018 equinox happens on September 23 at 1:54 UTC (or September 22 at 8:54 p.m. CDT); translate to your time zone. So as you read this, the due-east equinox sunrise might have already have happened for you. But maybe it’s not too late for you to catch the due-west equinox sunset?
It’s often said that – at each equinox – the sun rises due east and sets due west. And that’s true, no matter where you live on the globe. But why? And how can you visualize it?

The ecliptic and celestial equator intersect at the spring and autumn equinox points. The ecliptic represents the sun’s apparent yearly path in front of the constellations of the zodiac. The celestial equator is the imaginary great circle above Earth’s equator.
First you need to know this. An equinox occurs when the sun crosses the celestial equator. No matter where you are on Earth, the celestial equator intersects your horizon at due east and due west. See the diagram above to try to visualize that.
At its highest point in your sky, the celestial equator appears high or low, depending on your latitude. The imaginary celestial equator is a great circle dividing the imaginary celestial sphere into its northern and southern hemispheres, so, from the equator, it’s directly overhead, for example, wrapping the sky directly above Earth’s equator.
For purposes of today’s visualization, though, the height of the celestial equator in your sky doesn’t matter. What matters are these two things. One, the sun is on the celestial equator at the equinox. Two, the celestial equator intersects your horizon at points due east and due west.
Voila. The sun rises due east and sets due west on the day of the equinox, as seen from around the globe.

Where does the celestial equator intersect your horizon? No matter where you are on Earth (unless you’re at a pole), the celestial equator meets your horizon at points due east and due west.

Why does the sun rises due east and set due west at the equinoxes? The blue line is the celestial equator (always at your due east and due west points). The purple line is the ecliptic, or sun’s path. At the equinox, these two lines intersect. Illustration via JCCC Astronomy.
This fact – the sun rising and setting due east and west at every equinox – makes the day of an equinox a good day for finding due east and due west from your yard or other favorite site for watching the sky.
Just go outside around sunset or sunrise and notice the location of the sun on the horizon with respect to familiar landmarks. If you do this, you’ll be able to use those landmarks to find those cardinal directions in the weeks and months ahead, long after Earth has moved on in its orbit around the sun, carrying the sunrise and sunset points southward or northward.

Equatorial sundial by Tom Laidlaw. The north face of an equatorial sundial receives sunshine in spring and summer, and the south face receives it in autumn and winter. On the equinoxes, sunshine should hit neither side of the sundial, but only the edge.
Now let’s think about what an equinox really is. It’s an event that happens on the imaginary dome of Earth’s sky, but each equinox also represents a real point on Earth’s orbit. What happens at every equinox is very real – as real as the sun’s passage across the sky each day and as real as the change of the seasons.
Our ancestors didn’t understand the equinoxes as events that occur in the course of Earth’s yearly orbit around the sun. But if they were observant – and many were very observant indeed – they surely marked today as being midway between the sun’s lowest path across the sky in winter and highest path across the sky in summer.
And that’s where we are, in orbit, at this equinox.
We’re midway between the two extremes of the sun’s path in your sky.

The seasons result from the Earth's rotational axis tilting 23.5 degrees out of perpendicular to the ecliptic - or Earth's orbital plane.

An equatorial ring was used in ancient times in an attempt to determine the equinoxes. The ring plane is set parallel to the plane of the Earth’s equator. If the equinox happened during the daylight hours, the inside of the ring was expected to be completely in shade at the equinox. Image via Wikipedia
Bottom line: The 2018 September equinox comes on September 23 at 1:54 UTC – or September 22 at 8:54 p.m. Central Daylight Time for us in the central U.S. At each equinox, the sun rises due east and sets due west. The diagrams and explanations in this post are meant to help you visualize that.
from EarthSky https://ift.tt/2OHjveT

Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire